Investors crave certainty and when we don’t have a conclusive answer on a topic, our natural response is to sit on the sidelines.
The coronavirus pandemic has raised uncertainty about markets. Few investors saw the March crash coming, which led to a 35% decline in equity markets. Even fewer anticipated the strength of the recovery that followed.
Market timing is too difficult
The lesson during this period is something we have heard all too often: markets are unpredictable and trying to time markets based on news and headlines does not work.
We don’t like to hear that the future is uncertain, which is why many investors look for opinions from market commentators about what could happen, and this often leads to an attempt at market timing which is rarely successful.
There is a limit to how much information we can digest, and once we acknowledge that, we can look at strategies that allow us to generate returns without the need to time markets.
On the other side of the spectrum are investors who are too idle, often not investing whether markets are selling off nor when they are making new highs.
Avoiding markets when they make new highs may feel right intuitively. However, the reality is it often leads to missed opportunities and significant underperformance. Markets often continue to make new highs for an extended period of time and sitting in cash when rates are low can mean a negative return net of inflation.
Knowing what you don’t know
We know little about the virus, potential mutations and sustainability of immunisations, how reopening economies will play out or how long developing nations might struggle with exponentially growing cases.
Warren Buffett's offsider, Charlie Munger, summed it up neatly:
"This thing is different. Everybody talks as if they know what’s going to happen and nobody knows what’s going to happen.”
Economic impact: What we do know
- Global GDP will shrink in 2020.
- Certain sectors won’t go back to the way they were for a very long time, such as travel and tourism sectors while other sectors will benefit over the long term.
- Central banks will continue to support economies by any means necessary. The consequence of this is higher deficits and lower interest rates.
- Reserve Bank of Australia Governor, Philip Lowe, has made it clear that low rates are here to stay and while negative rates are “highly unlikely” the central bank will continue to use yield curve control as the preferred monetary policy tool.
- Looking at historical trends globally, following the 2008 GFC, central banks also lowered interest rates to stimulate the economy. The US lowered rates to near zero for eight years and while they raised them in 2016, they quickly went back down to zero. The European Union kept rates near zero since 2009 and went below zero in 2014. Japanese rates have been near zero since 1999 and went negative in 2016. If history is any guide, waiting for interest rates to rise may result in years of underperformance.
Major Central Bank Rates
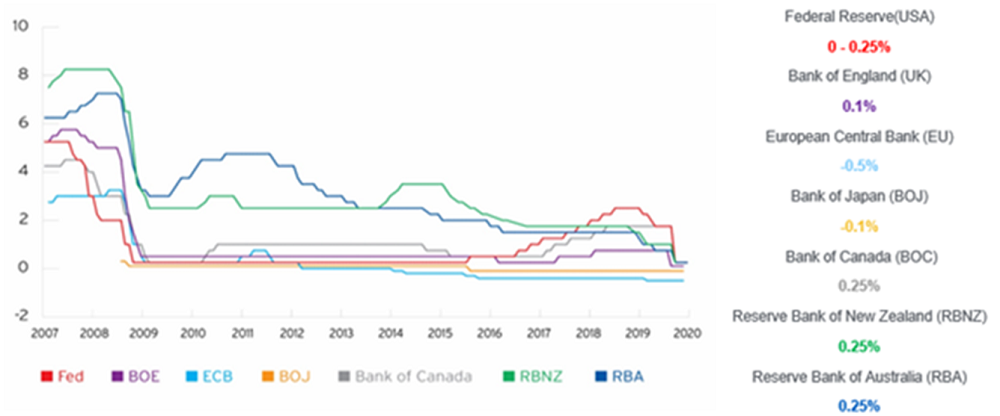
Source: Bloomberg
Five strategies for uncertain markets
Here are some strategies that investors can employ that mitigate the risk associated with timing markets or remaining idle.
1. Invest with less directional payoffs: certain investments may allow investors to gain indirect exposure to equity markets while offering some degree of capital protection. These investments can be tailored to modify the risk return payoff of the underlying exposure. Structured notes are one such vehicle. One of the most popular structured notes allows investors to receive an unconditional coupon payment as well as profiting whether the chosen basket of shares go up, stays flat or falls by up to 30%. This means investors can choose stocks they see value in without having to time the bottom of the market.
2. Look for reliable income: There are certain investments that offer unconditional income, like corporate bonds or structured notes. This provides some certainty in an otherwise uncertain environment. This is a much more sustainable source of income for investors, provided the issuer does not default, when compared to dividends, which even for blue chip names may be cut or suspended during an economic slowdown.
3. Stay cautious and minimise cash investments: Central banks around the world have reacted in a coordinated manner and have successfully avoided economic disaster. The liquidity injection to date is approximately $US15 trillion, which is 17% of global GDP. One of the long-term consequences of money printing is the devaluation of currency values and over time inflation erodes purchasing power. Cash is especially problematic when interest rates are so low and likely to stay low for an extended period. The rate of return is negative net of inflation.
4. Consider absolute return strategies: this refers to the ability to generate a positive return even when equity markets are falling. They look beyond a basic equity and bond portfolio to include unconventional assets for uncertain times. These strategies typically generate a moderate return with lower levels of volatility.
5. Diversify across uncorrelated assets: when creating a resilient portfolio, investors need to look at asset classes that have low correlation for example, adding bonds and gold exposure to an equity portfolio can help cushion portfolios if there is a prolonged downturn in equity markets.
Peter Moussa is an Investment Specialist - High Net Worth at Citi Wealth Management. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.
Citi is a sponsor of Firstlinks. For more Citi articles and papers, please click here.