With reporting season well and truly behind us, we thought we’d take a look at the state of Listed Investment Company (LIC) balance sheets and their dividend coverage.
The company structure of LICs allows them to retain earnings and regulate the payment of dividends in any given year. This is an advantage LICs hold over trust structures. As a company, they can transfer after-tax profits to their dividend profit reserves as a prudent measure to improve the capacity to pay future dividends, consistent with forward policy guidance.
Some LIC dividends draw on previous reserves
With an estimated overall 25% decrease in dividends paid by ASX companies over 2020, it is unsurprising that in in the first half of FY21, most equity LICs paid out more in dividends than they reported as net profit, thereby creating payout ratios greater than 100%, as shown below.
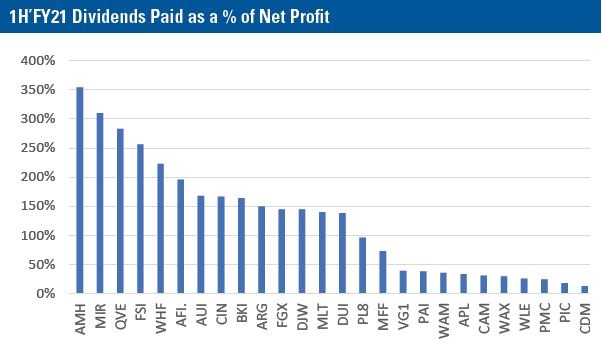
Source: Iress, IIR
We see that many of the LICs in our Australian Shares - Large Cap and Mid Cap sectors that relied on dividend revenues had payout ratios greater than 100%. However, LICs that rely more heavily on capital gains to generate returns or had global exposures were able to book realised gains to boost their net profit and thereby reduce their payout ratios.
While payout ratios of more than 100% are clearly unsustainable in the long run, some LICs have the ability to tap their retained profits/reserves to make up the shortfall, while others elected to prudently reduce their dividends to reduce the burden on their cashflow and balance sheets.
How many years of dividend coverage do LICs hold?
To check the sustainability of LIC dividends, we look at how many years LICs in each category could maintain current dividend levels given the latest reported retained earnings/profit reserve.
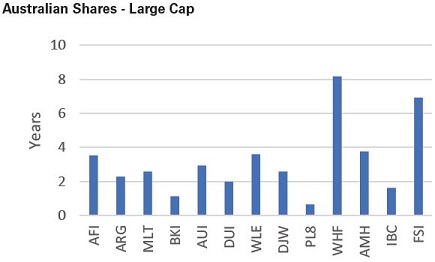
On average, the Australian Large Cap category has 3.2 years of dividend coverage. WHF and FSI have the greatest number of years of dividend coverage, at 8.1 years and 6.9 years, respectively, if they were to maintain the current dividend amount. Both these companies were able to draw on reserves to maintain and in the case of WHF increase the dividend throughout the volatility of 2020.
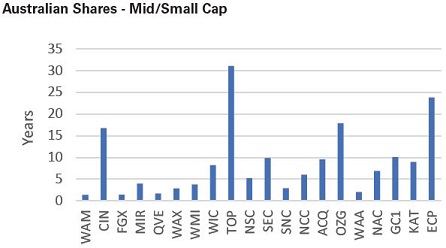
TOP, ECP, OZG and CIN all have in excess of 15 years’ dividend coverage. Taking these four outliers out, the Australian Mid/Small Cap category has an average of 5.3 years dividend coverage.
There are only three LICs with less than two years of dividend coverage in the category (WAM, FGX and QVE). LICs focused on the smaller end of the market are more likely to rely on capital gains for the payment of dividends with lower levels of income typically generated through the portfolio. A strong first half of FY21 in the markets saw some LICs increase their profit reserves and boost their coverage ratios.
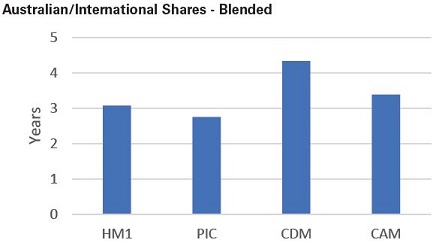
The Blended LIC category has a healthy level of dividend coverage as a group, with PIC having the lowest level of coverage at 2.8 years. HM1 paid an inaugural interim dividend for FY21. We have assumed the company will maintain the dividend for the final dividend for the purposes of this analysis. CDM’s portfolio performed strongly in the first half of FY21 which saw the profit reserve increase substantially and allowed for the company to maintain its dividend.
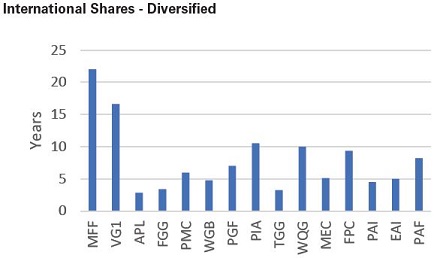
The International Shares-Diversified LIC category has a reasonably healthy level of retained earnings/profit reserves as a group. MFF and VG1 have the greatest level of coverage. The gains in VG1’s portfolio saw a significant increase in the profit reserve and allowed for the company to increase its dividend. PIA, WQG, FPC and PAF all have dividend coverage of 9+ years based on dividend declared for the CY2020.
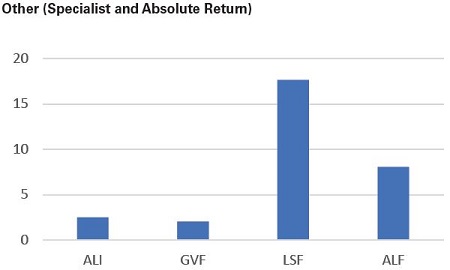
In the Other category, LSF and ALF both have healthy dividend coverage. LSF paid and inaugural interim dividend and is yet to pay a final dividend so we have calculated the dividend coverage level based on the company maintaining the interim dividend amount. In the event significant franking credits are generated, we would expect the company to start paying out a greater amount of retained earnings as dividends.
Relevance for a steady income stream
In summary, the level of dividend coverage should be considered by investors seeking a steady income stream. For those LICs that have many years of coverage, investors can be confident that there will be reduced volatility in their dividend income.
We note, companies will often seek to frank dividends to the maximum amount possible and therefore the extent of dividends may be impacted by the level of franking credits available. On the other hand, those LICs with a lower level of coverage may be susceptible to a reduction in dividends in the event the portfolio does not perform to expectations.
Claire Aitchison is Head of Equities & Funds Research at Independent Investment Research. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual, and is based on an understanding of accounting treatment for LICs at the time of publication.