Investors are faced with a significant and growing challenge. Stretched government balance sheets and an ageing population will likely place greater emphasis on retirees to ‘self-fund’ their retirement. At the same time, the expectations for market returns have fallen in line with record low interest rates in Australia and elsewhere.
The traditional safe haven of term deposits is now offering on average just 1.5%, which may not even keep pace with inflation.
So for most of us, the requirement to take some investment risk will be essential to achieve our long-term savings goals. This is where the options can get a little complicated, so let’s break it down.
There are many ways to take more risk, but let’s focus on the two key actions that can easily be implemented within your portfolio: changes to asset allocation and investment strategy selection.
Changes to asset allocation
In its simplest form, varying your equity versus bond mix can be an effective way to match your required return to your investment goals, but the potential for extra return does not come without taking on added risk.
Too much risk and you may not be able to stay the course through the inevitable market downturns on the journey to achieving your goal. Behavioural mistakes made along the way can cost years of investment returns, so best to match the risk of the strategy to your own tolerance.
Strategy selection
Within each asset class, another way to seek a higher return is through the strategies that you select for your investment portfolio.
An active investment strategy generally seeks to take positions that differ from broad cap-weighted market indices, to deliver a higher return. Unlike changes to your equity/bond mix, which can increase the total risk of your portfolio, selecting an active strategy introduces what is referred to as ‘active risk’.
To borrow a driving analogy, if the most direct route to your destination, which may be a main arterial road or freeway, is akin to a cap-weighted index, then using your local knowledge of back roads and traffic conditions to arrive at your destination ahead of time, could be considered the active strategy equivalent.
Traditional active managers employing skill and experience to outperform is not the only way however.
Over the last few decades, other strategies have emerged which can be used to pursue outperformance. These strategies - commonly either quantitative strategies employing sophisticated modelling techniques, or factor-based strategies seeking to harvest identified risk premia - endeavour to deliver a positive ‘active return’ against a benchmark.
To extend the driving analogy, systematic strategies could be likened to the rise of driving algorithms, such as Google Maps, which help to get us to our destinations faster by analysing data sets of past and present driving conditions.
Whether you prefer to test your own driving skill, utilise Google Maps or simply take the direct route, understanding the likelihood for success, and the risk you are taking if your choice doesn’t work out, is critical to making an informed decision.
Active risk
Active risk is typically measured in terms of the expected difference between the returns of the strategy and the returns of the underlying benchmark, which more often than not will refer to a comparable cap-weighted market index. You can look for active risk indicators from the fund manager which may be disclosed as ‘tracking error’ or ‘active share’.
Other indicators of active risk include the number of securities held by the portfolio, the maximum position size in any one security, the rules listed for deviations of sector or country weights in the case of a global strategy, and past results.
The spectrum of risk
At the lower end of the spectrum, market cap index funds can be characterised by low cost, low-to-no active risk, and high transparency owing to the rules-based nature of market cap indices.
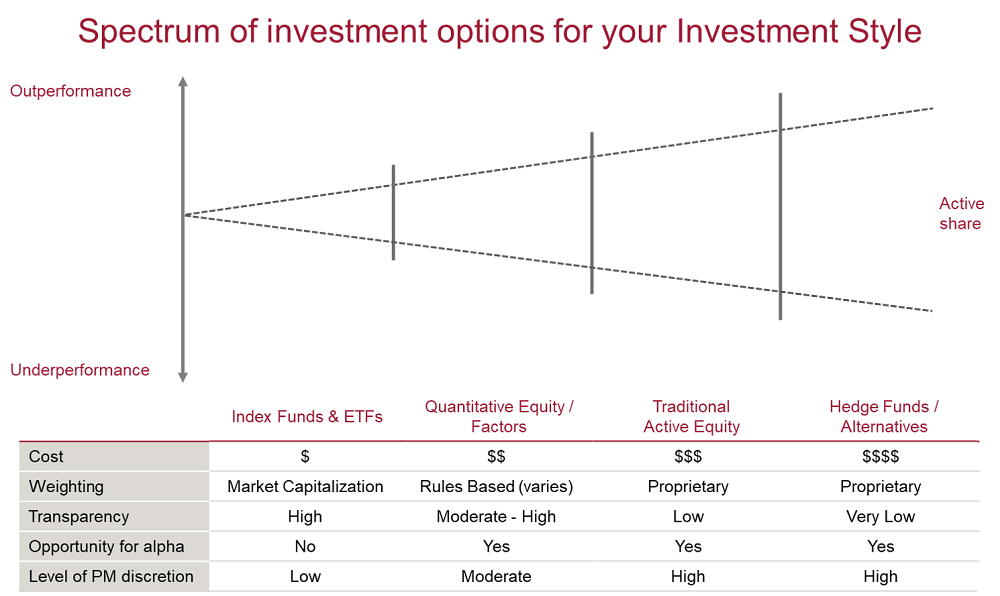
Systematic strategies such as factor funds can span a broad spectrum when it comes to active risk, however, most follow a set of rules which drive the weighting of securities in the portfolio, providing transparency of approach, assuming the rules are disclosed, and are typically lower cost than more traditional active strategies.
Traditional active strategies come in many forms, from highly-diversified, low active risk approaches, to very concentrated, high active risk strategies. The cost you are willing to pay should be scaled according to the level of outperformance you expect and the perceived skill of the manager.
Your unique circumstances
Where you end up with your choice is highly personal, as a successful strategy is one that is structured to deliver on your investment goals. Recognise that your asset allocation choice and where you land on the growth / defensive spectrum will be the main driver of your overall return.
Patience is critical to success and remains an accessible edge for those who possess it, whether you are a professional investor responsible for the goals of others, or an individual investor saving for your personal goals.
Aidan Geysen is Head of Investment Strategy at Vanguard Australia, a sponsor of Cuffelinks. This article is for general information purposes only and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.
For more articles and papers from Vanguard Investments Australia, please click here.