About half of Cuffelinks readers engage the services of financial advisers to help them manage their life savings. Most will meet with their adviser, review their portfolio and then listen to their adviser’s recommended changes to these portfolios. This process of managing client money is old-fashioned, clunky and reactive. There is a better way.
Acceptance of Managed Accounts
Managed Accounts have been around for a while but over the last few years their popularity has soared, not only in Australia, but also in the UK and the US. There is good reason for this as the benefits of using Managed Accounts are significant and varied. According to the 2019 Netwealth Advice Tech Report, 43% of advice firms now use Managed Accounts to run part of their client portfolios, up from 35% in 2017. A recent IMAP/Milliman survey revealed that $62 billion of client funds are now managed via discretionary portfolio methods, double the level of just three years ago.
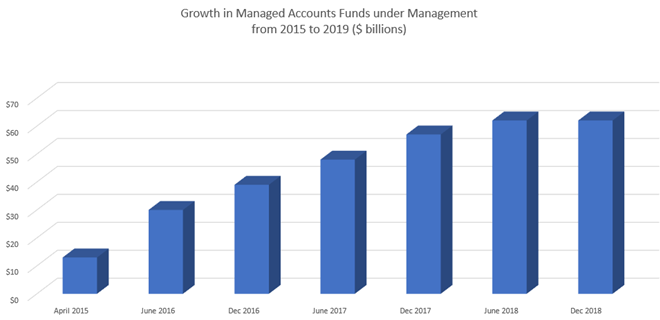
Source: IMAP Milliman
A Managed Account in its simplest form is an auto-rebalance tool. It permits the advice firm discretion to make changes to their clients’ portfolios without requiring their written approval. This is how superannuation monies are managed in industry and retail funds. The manager has strict limits on the amount of risk that can be taken and the type of assets that can be purchased, and must adhere to these limits.
The Managed Account benefits
Managed Accounts offer a range of benefits that offer clients and their advisers increased flexibility.
First, the money is managed by a professional investment committee, rather than by an adviser who occasionally reads the Fin Review and a stock-tipping sheet. While portfolio outperformance is not guaranteed, the likelihood of things going badly wrong are reduced.
Second, the client’s funds are managed in a much more proactive manner as portfolio changes can be made in an instant. Contrast this with the traditional process where changes were generally only made at the client meeting, which may happen just once or twice a year.
Third, Managed Accounts are more progressive and egalitarian than the traditional way of managing money. Currently, if changes need to be made, it’s inevitably the adviser’s larger clients who will be called first. With a Managed Account, all portfolios of the same risk profile are changed at the same time, which also offers scale benefits.
Fourth, Managed Accounts are transparent. Portfolio performance is published each month and is benchmarked against an equivalent risk profile. There is no hiding, obfuscation and evasiveness. “How are we doing?” is now easier to answer. We benchmark our clients' portfolios against their CPI+ targets and against a basket of comparable portfolios every month.
And fifth, with advisers freed from the tyranny of trying fruitlessly to add value by picking BHP over CBA, they can actually get on with the job of providing strategic financial planning advice, focussing on the clients' wealth plan and helping them achieve their important goals in life.
Sounds good so far.
Are there any disadvantages?
Yes. A Managed Account run by a professional investment committee will likely charge a portfolio fee. This is typically in the region of 0.2% - 0.3%, though lower rates are commonly offered for larger portfolios. This is an additional cost. However, most Managed Account providers are able to recoup most, if not all, of this cost in two ways.
First, by negotiating lower management expense ratios (MERs) from fund managers. With scale comes lower fees, and Managed Accounts offer scale. It’s important to check that your provider passes these rebates on to you, the client, in full. And second, many Managed Account providers are now offering lower financial advice fees if client portfolios are run in a discretionary manner, due to the reduced administrative burden.
It might be time to talk to your adviser about Managed Accounts. They are not suitable for everyone, but they are a big part of the future of advice.
Jonathan Hoyle is Chief Executive Officer at Stanford Brown. This article is general information and does not address the circumstances of any individual.