There is no denying that we live in a world of short-termism. From the 24-hour news cycle and daily market moves to the relentless focus on the latest set of company earnings, we are always grappling with new information flooding our way. We often overtrade as we become impatient and feel the need for action. This begs the question, does the market reward the active managers and other investors who can sit tight and invest with a long-term lens?
A report by the Thinking Ahead Institute (part of Willis Towers Watson) called 'The search for a long-term premium' explores this question and offers interesting insights. The study identifies eight fundamental building blocks of long-term value creation. These factors can be categorised in two broad camps:
- Strategies that provide long-horizon return opportunities
- Strategies that lead to lower long-term costs and/or mitigate risks
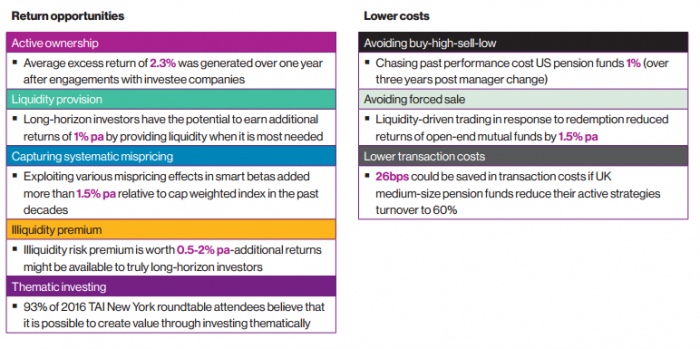
Long-horizon return opportunities
1. Active ownership and investing in long-term oriented companies
Research by McKinsey has found that firms create value by taking a long-term approach. Investors can exploit this in two main ways. The first is that skilful investors can identify and own companies who have a genuine long-term focus. Alternatively, investors can engage with companies they own to improve performance. The research suggests investors can expect to harvest an additional 2.3% abnormal return the following year.
A further study analyses the 183 companies CalPERS has actively engaged with between 1999 and 2012. Three years prior to the engagement, these companies underperformed the Russell 1000 Index by 38.9% on a cumulative basis. In the five years following CalPERS’ engagement, on average, these firms generated cumulative returns of 12.3% above the index.
2. Liquidity provision
Long-term investors can act as providers of liquidity in times of market distress. By providing liquidity when it is most needed, investors can harvest a premium of 1% per annum. When investors require liquidity, they sell at below fair value while long-term investors can exploit this through purchasing at below fair value with cash held in reserve. Further, long-term investors who provide liquidity serve a social good as it helps stabilise markets in volatile times.
3. Capturing systematic mispricing
Exposure to smart beta strategies can help generate an additional excess return of 1.5% per annum. Rob Arnott of Research Affiliates found that all alternative weighting strategies have outperformed the cap-weighted benchmark over the long term. This may be a consequence of unintended value and small-cap tilts which are often unavoidable unless one holds a portfolio that has a positive relationship between price and portfolio weights (such as a cap weighted index).
4. Illiquidity premium
The illiquidity risk premium (IRP) estimated at between 0.5% and 2% per annum can be harvested through exposure to long-term illiquid assets. As investors invest in these illiquid assets, they demand a higher risk premium for their inability to quickly sell down their assets as needed.
5. Thematic investing
Themes are often easy to identify but the scale and rate of change is difficult to anticipate. The world is running out of oil, renewable energy can save the planet, many countries have ageing populations and technology is changing our lives. However, such investments are often neglected as they are hard to time, particularly when investing with a short-term lens. While there is no empirical evidence supporting that thematic investing generates excess return, 93% of the 2016 Institute of New York roundtable attendees believe thematic investing to be value enhancing.
6. Avoiding buying high and selling low
Investors typically sell winners and hold onto losers. As a stock performs well, we want a piece of the action, while when a stock performs poorly, we hold on and hope for a recovery. We typically end up buying high and selling low. Jason Hsu found that mutual fund investors have forgone 1.9% per year due to poor timing decisions. Short-term trading can at times be a mug’s game.
Cost reduction and loss mitigation strategies
7. Avoiding forced sales
Investment funds often engage in short-term trading driven by liquidity needs. In particular, redemptions can result in ‘fire sales’ where managers are forced to sell assets below fair value, destroying value in the process. One study has found that liquidity-driven trading in response to mutual fund flows reduced abnormal returns in US open-ended mutual funds by 1.5% to 2% per annum. A second study found the cost to be 112 bps per annum. While closed-fund structures have limitations, forced selling can result in value destruction.
8. Lower transaction costs
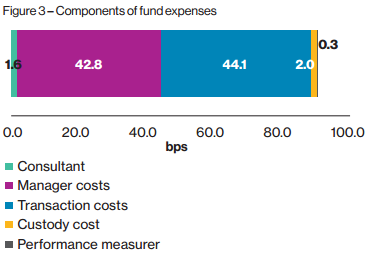
Willis Towers Watson’s ‘UK Food Chain’ study estimates the size of each component of fund expenses based on a medium-sized UK pension fund. Transaction costs account for 44 bps, or almost half of all fund expenses, as shown below.
Components of fund expenses
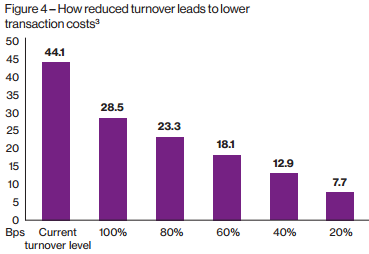
In addition, the next figure shows that reduced turnover levels can substantially reduce transaction costs, significantly improving investment outcomes.
How reduced turnover leads to lower transaction costs
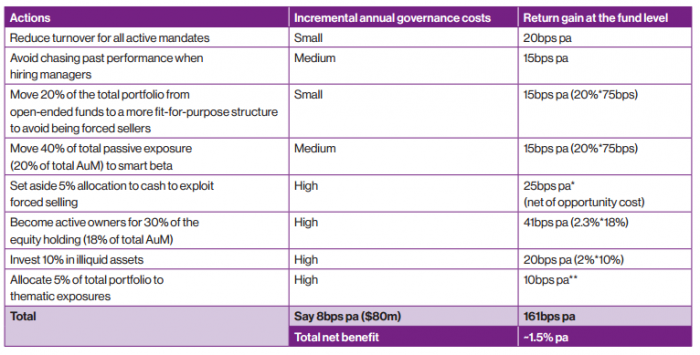
Note it is not appropriate to sum the return potential of the eight building blocks, which would yield an incremental return of approximately 10%, as these factors are correlated.
A snapshot of additional incremental returns
Bringing together all eight factors, the table below presents potential benefits for a large asset owner investing with a long-horizon approach. The Thinking Ahead Institute observes this investment approach yields a potential incremental return of 1.5% per annum over the long run.
To put this into perspective, a $50,000 portfolio invested for 20 years returning 6.5% per annum would net a healthy $176,000. However, a return of 8% per annum would turn $50,000 into a whopping $233,000. What a difference a few percentage points can make in the world of compounding.
There is a strong belief that a long-term premium exists. The challenge, of course, is to harvest it.
Wilbur Li has worked at Yarra Capital Management (fixed income), PwC (debt and fixed income) and Unisuper (global equities).