The last three years have been eventful for bank shareholders, with each year bringing a new set of worries predicted to bring the banks to their knees. 2020 saw capital raisings from NAB and Westpac missing its first dividend since the banking crisis of 1893, as experts forecasted 30% declines in house prices and 12% unemployment! Then 2021 saw the banks grappling with zero interest rates and APRA warning management teams about the systems issues they may face from zero or negative market interest rates expected to come in 2022. This year, the concerns have switched to the impact of sharply rising interest rates on loan growth and bad debts.
In this piece, we will look at the themes in the approximately 900 pages of financial results released over the past two weeks, including Commonwealth Banks 2022 results, awarding gold stars based on performance over the past six months.
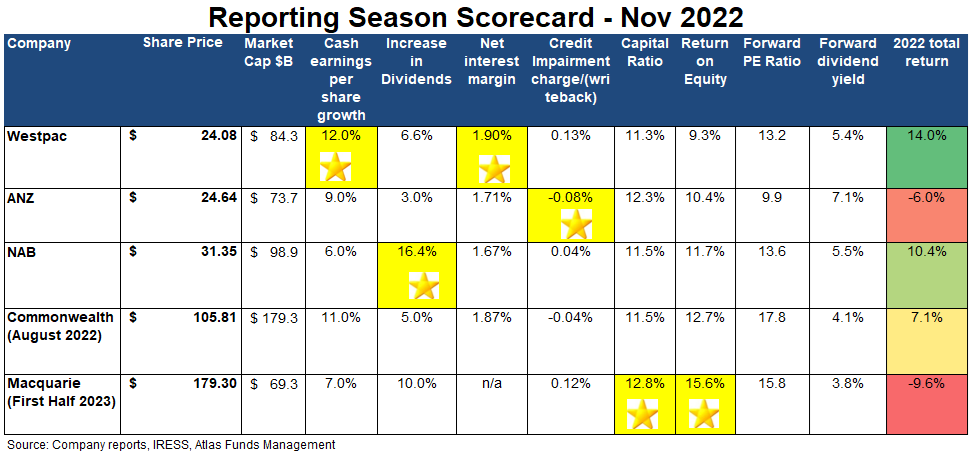
Rising net interest margins
Net interest margins were a major topic during the November banks reporting season, with most investors going straight to the slide on margins in the voluminous Investor Discussion Pack (in the case of Westpac, it was page 22 of the 139 pack). Banks earn a net interest margin [(Interest Received - Interest Paid) divided by Average Invested Assets] by lending out funds at a higher rate than by borrowing these funds from depositors or wholesale money markets.
When the prevailing cash rate is 3%, it is much easier for a bank to maintain a profit margin of 2% than when the cash rate is 0.1%. Rising interest rates increase the benefits banks get from the billions of dollars held in zero or near-zero-interest transaction accounts that can be lent profitably. Net interest margins can expand faster if the bank is quick to raise loan rates, slow to increase rates paid on term deposits and incurs minimal loan losses. In its result, Westpac revealed that as of September 2022, the bank held $252 billion in transaction accounts earning minimal to no interest.
The November 2022 reporting season saw net interest margins increase for all banks. The banks more heavily exposed to mortgages (CBA and Westpac) traditionally have higher margins than the business banks (NAB and ANZ) which face competition from international banks when lending to large corporates.
Westpac posted the highest net interest margin in November, with 1.90%. However, Commonwealth Bank may report a higher margin in February 2023 because their books closed on 30th June, and CBA's financial statements did not capture much of the rate increases seen in 2022. Over the last six months, Westpac increased its net interest margin by 0.05%; while this sounds like a minuscule amount, this small increase equated to $564 million in additional profit when multiplied across the bank's $740 billion loan book!

Bad debts
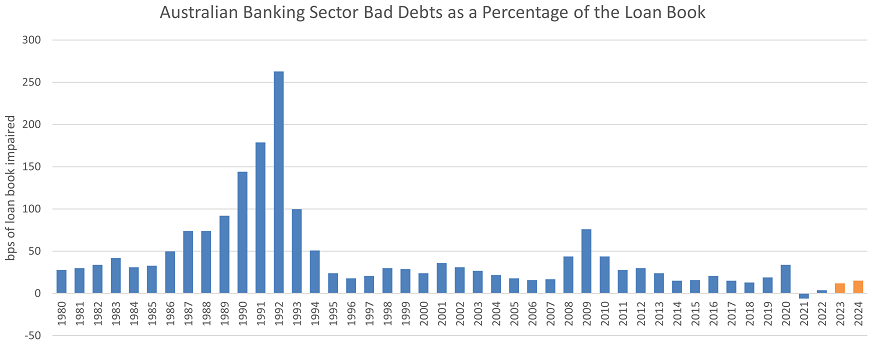
After net interest margins, the second most important number in every bank's financial reports in 2022 was bad debts, with investors looking to see if rising interest rates have caused losses on loans made. One of the biggest drivers of earnings growth over the last few years has been the ongoing decline in bad debts at a time when they were expected to spike sharply on rising unemployment and crashing house prices. Low bad debts boost bank profitability, as loans are priced assuming that a certain percentage of borrowers will be unable to repay and that the bank will incur a loss on the loan. From the below chart, since the 1991 recession, the normalised long-term level of bad debts has been around 0.3% of total loans for Australia's banks.
Bad debts remained low in 2022, with all banks reporting negligible loan losses; ANZ reported the lowest level with a positive 0.08%. This positive number occurred as new loan losses were offset by write-backs and recoveries from previously taken provisions.

Dividends
As can be seen in the first table, all banks increased their dividends in the most recently completed reporting season. However, for all banks, there was an element of catching up for reduced payments to shareholders in 2020 after APRA placed a cap limiting dividends to 50% of earnings and the ongoing uncertainty in 2021 from Covid-19 and associated lockdowns. NAB won the gold star by increasing their dividend by 16% to 78 cents per share in November, though this remains below the 83 cents paid pre-pandemic. Macquarie Bank increased its dividend by 10% to be the only bank paying a higher dividend in 2022 than in 2019. As a global investment bank, Macquarie Bank has enjoyed a good pandemic, growing earnings over the past three years and profiting from market volatility.

Expenses
Australia's banks operate in a competitive oligopoly, largely selling an undifferentiated product (loans) where their competitors have a similar cost of production (capital from depositors and wholesale capital markets). Consequently, moves to gain a higher market share and increase profits by discounting loans are swiftly matched by the other banks. However, banks can grow profits by reducing their expense base, which seemingly expands each year.
Containing growth in expenses has proved challenging for the banks, with low unemployment contributing to wage growth and the need to hire more compliance staff after the 2018 Banking Royal Commission. Additionally, compliance teams have grown in response to the Commonwealth Bank and Westpac getting hit with hefty penalties from AUSTRAC for not complying with Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing Act 2006.
While there was minimal discussion around cutting expenses by closing branches, Atlas sees that rationalising the branch network will be the easiest way for banks to grow earnings. On average, the significant banks have around 800 branches across Australia. Over the past decade, there has been a big decline in customer visits to these branches, as most bank transactions are now conducted online or via smartphones. Indeed, last week Westpac announced that over the past 12 months, the bank had processed 22 million physical transactions in a branch but 690 million digital transactions. Westpac wins the gold star for expense control, cutting their cost base by $766 million as a result of reducing headcount by close to 5,000 employees and closing 119 branches and 200 ATMs.

Our take
Investing in Australian banks is one of the major questions facing institutional and retail investors alike, with the banks comprising 25% of the ASX 200. We expect the banks to deliver over 10% earnings growth over the coming year benefitting from higher net interest margins and low bad debts from historically low unemployment levels. Though earnings do face headwinds from lower credit growth, normalising bad debts and reduced earnings support from provision write-backs. However, if investors examine the broader Australian market, the banks look relatively cheap and are well-capitalised.
The banks are in a much stronger position in 2022 than they were in 2008, going into the last rate tightening cycle. In 2008, the major banks held very skinny Tier 1 Capital Ratios of around 5% of risk weights assets (~11.5% in 2022), and the unemployment rate was over 5%, much higher than today. As ANZ's CEO said in his presentation, it is not falling house prices that cause loan losses but falling house prices combined with job losses.
Additionally, the banks' loan books are cleaner in 2022 than they were 14 years ago, with a greater focus on domestic lending to housing and small enterprises. In 2022 there have been no major corporate collapses and no large companies with obvious issues, such as ABC Learning, Allco, Babcock and Brown or Centro.
Furthermore, the foreign adventures in the UK and Asia that caused problems in 2008 have mostly been either sold or demerged. Over the past decade, Australia's banks have retreated to their home market and are now less impacted by a recession in Europe or the USA. All of this augurs for a more benign loan loss cycle in the coming years, and in this situation, bank share prices will be re-rated higher.
Hugh Dive is Chief Investment Officer of Atlas Funds Management. This article is for general information only and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.