The future of offices in a post-pandemic world continues to be a topic of robust conversation.
Most airtime on the subject has been given to dramatic statements like “expect the death of the office” – perhaps recycling articles from the past decade that incorrectly asserted a retail apocalypse was nigh! The reality is that, as retail has adapted to the internet age – and survived – so too will office spaces adapt to these changing conditions1.
It can be easy to fear the worst, especially as reports of landlords handing keys to the bank; assets sitting unoccupied; and valuations declining 80% take up the front page of newspapers.
It’s important, however, to understand that these events have been limited to the US, a challenged market with different financial, social, and real estate context. The outlook for office in Australia is markedly more positive for several reasons.
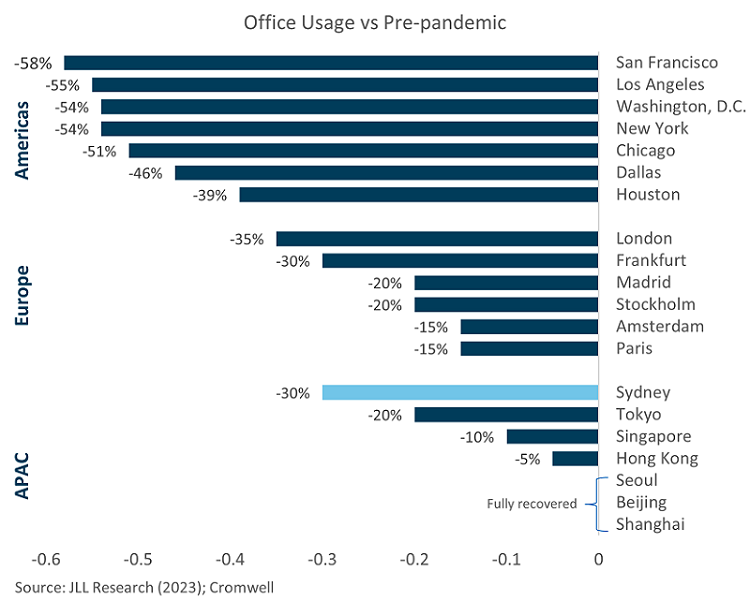
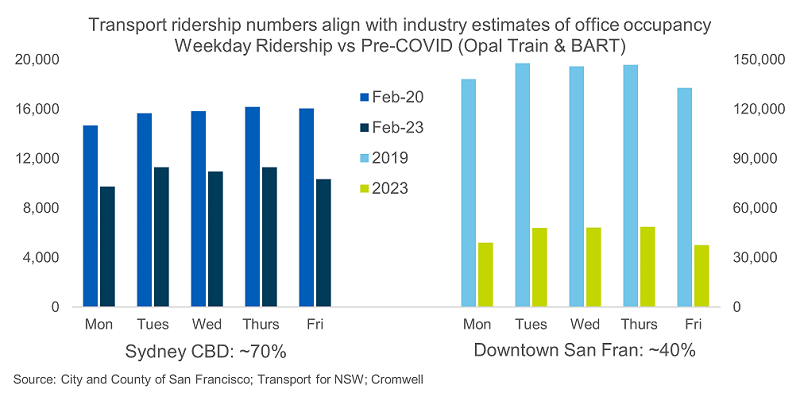
Higher office occupancy
Propensity to return to the office appears to be driven by a number of factors, including cultural expectations (e.g., Tokyo/Seoul); industry composition (e.g., finance vs tech); and ease of commute (e.g., rapid transit vs LA traffic). While workers around the globe highlight commute time as the most important driver of returning to the office2, another critical factor is the micro-location of each office building. In addition to influencing commute time, different locations can vary significantly in terms of crime and safety risks, amenity (e.g., restaurants), and environmental desirability (e.g., proximity to water/green spaces).
Australia measures up attractively on these characteristics, offering reliable rapid transit, exceptional proximity to desirable environmental features, a high density of quality amenity integrated throughout the CBDs, and very low rates of crime. The return to the office should gather more steam in the coming months as large employers mandate a minimum number of days in the office per week, as announced recently by NAB and CommBank. However, over the long-term, locations and assets which can attract employees through choice rather than coercion will outperform.
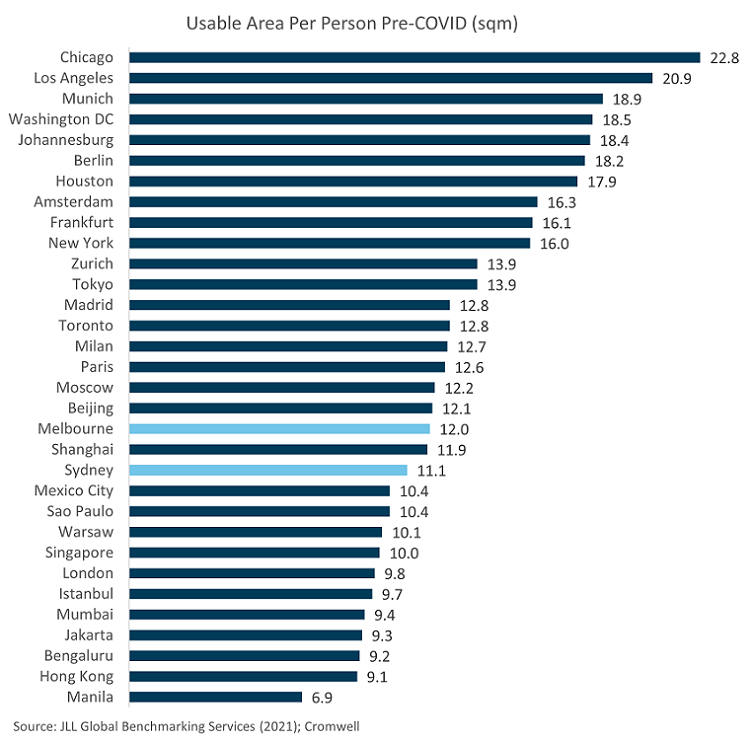
Expanding space requirements
One of the forces expected to offset the impact of remote work is the expansion of workspace ratios – the amount of office space per employee. Forty years ago, in the days of private offices, Australian offices had more than 20 square metres (sqm) of space per employee. Over time, as occupiers sought more ‘bang for their buck’, desks became more tightly packed together and the corner office was sent to the scrap heap.
The result has been densification of the workplace, with the pre-COVID workspace ratio sitting at 11.1 sqm per employee for Sydney and 12.0 sqm for Melbourne3.
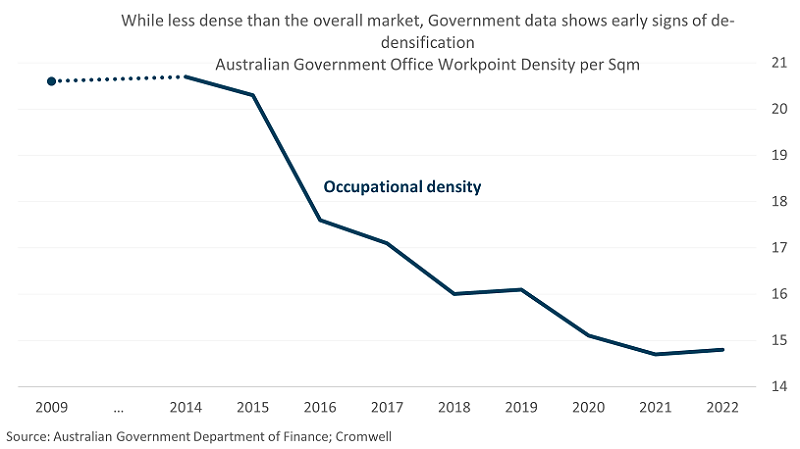
The experience of the pandemic has initiated a shift in the purpose of the workplace and workstyles. The office is increasingly becoming a place for collaboration and social connection rather than focus work, meaning a greater need for meeting, gathering, and collaboration spaces. There is also a need to lower density and make workplaces more comfortable from an employee wellbeing and retention perspective, as employers fight for top talent. Studies have shown that inadequate privacy and space is the dominant cause of workspace dissatisfaction4.
In the US, markets such as Chicago and Los Angeles have ratios above 20 sqm per employee, with even New York at 16.0 sqm3. The pandemic-initiated evolution of the work environment can be achieved in these markets by simply recalibrating (and even shrinking) existing footprints.
Contrast this environment with Australia, where workspace ratios are below the global average of 13.3 sqm3 and potential space efficiencies are limited. In this market, the recalibration will likely require additional space, providing a source of demand and limiting the amount of rent-dampening excess stock.
Appropriate financing
Earlier in the year, some high-profile office defaults in the US by Brookfield, and a PIMCO-owned landlord, kicked off concerns about a real estate debt crisis. Risks are certainly elevated in the US, given the aforementioned demand challenges, which will pressure serviceability and put significant downwards pressure on valuations. While pockets of distress may emerge in Australia, the likelihood of a widespread crisis is much lower. Banks remain confident in Australian commercial real estate, increasing their exposure by 5% in December 2022 compared to a year ago5. Loan quality has also remained stable, with non-performing commercial property loans as a share of total exposure unchanged at 0.5%.
Most importantly, the office demand outlook in Australia is much more positive. Solid cashflow will support serviceability as debt rolls onto higher interest rates and help prevent valuations from declining to the extent that is expected in the US. Australia’s lending market is also well regulated, diversified, and strong, and doesn’t face the concentrated exposure or balance sheet issues that smaller regional banks in the US have been contending with throughout 2023.
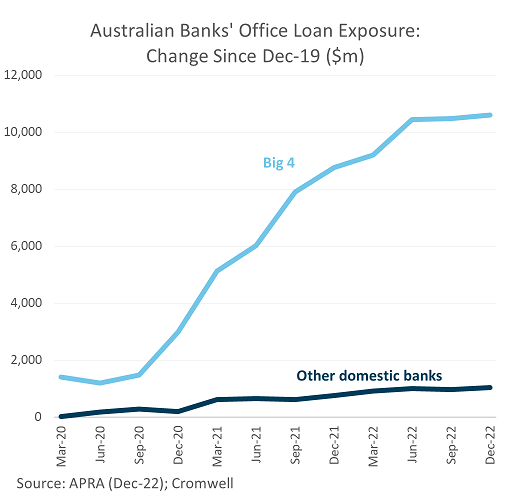
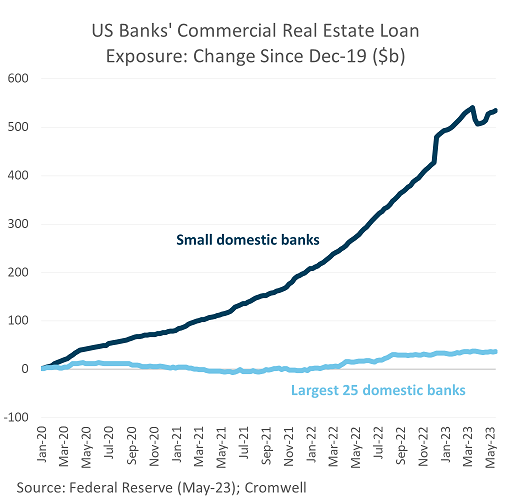
Additionally, Australian gearing is more conservative with typical loan-to-value (LTV) ratios pre-pandemic of 55%, compared to 72% for the US6. While lending conditions have tightened somewhat over the last six months (LTVs now 50%), the US has seen significant tightening (to 57%), contributing to a significant funding gap which will need to be plugged with discount-seeking capital.
The final word
Office is going through a period of change, and assets need to evolve to meet the needs of post-pandemic workstyles. While there will be challenges – and opportunities – as a result, the current narrative erroneously extrapolates issues from offshore to the domestic market.
Australian office is well-placed to contend with increased rates of remote working and tighter capital markets given its resilient demand drivers, quality of stock, and sensible financing arrangements. Skilled managers with the expertise to identify underappreciated assets and adapt them to the future of work will continue to deliver strong investment returns.
1 The Future of the Central Business District, May 2023 (JLL)
2 The Global Live-Work-Shop Report, November 2022 (CBRE)
3 Benchmarking Cities and Real Estate, June 2021 (JLL)
4 A data-driven analysis of occupant workspace dissatisfaction, August 2021 (Kent, Parkinson & Kim)
5 Quarterly authorised deposit-taking institution property exposures, December 2022 (APRA)
6 Analysing the Funding Gap: Asia Pacific, May 2023 (JLL)
Colin Mackay is a Research and Investment Strategy Manager for Cromwell Property Group. Cromwell Funds Management is a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is not intended to provide investment or financial advice or to act as any sort of offer or disclosure document. It has been prepared without taking into account any investor’s objectives, financial situation or needs. Any potential investor should make their own independent enquiries, and talk to their professional advisers, before making investment decisions.
For more articles and papers from Cromwell, please click here.
From the team at Firstlinks: Congratulations to Cromwell on its Cromwell Phoenix Property Securities Fund being awarded ‘Australian Property Securities Fund of the Year ’ at the Money Management 35th Annual Fund Manager of the Year Awards 2023.