It is budget time again in Australia, and the nation is heading for its first Federal Government surplus since 2008, mostly from good luck with China and commodities.
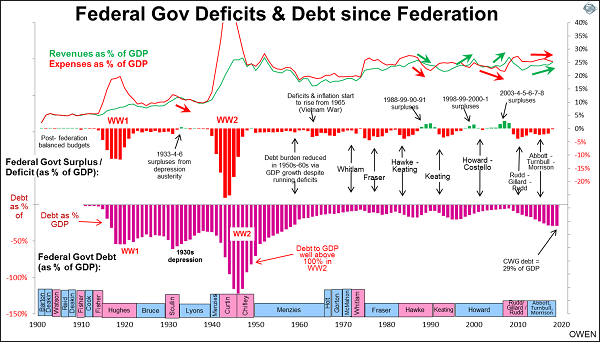
Here is a chart showing the Federal Government’s deficit and debt position since 1901. The upper section shows revenues (green line) and expenses (red). The middle section shows the resultant annual surpluses (green bars – look hard!) or deficits (red bars). The purple bars in the lower section show the level of Federal Government debt. All are expressed relative to total national output (GDP) each year.
Click to enlarge
A brief history of budgets
The Federal Government ran balanced budgets in the early years following Federation but it had very few functions prior to the introduction of Federal Government pensions in 1909. World Wars I & II changed all that, requiring massive war-time deficits and debt build-ups. These were finally brought under control by the 1950s and 1960s booms. The Government still ran small deficits (1-2% of GDP) but rising tax revenues from the booming economy were enough to pay for expanding services and nation-building projects, and still reduce the debt/GDP ratio down to low levels by the 1970s. The current level of debt relative to national output is the highest it has been since the late 1950s.
Producing a government surplus can be done in one of two ways: by cutting costs or increasing tax revenues, or sometimes both. Most of the time the surpluses have been a result of windfall revenue gains, mostly from fortuitous mining booms. The problem is that costs are controllable, but tax revenues depend on mining booms that are based on global commodities price cycles outside our control.
Only rarely have surpluses been achieved by cutting costs. This was the case with the 1930s surpluses. Australia did not follow Roosevelt’s big spending approach in the US. Instead we had to endure harsh ‘austerity’ cost-cutting imposed by London bankers. The government wasn’t able to borrow anyway after it defaulted on its debts in 1931. Arguably the austerity cuts prolonged the depression and stunted the recovery.
The only other period of surpluses produced by cost cutting was the four-year period from 1988 to 1991 by Hawke and Keating. Commodities prices and tax revenues were falling but they were able to produce surpluses by cutting costs by even more, resulting in the deep 1990-91 recession.
The Howard Government had two spells of surpluses – four years from 1998 to 2001, and then another five years from 2003 to 2007 (or six years if you count the 2007-08 year during which Rudd came to office, when boom-time mining revenues were still flowing in prior to the GFC). Both of these surplus spells were driven by windfall tax revenue gains – first from the 1990s ‘dot-com’ boom and the second from the 2003-08 mining boom. Government spending was also reducing during the whole period – from 25% of GDP in 1996 to 21.7% in 2007. But because most of the gains were from boom-time tax revenue rises, the windfall surpluses quickly disappeared when the booms ended.
If the Federal Government achieves a surplus in the current 2018-19 year it will be mainly thanks once again to fortuitous tax revenue gains from the mining boom, not because of cost management. In the past five years the population has grown by just 8%, but government spending has risen by an incredible 21%. By sheer luck the mining boom has increased revenues by 27% but windfall gains like these are not sustainable.
Ashley Owen is Chief Investment Officer at advisory firm Stanford Brown and The Lunar Group. He is also a Director of Third Link Investment Managers, a fund that supports Australian charities. This article is for general information purposes only and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.