A combination of bank shares plus put options to protect against a fall in the value of those shares looks attractive at the moment. Grossed-up dividend yields are relatively high and the price of options on banks shares are relatively low. That is a happy combination, especially for SMSF investors.
Say that an investor thinks that ANZ shares have plenty of upside because the global search for yield will eventually bring investors back to all the major Australian banks, and especially to ANZ which is priced 25% lower than its high point of $36.80 in April 2015.
But the investor is concerned about the downside risk of bank shares in this period of greater economic uncertainty – there are many credible scenarios in which bank shares fall steeply over the next six months. Our investor wants to participate in any upside in ANZ shares, but for the next six months the downside risk is too much. What can be done?
A simple strategy for participating in the potential upside, but limiting the downside risk for a fixed period, is to own ANZ shares but protect them with put options.
Put option example
Sophie owns 1000 ANZ shares which are currently priced at $27.25. She wants to hedge against a fall in the share price below $27.00 between today (early January 2016) and the end of June 2016. Sophie is investing through her SMSF which is in the pension phase (rather than the accumulation phase), so we can ignore tax.
Sophie can buy 1000 put options on ANZ shares with an exercise price of $27.00 and a maturity date of June 2016 at $1.68 each.
Each put option allows her to put one ANZ share to the ASX (the seller of the options) and receive $27 in exchange. The option can be exercised (at Sophie's discretion) any time up to the expiry date of 23 June 2016 (the Thursday before the last Friday in the month, a standard expiry date set by ASX).
Pay-off to hedged and unhedged ANZ shares
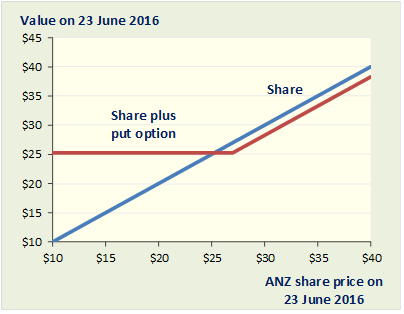
The graph above shows what the value of Sophie's investment in ANZ shares will be on 23 June 2016 (y axis) as a function of the price of ANZ shares on that date (x axis). The blue line is the value of shares that are left unhedged and the red line is the value of the shares plus puts (including the original cost of buying the puts).
The red line shows that once Sophie has purchased a $27, June 2016 ANZ put option for each of her 1000 shares, her investment in ANZ shares cannot fall below 27.00 - 1.68 = $25.32 in value. If instead of falling the share price rises, then Sophie doesn't need protection and will ignore the puts (which will expire unexercised).
Buying puts v 'going to cash'
Many investors have eliminated their exposure to the downside risk of ANZ shares by selling; that is, exchanging bank equity for a bank deposit. That achieves perfect capital preservation and locks in a six-month return of about 1.4% (based on 2.80% per annum for six-month term deposits).
The ANZ share and put combination does not provide full capital preservation but it does participate in the upside if ANZ shares rise, and it limits the damage to a return of no lower than -2.4% if the ANZ share price falls.
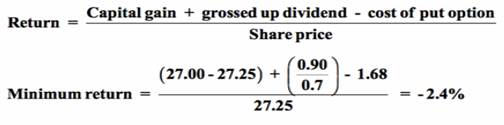
I am assuming here that ANZ's dividend, due in mid-May, will be 90 cents per share – a rise of 4.7% from the 86 cent dividend paid 12 months earlier. The dividend could, of course, be cut (as it was in 2009), or even reduced to zero, in which case the return to the share plus put would be -7.1%. However, if ANZ is forced to cut its dividend then Sophie will be very glad that she protected her shares with a put.
Relatively cheap put options?
Above I said that put options on bank shares are currently relatively low cost, but low cost compared to what?
A crucial driver of option prices is the expectation investors have about the future volatility of the price of underlying shares. Volatility is an option owner's friend. For instance, after Sophie buys ANZ put options, then higher volatility in the ANZ share price can only help her. If the volatility expresses itself as a big increase in the share price, then Sophie will benefit from that increase through ownership of the share. If volatility appears as a big price fall then no matter, Sophie has the put option to protect her. The higher the expected volatility, the more investors are prepared to pay for options that allow them to participate in the upside but be protected from the downside of large price movements.
Implied volatility
The relationship between expected volatility and the price of options is direct. If we know the expected volatility, then the famous Black-Scholes equation gives us the price of an option. Likewise, if we know the price we can work backwards to the expected volatility. This is the implied volatility of the option (volatility being implied by the price). The implied volatility provides a means of comparing the price of options across different stocks. And, a means to compare the price of options on a single stock, like ANZ, from day to day to say whether they are 'expensive' or not.
For instance, let’s compare the cost of protecting ANZ shares with options to the cost of protecting BHP shares. It cost Sophie 6.2% of the price of the ANZ share ($1.68/$27.25) to buy protection at close to the current price ($27.25) for six months. To achieve the same protection of a BHP share would currently cost her 13.1% of the BHP share price.
Protecting BHP shares is currently more expensive than protecting ANZ shares which reflects the difference in the implied volatilities of the shares. The implied volatility of BHP shares is currently about 40% but only about 20% for ANZ.
That 20% is not a historically low implied volatility for ANZ shares, but it is low when we consider how much uncertainty hangs over the global banking sector. If you think that more volatility is coming than the market is building into the put price (as I do) then you believe put options are currently selling at low prices.
Benefits of put option protection
Note that to participate in the upside but limit downside risk investors could use call options instead of put options. In that strategy the investor puts their money in the bank (instead of buying the share) and buys a call option (instead of a put option). In this strategy, if the share price fell then Sophie would have the money in the bank. If the share price rises, then Sophie can use the money in the bank to 'call' the share to her; that is, she can exercise the option to buy (not sell) an ANZ share for $27 (the strike price of the call option).
The equivalence of these alternative put and call strategies for eliminating downside risk creates a tight relationship between the prices of put and call options, which is known as put-call parity.
For an SMSF to be able to buy options, the fund's investment strategy and trust deed must allow the purchase of options. The fund must also have a derivative risk statement that sets out how options are being used to hedge risk.
Protecting shares with options for a short period of time can be a helpful strategy for investors, but there is a lot to know about option strategies, so seeking professional advice is highly recommended.
Dr Sam Wylie is a director of Windlestone Education and a Principal Fellow of the Melbourne Business School. Sam consults and teaches programmes for corporate and government clients and can be contacted on LinkedIn here. This article is for general education purposes and does not address the needs of any individual investor.