What do Galileo Galilei and a member of the flat earth society have in common? The answer, we think, goes to the core of how contrarian investing works.
While both reject the accepted view of the world, flat earthers’ views seem to stem from a scepticism of the prevailing order and an unwillingness to accept the facts laid out for them. Galileo’s objections, on the other hand, were based on the rigour of fundamental research. He was willing to stand apart from the crowd, but that wasn’t his goal, it was the natural outcome of his bottom-up research.
In the same way, contrarian investing isn’t just about blindly betting against the crowd – most of the time stocks are cheap for a reason – it is about being willing to look differently in the short term to stack the long-term odds in your favour.
In simpler terms, it is about having the courage to buy when others are fearful and the discipline to sell when others are greedy. The trick to remaining contrarian throughout the market cycle is being able to do it consistently in both directions, even when the market is against you.
Although there are many reasons why markets might overlook a company, a few come up regularly. Here we outline examples using some of the opportunities we’ve been uncovering in Japan and Korea.
Too much focus on short-term headwinds
Korea’s leading online broker, Kiwoom Securities, is a good example of this. The stock currently trades at 0.6 times its trailing book value and 4 times normal earnings. This is largely because investors have been concerned that the challenging stock market that faces us all is likely to negatively affect the company’s profits in the short term. We don’t disagree, but if you look beyond these short-term concerns and focus instead on management’s track record of delivering outstanding fundamental growth and the attractive business opportunities available to Kiwoom – the potential looks compelling.
Kiwoom Securities Co Ltd stock price chart, 5 years
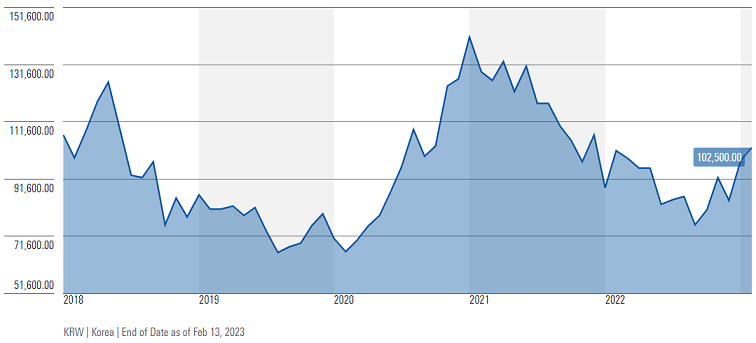
Source: Morningstar
Kiwoom’s management appears to share our view, having launched two opportune share buyback programmes last year—only the second and third buybacks in the company’s entire history. We typically take a positive view of a decision to repurchase shares, both because it increases the intrinsic value of the remaining shares and since it is often a sign of confidence in the outlook for the long-term fundamentals of the business.
Furthermore, the firm’s earnings and dividends could inflect in the years ahead, thanks to welcome regulatory relief. Recently, a new government has acknowledged the ‘Korea discount’ on the country’s shares, and seems prepared to take steps to remove it, for example by improving access to foreign investors by relaxing special ID registration. Should this occur, Korean shares could enjoy higher valuations.
Focusing on ‘sectoral woes’ rather than individual prospects
Banks are a classic ‘value’ sector that stand to benefit from favourable exposure to a changing economic regime, yet the sector is down more than 10% this year. Over the last 13 years, near-zero interest rates hurt banks’ lending margins, while regulations have limited their growth and payouts to shareholders.
But as the environment shifts, we have found increasingly compelling opportunities among banks globally, but particularly in Asia where financials generally seem a bit behind those in Europe and the US.
On current profits and payouts, banks like Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group in Japan, trade at 8-9 times earnings, with dividend yields of about 4%—which is already appealing. Japanese banks tend to have their balance sheets in order, they’re relatively well-capitalised, and they’re in a supportive environment where regulators want them to earn more money and are happy for them to pay that out to shareholders.
Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group stock price chart, 5 years
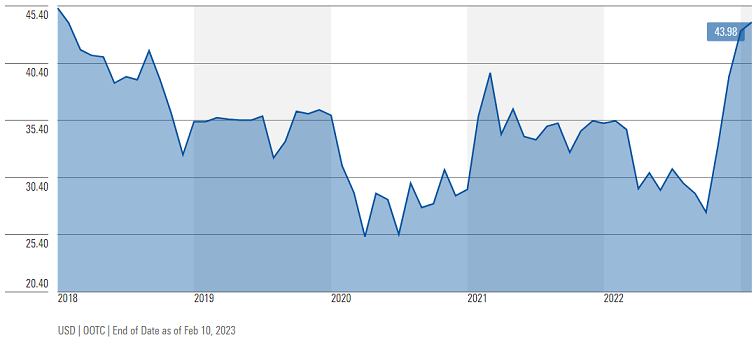
Source: Morningstar
But where Japanese banks could truly shine is if interest rates rise in Japan. With inflation now running well above the official 2% target and the Japanese yen having touched decades-low levels against the dollar, the Bank of Japan may soon have to raise interest rates.
If they move from zero to 2%, the earnings of Japanese banks could approximately double, leaving them on 4-5 times earnings with 8-10% dividend yields—which in our view is far too cheap. With the stocks trading at a 40% discount to book value today, we pay very little for that upside potential. When, or indeed whether, such a policy shift may come, we cannot be sure. But we think there are positive signs of change.
Focusing on the glamour rather than the growth
There are several examples within our portfolios of companies that we believe are trading for less than they are worth because they are in unglamourous industries like materials or manufacturing. A consequence of ‘The Great Misallocation’ that we’ve talked about previously, where market sentiment has driven money towards more wasteful places rather than more useful places.
In this environment ‘boring’ businesses are often overlooked despite generating exciting profits, in favour of more interesting ‘story’ stocks. Take Asahi Kasei, a Japanese chemicals-oriented conglomerate, for example.
In 2015, shares of Asahi Kasei were under a cloud due to a data falsification scandal in its concrete piling business—a small subset of its wider housing unit, which accounted for 30% of the company’s profits at the time. We believed the market was overreacting. In most regions, the company had stopped selling precast concrete piles in 2013, and the company’s main housing brands used an entirely different construction method to the houses affected by the scandal. Leaning against the pessimism, we were able to buy the company at near-record low valuations relative to the Japanese market, which was rewarding as the clouds lifted in time.
Asahi Kasei stock price chart, 5 years
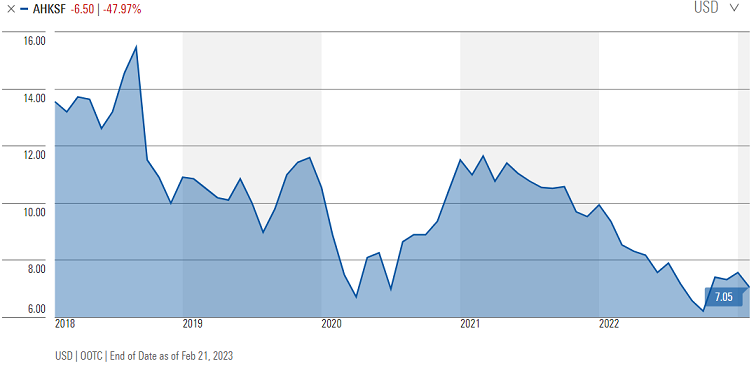
Source: Morningstar
Now, one of Asahi Kasei’s crown jewels is a US-based medical device company called Zoll Medical. Zoll sells a range of products centred on defibrillators and other devices used for critical care, including a wearable ‘LifeVest’ for patients at risk of sudden cardiac arrest. Protected by patents and supported by a large sales and distribution network, LifeVest gives Zoll a formidable competitive position, helping the company earn operating margins in excess of 20%. And Zoll is not the only part of the company’s healthcare business. In total, we believe this sector alone accounts for roughly 100% of Asahi Kasei’s current market cap despite only accounting for one quarter of its operating profit – which seems exciting to us.
A disciplined investment process
This also provides a good segue to the other side of the contrarian coin – the need for discipline when markets are heading off in the opposite direction.
Much of our focus remains on price and, importantly, whether we think the stock is trading below what we think it is worth. Over our 30-year history, there have been lots of companies we would have loved to own, had they been cheaper. But because they were too expensive, we stayed away.
In 1990, for example, we had no Japanese holdings, even though the Nikkei made up 42% of the global index, while in 2000, our exposure to so-called TMT (Technology, Media and Telecom) stocks was only 2%, compared to a 40% weighting in the global market. And, more recently, we were significantly underweight US stocks. In 2021, US stocks accounted for 66% of the world index but only around 30% of our portfolio - a position that made the past few years decidedly painful.
But as ‘The Great Misallocation’ that we’ve witnessed in markets starts to unwind, and valuation gaps start to close, we think our active, contrarian approach to stockpicking, with a focus on business fundamentals and valuations, will allow us to uncover many more opportunities like the ones described above.
Eric Marais is an Investment Specialist at Orbis Investments, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This report contains general information only and not personal financial or investment advice. It does not take into account the specific investment objectives, financial situation or individual needs of any particular person.
The forthcoming Active Advantage conference - jointly hosted by Orbis, MFS and Baillie Gifford - is a unique opportunity to hear directly from industry leaders examining the transformative long-term value an active approach can have on investment portfolios. This exclusive dialogue for advisers and institutional investors, examines local and global research into the critical factors we believe underpin good investing, and the key dynamics influencing investment decisions in the current environment. Register now for this unique event.
For more articles and papers from Orbis, please click here.