In Part 1 of this series, we showed that the company tax rate has no impact on the amount of after-tax dividend received by an Australian shareholder.
This Part 2 examines whether a company should retain earnings or pay them as dividends to shareholders. Fund managers often advise that it is best for companies to retain profits and redeploy the capital to generate attractive returns. This advice ignores the tax implications for different types of investor.
Better for superannuation and pension funds to receive dividends
Retaining after-tax profits in a company in Australia means that from each $100 in company profit before tax, $70 is reinvested by the company (after the 30% tax). The cost to a shareholder of investing that $70 in the company is the forgone after-tax dividend.
This is $53 or $65.50 for an individual after tax, depending on the personal tax rate. This might seem a good deal for these shareholders, but the deal becomes less than favourable when capital gains tax (CGT) is taken into account.
For a superannuation or other low tax-paying shareholder, however, the retention by the company is singularly unattractive. The cost to the shareholder of investing that $70 is the foregone after-tax dividend of $100 if the shareholder is a pension fund or $85 if the shareholder is a superannuation fund. Neither of these represent an attractive means of adding $70 to their investment in the company. Companies do need to retain capital in order to continue to operate and to expand but retaining some of their after-tax earnings is an easy and indeed lazy way for the directors to grow capital.
CGT implications make it even worse
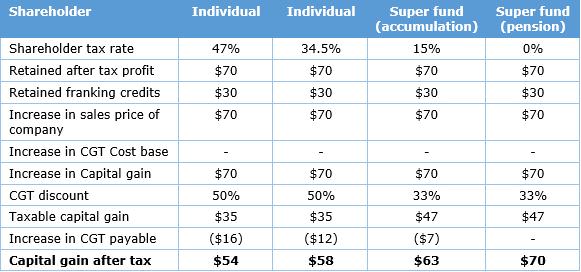
Consideration of CGT does not improve the position. Retaining an after-tax profit of $70 within the company rather than distributing it as an increased franked dividend only makes sense if it increases the value of the company by at least $70. For CGT purposes, the retained after-tax profit does not change the cost base for future calculation of CGT.
If the shareholding is sold having held the shares for more than 12 months, the position becomes:
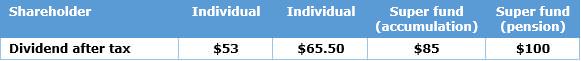
Consider the ‘dividend after tax’ scenario modelled in the table last week, reproduced below.
The impact on a shareholder of investing $70 into an Australian company because the company did not distribute a dividend and retained the $70 will be:
- individual shareholder on a marginal tax rate of 47% - instead of receiving an after-tax dividend of $53, the after-tax benefit if sold at that time would be $54, or close to a line-ball.
- individual shareholder on a marginal tax rate of 34.5% - instead of receiving an after-tax dividend of $65.50, the after-tax benefit if sold at that time would be $58.
- superannuation fund shareholder on a tax rate of 15% - instead of receiving an after-tax dividend of $85 the after-tax benefit if sold at that time would be $63.
- pension fund shareholder on a tax rate of zero - instead of receiving an after-tax dividend of $100 the after-tax benefit if sold at that time would be $70.
Both the superannuation fund and pension funds would be significantly better off if the company distributed the profits rather than retained then in the company, and then raised new capital as required in other ways, including from the shareholders who received the dividends.
The case for dividend reinvestment rather than retaining earnings
Retained after-tax earnings is an easy and lazy way for company directors to increase or retain capital but it is a conspiracy against low tax-paying Australian shareholders. The alternatives would be for the directors to justify the need to raise capital by a share offer to shareholders and the market.
Of course, directors could encourage dividend reinvestment by making it more attractive. With dividend reinvestment, the company retains the after-tax amount of $70 but the benefit of the franking credit is distributed to the shareholders.
Further, for tax purposes, the shareholder has invested $70 in the company and this is reflected as an increase in the cost base for future CGT purposes whenever the shares are sold. The company’s value has still increased by $70 but so has the cost base so there is no immediate CGT liability if the shares are sold at this time.
Company directors should be asked why they do not seem concerned at the tax inefficiency of retaining after-tax profits.
(Note that no comment is made here on the proposed Labor Party policy to stop refunds of excess franking credit. Labor is not proposing an end to dividend imputation, and there is too much uncertainty about whether Labor will be elected, whether they will change their policy or whether they can pass it into legislation).
Graham Horrocks is an actuary specialising in financial planning and superannuation, and a former General Manager, Research & Quality Assurance, with Ord Minnett. Since 1999, he has been an independent financial adviser. The article was reviewed by Geoff Walker, former Chief Actuary at the State Bank of New South Wales and winner of the 1989 JASSA Prize for published research on the implications of the then relatively-new dividend imputation system.