It’s difficult to imagine the landscape without them. Indeed, history has shown that they’re too big to fail. However, revelations from the Financial Services Royal Commission have certainly taken a toll on how we perceive our major banks.
As investors, we have been long-term beneficiaries of the regular dividends they pay and yet some of the conduct uncovered has been reprehensible. So as investors, how should we look at banks in the future?
For me, there are three key areas to consider:
1) The importance of managing risk
Since the GFC, banks have made many changes to shore up what were already strong capital foundations. Capital ratios have risen almost three-fold in 10 years to ‘unquestionably strong’ levels. Liquidity management has also strengthened with banks switching to more stable sources of funding and increasing their holdings of liquid assets. As a consequence, Australian bank return on equity (ROE) has slightly decreased to around 12% but still remains strong by international standards (around 8% for large US banks).
Today, we’re largely at the tail-end of this shoring up process, although as highlighted by the Royal Commission, there’s still some work to do to mitigate operational risk stemming from poor culture. To date, the financial implications for ‘banks behaving badly’ have been relatively minor, but the consequences of reputational damage could significantly impact profitability if it continues.
2) A slowing credit market
In the last 12 months the credit market has noticeably slowed, as shown below. This is likely to continue, at least on the investor side, as a result of households becoming more cautious and banks tightening their lending standards. With household debt at high levels relative to global benchmarks, this isn’t altogether a bad thing. In fact, longer term it will have a positive impact on our financial security as Australia and the banks will be more resilient to a downturn.
Credit growth (six-month-ended annualised)
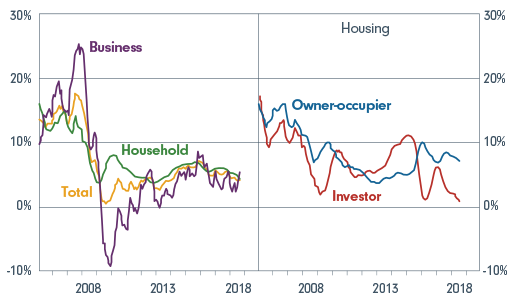
Source: APRA, RBA
Shorter term however it does have a couple of implications for the majors:
- Fewer loans mean less profit.
- Tighter lending practices mean more stringent checks and balances which increases the time it takes to process a loan application.
Tighter lending standards have meant more paperwork because it’s new and the process is still quite manual. Over time, it will become increasingly automated making the process much faster and importantly cheaper. We can expect to see technology projects replace people as the need to reduce the cost of labour intensifies.
3) Disruption from an intruder
In the last 10 years, we have witnessed some remarkable changes in market leadership in other industries. Established Goliaths have fallen as disruptors have swept in and completely sidelined their business models. So, could something like this happen to the major banks?
There will continue to be smaller companies which pick off individual niches. For example, OzForex in foreign exchange and AfterPay in payments. But when it comes to the core banking operations, Australian banks have invested heavily in technology particularly around service and convenience and a disruptor would have to offer something unique to displace them in a material way. This is especially true in banking, given the time it takes to establish the ‘trust’ many of us seek from our institutions.
Perhaps what strikes me most about Australia’s banks is their ability to adapt. Whether it be self-regulation to strengthen their financial health or investing heavily in technology to meet the changing needs of their customers, they really are the ultimate market chameleons. And they’ll need to be.
The GFC proved they were ‘too big to fail’ but today the message from the Royal Commission is clear - they’re 'too big to behave badly'.
Kate Howitt is a Portfolio Manager of the Fidelity Australian Opportunities Fund. This document is issued by FIL Responsible Entity (Australia) Limited ABN 33 148 059 009, AFSL 409340 (‘Fidelity Australia’), a member of the FIL Limited group of companies commonly known as Fidelity International. This document is intended as general information only. You should consider the relevant Product Disclosure Statement available on our website www.fidelity.com.au.
Fidelity International is a sponsor of Cuffelinks. For more articles and papers from Fidelity, please click here.
© 2019 FIL Responsible Entity (Australia) Limited. Fidelity, Fidelity International and the Fidelity International logo and F symbol are trademarks of FIL Limited. FD18634