Some years ago, we tagged the crowding out of super funds from investing in limited-capacity smaller funds as the ‘Allocation Gap’. Many larger funds and consultants like the performance of these managers but with insufficient capital allocation for a large super fund to move their total performance needle, it was not justified.
At the same time, limited-capacity managers did not want a concentration of money from a single client. Hence money stopped flowing to good small managers and alpha was left on the table for other investors, but not the big super funds. The Allocation Gap is still alive today, especially in the microcap space, except now there are further considerations around performance fees that challenge investors.
The investment rationale for limited-capacity equity investment managers is well known; small boutiques focused on less scalable ideas because of liquidity, for example. But to harvest good things in small packages requires a sustainable business model and appropriate pricing. In the case of microcaps, where liquidity is limited and managers need to cap their FUM, performance fees are widely used to bolster the business economics.
This practice should not bother serious investors provided the fee structures are fair.
Smaller companies can produce dramatic relative outperformance
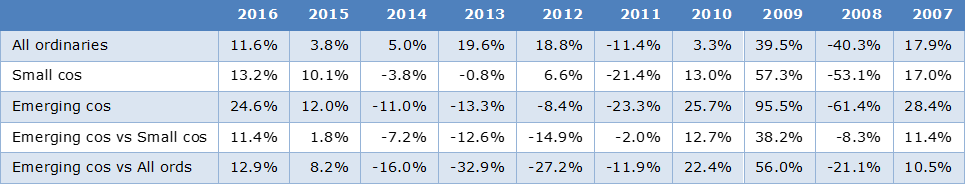
As the table below shows, the performance of ASX small and emerging companies indices varies considerably relative to the broader All Ordinaries index. The relative performance of the Emerging Companies index and the other indices has been very high in the past 10 years, ranging from negative 33% (-15%) to positive 56% (+38%) versus All Ords and Small Ords respectively. When the smaller companies ‘run’ they can produce dramatic relative performance in both absolute and relative terms.
Further, the small and microcap managers’ performances can add an additional volatility in investor returns. It is well established that small and micro-cap managers outperform their relative benchmarks strongly in some periods and yet underperform in others, whilst importantly many outperform over the longer term.
A set of eight microcap managers we reviewed outperformed the S&P Emerging Market index by an average of 3 to 4% per annum during the past 13 years and by about 7% per annum over a 10-year period. Managers outperformed by double-digit amounts in some years and would have charged very high performance fees. In subsequent years, underperformance was common. Other research has found that smaller cap fund managers have a higher probability of generating larger value add compared to the average large cap fund manager.
Investors carry the costs of fee structure
The important point is that this manager excess return volatility can have significant implications for the investor’s periodic fee expense. With a typical performance fee of 20% in excess of the benchmark, a manager may earn a multiple of its base fee in one year only to underperform in subsequent periods. When the high-water mark recovery period is long, and it can be many years, it is the investor who carries the cost of having paid out for unsustained outperformance.
Such is the potential for high performance fees in bumper years — think 20% fee on excess performance of 10 - 20% — questions come to mind. Does the presence of a performance fee change a microcap managers’ behaviour? Further, can there be temporal alignment of interests between the manager and the client, when the shorter the period under review for paying out performance fees, the less reliable is the track record data. We know good managers can underperform or have very little value-add primarily because of market noise, and the reverse applies for unskilled managers who experience a run of better fortune.
Managers should smooth the impact
To deal with this, where performance fees are accepted practice (as with microcaps), we suggest smoothing the impact of large performance fees on the investor by staggering the payment of the fee for a vesting period after it is earned. For example, the manager might be paid in three one-third installments. This method could be applied over shorter or longer periods with different proportions and can be integrated into the high-water mark.
In the longer term, the manager will receive its duly-earned fee while the investor will incur a smoothing of the cost. The investor would have gained a put option by deferring the fees of the manager in case the performance deteriorates after the initial period (that is, strong first-year performance, say 10% excess return, is not followed through in the second and third year, say -5% in the second year and 0% in the third year).
Opportunity to harvest returns left by large funds
The Allocation Gap is crowding out big super funds from microcap alpha and beta opportunities because of their scale and the manager’s capacity allocation across clients. This is an opportunity for smaller funds and investors to harvest the returns ‘left on the table’ by their larger peers. Performance fees can be an acceptable feature of limited-capacity microcap funds, but it is important that the impact of high periodic performance fees on the investor is reasonable, as such performance is often not sustained.
Dr Steven Vaughan is Managing Director and Sriram Srinivas is Research Assistant at Queen Street Partners. This information is general only and does not take into account the personal circumstances of any individual.