Superannuation funds generally benchmark their domestic fixed income asset allocation against a market capitalisation weighted investment grade bond index such as the S&P/ASX Australian Fixed Interest Index or the Bloomberg Composite Ausbond Index. Bonds are included in these indices if they meet certain criteria (such as Australian dollar denominated, fixed rate, minimum issue size, investment grade rating) and are weighted in proportion to their market value.
Index is heavily concentrated and unrepresentative
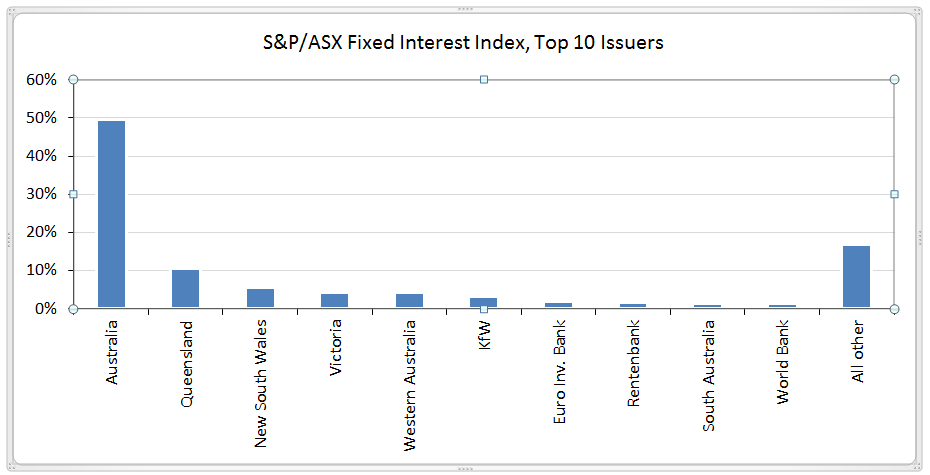
Diving into the S&P fixed interest index, the top 10 issuers are either Commonwealth or state governments or European development banks. The largest non-government issuer is KfW (Kreditanstalt für Wiederaufbau), a German development bank.
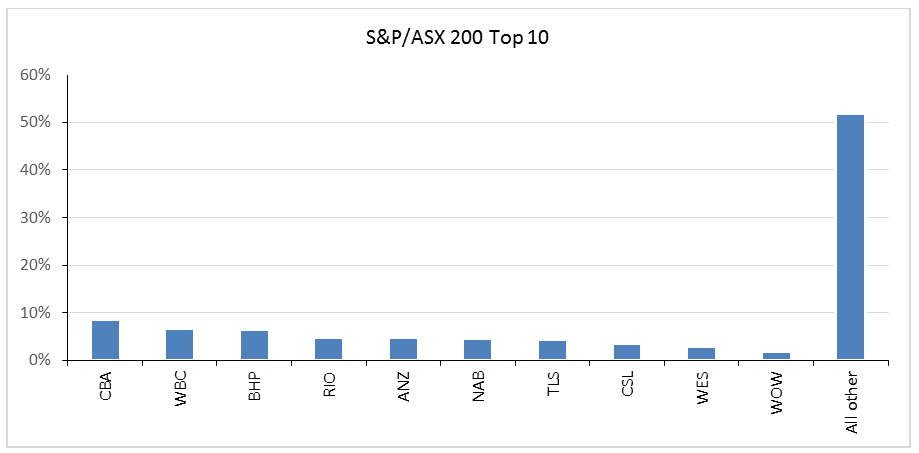
The top 10 issuers comprise 83% of the index. The total index has a modified duration of 5.2 years and a yield to maturity of 2.14% (at time of writing). Investors might be surprised that no Australian company (for example, any of the big four banks) makes the top 10, while Australian governments occupy the top five positions.
By comparison, the top 10 issuers in the S&P/ASX 200 equity index account for only 48% of the total market value, and even this is concentrated by global equity index standards.
There are approximately $650 billion worth of government bonds and $500 billion of non-government bonds on issue in Australia. About a third of the Australian non-government bond universe is comprised of bonds issued by non-residents, rising dramatically from last to the largest share in the last 15 years, pausing slightly during the GFC (but nowhere near as much as asset-backed securities).
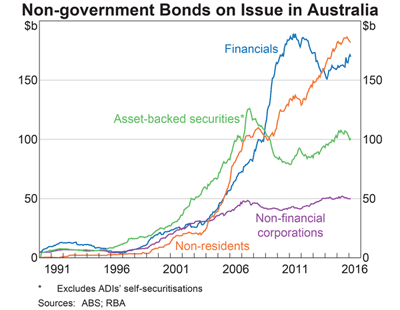
The next biggest category is financials, which is dominated by the bonds of the big four banks.
Only about $50 billion are comprised of domestic non-financial corporates. That is, only about 10% of non-government bonds are what you would typically consider Australian corporate credit.
This is tiny when compared with the loan market. According to APRA data, Australian banks have loans to Australian non-financial corporates of more than $650 billion.
Traditional composite bond funds are meant to provide investors with a balanced exposure across borrower types. Investors should understand the components of any fixed interest index and judge how representative of the desired underlying investment universe the index really is.
Alexander Austin is Chief Executive Officer of Infradebt, a specialist infrastructure debt fund manager. This article provides general information and does not constitute personal advice.