In a recent article (Cuffelinks, 21 February 2014) I showed that longevity has continued to increase steadily since the 1800’s after being relatively stable for at least 2000 years. These increases accompanied the onset of the industrial age and the growth of science. New discoveries, inventions and social strategies have combined to increase the lifespan of a baby from 35 to 82 in just over 200 years.
One school of thought believes that increasing community longevity is the result of a ratchet effect – the more we learn (and contribute to increasing longevity), the more we retain the wisdom of our older population which in turn helps to further increase longevity. Increasing longevity then plays a part in further longevity increases. Definitely one for the philosophers.
How long and how well?
Until about age 50, people typically take little interest in their own lifespan other than to insure against its untimely end. However, people over 50 are increasingly aware they might live well into their 90’s. There is a growing realisation that how they manage their remaining years will strongly influence just how long and how well they might live.
Longitudinal studies (studies of the same people over an extended period) are revealing how the lifespan of older people is panning out. The following table shows how – on average – things are shaping up at age 65 and beyond.
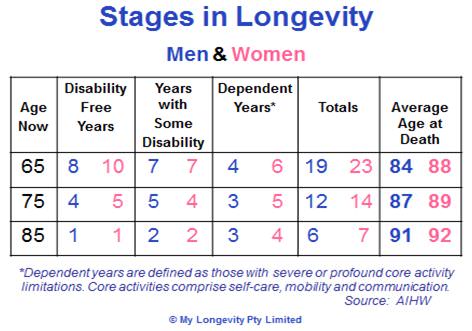
These numbers, from the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, are useful for people looking to make informed decisions about managing their futures. While accepting the limitations of applying this general data to an individual, there are some important planning opportunities. For example:
- At the age of 65, for both men and women, over half their remaining years are lived with some disability and ultimately dependency.
- For most people still alive at 85, around half their remaining lives are will be spent with severe core activity limitations.
- There is a survival bonus: the longer you live, the longer you are likely to live and the additional years are likely to be with less disability. Looking after ourselves physically and mentally could pay off now as well as later.
- Expected dependent years decline with increasing age (it’s clearer in the numbers above at the next decimal point). This is contrary to most people’s expectations.
- The gender differences are striking. Currently, women live longer but seem to be in worse shape than men over time. Could this be rectified at the personal level?
In interpreting this research and applying it to our own lives, we should note:
- These findings show how things are now. However, knowing this information, enables us to take action to influence our own outcomes.
- As we age, we become more different from each other, not more alike. We can address what is important to us individually, not just follow ‘trends’.
In 20 years from now, this table could (and probably will) look a lot different. Just how different will depend on what we do in the meantime.
Longevity awareness should improve decision-making
Personal longevity awareness can lead to better decisions. What is ‘longevity awareness’? At the personal level, I use the definition ‘seeing the future and planning for it’. Can we really plan for our longevity?
Ten years ago our thinking was still dominated by the tolling bell of the Life Tables, the deeply ingrained notion of retirement and the fear of disappearing into a grey and formless future after age 65. These limitations have been largely washed away by waves of reliable information about the potential richness of later life. But how many people realise this?
Greater longevity awareness can impact on personal and community decisions. We should be making better decisions affecting our health, employment, housing and social support as we age, along with many other strategies.
Perhaps we should be working longer, believing that there will be enough quality time left at age 70 or more to achieve our ‘retirement goals’ with time to spare.
We can develop a plan for tackling the spectre of dependency by addressing now the factors which lead to it – such as frailty and poor balance, muscle loss and declining cognitive awareness. Understanding more about our possible timeframe at least gives us the choice of whether we will take action or not.
Longevity awareness is becoming at least as important as financial literacy in helping people achieve and maintain the greatest possible independence. Greater longevity awareness, both in number and quality of years, will improve our personal decisions, our community decisions and our lives.
David Williams began longevity research in 1986 and was a Director with RetireInvest and CEO of Bridges. He chaired the Standards Australia Committee on Personal Financial Planning. David founded My Longevity Pty Limited in 2008.