Historically, investors have looked to Australian Real Estate Investment Trusts (A-REITs) as a medium-to-long term property investment option, providing a sound base of distribution yield, capital growth and with the added benefit of liquidity. The A-REIT market offers retail investors an opportunity to invest in some of the highest quality real estate in Australia with strong lease covenants, such as ASX listed corporates, Governments, multinationals, and national tenants. Strong lease covenants ensure contractual rent commitments flow-on to investors in the form of distributions. The large scale of A-REIT property portfolios and consequent tenant diversification ensures that a single tenant expiry is unlikely to negatively impact investors distributions.
A-REITs can diversify your investment portfolio by exposure to the core property sub-sectors of industrial, retail, office and to the emerging alternate sectors of seniors living, affordable residential rentals, self-storage, healthcare, data centres and the build-to-rent residential sector. Many of these nascent high growth alternate property sub-sectors will capture the convergence of societal megatrends, such as urbanisation and technology, affordable housing and ageing demographics, to cite just a few.
The asset quality of the A-REIT sector is best reflected by the basic property fundamentals – a weighted average lease expiry (WALE) of 5.5 years and an overall average occupancy level of 98.3%. The robust capital structure of the sector is illustrated by a look-through gearing level of 25% (debt/assets), an interest coverage ratio of 5.0x (excluding large fund managers such as GMG and CHC) and debt maturity of 4.8 years with 76% hedging.
The sector is cheap – on all metrics
The A-REIT market is one of the most interest rate sensitive parts of the Australian equity market and it has been under considerable pressure due to heightened uncertainty on the outlook for both short term cash rates and 10-year Government bond yields. Interest rate markets have been adjusting after central bank quantitative easing policies destroyed the term structure of interest rates – a normal positive shaped yield curve.
The rising cash rate has increased the cost of debt finance and reduced distributions. Meanwhile, the upward movement in 10-year bond yields is working its way through property valuations as property capitalisation rates and discount rates are adjusted higher to reflect increased risks relative to bonds.
A-REITs are now trading at 12% below pre-COVID levels compared to the broader ASX market at 13% above pre-COVID levels. The market is pricing A-REITs at a 25% discount to their Net Tangible Assets (NTAs), and the sector has only been this cheap during two other periods: the GFC and Covid-19.
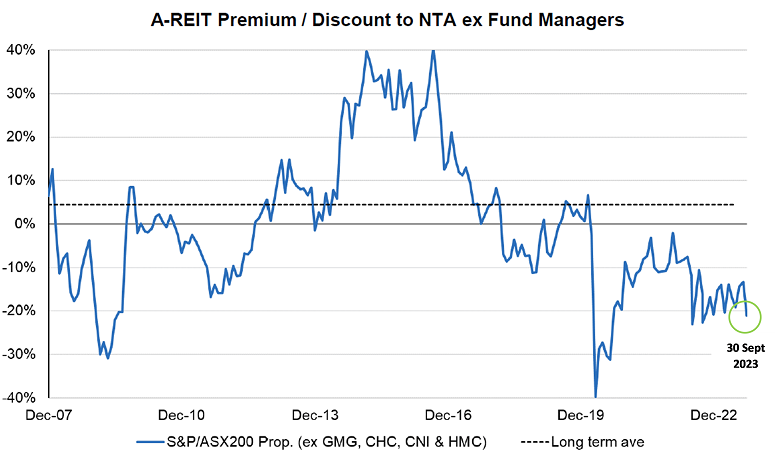
Source: UBS.
The market is pricing the sector property capitalisation rate (ex-GMG) at 6.6% or 150bps above the sector’s stated capitalisation rate of 5.1%. The capitalisation rate is the rate of return on a property based on the net operating income that the property generates.
Even with the expected property devaluations to occur this financial year, we think the market is excessively pricing this in. As a result, the sector distribution yield is 5.0%, with 3.0% per annum distribution growth forecast for the next three years (ex-GMG and CHC).
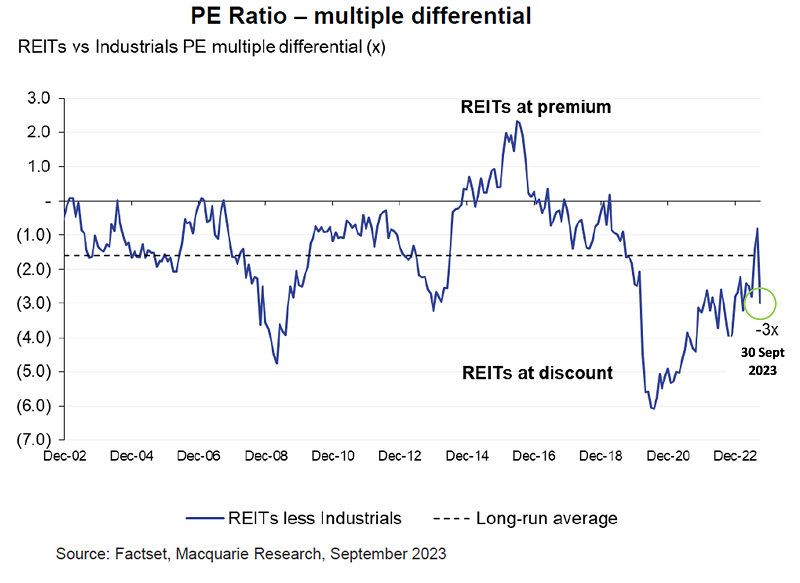
On a price to earnings (PER) multiple, A-REITs also look inexpensive, trading at 14x versus the broader equity market’s 17x. The PE differential of 3.0x is above the long-term average of 1.6x, as the chart below shows.
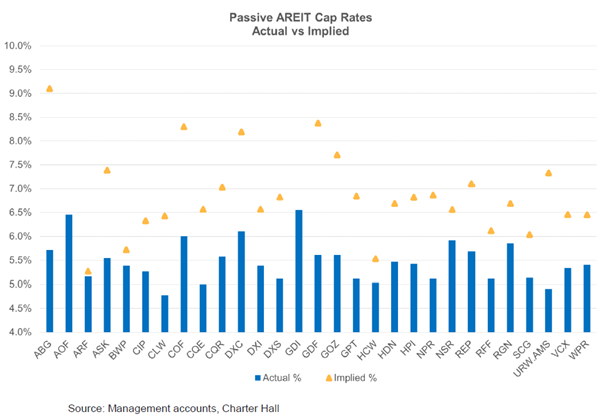
Another way to assess the value in A-REITs is through the implied pricing for the passive A-REITs or the rent collectors (non-fund managers). The A-REIT market is pricing the rent collectors for a further 20% fall in value or an implied property capitalisation rate of 7.2% versus the reported cap rate of 5.5% at June this year.
Other upside
The current environment is a chance for quality managers to showcase their capital management skills by executing buybacks or continuing to sell assets and reduce debt.
Merger and acquisition (M&A) activity is also likely. In every A-REIT cycle, M&A happens either within the sector, public to private takeouts or even foreign property groups taking advantage of cheap listed property portfolios combined with a low Australian dollar. Listed plays, Hotel Property Investments (ASX: HPI) and National Storage (ASX: NSW) have attracted suitors in the past.
We’re motivated by the opportunity for capital growth driven by the dislocation between the pricing of listed securities relative to underlying asset values and strong underlying sector fundamentals. Our own A-REIT Fund enables us to offer investors a portfolio of underlying property exposures beyond the traditional core real estate sectors of office, retail and industrial. This allows us to tap into emerging real estate growth sectors, many of which are exposed to megatrends. These growth sectors include seniors housing, affordable residential rentals, data centres, self-storage, childcare, and healthcare.
Mark Ferguson is Head of Charter Hall Maxim Property Securities at Charter Hall Group, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is for general information purposes only and does not consider the circumstances of any person. There are risks inherent in every investment. You should conduct in-depth research before deciding whether to invest, and if you are in any doubt, you should consider consulting your financial adviser, stockbroker, or other professional advisers.
For more articles and papers from Charter Hall, please click here.