The superannuation changes that started on 1 July last year were not just about capping the amount of capital that can be transferred to the retirement pension phase. They also included big changes to tax deductible and non-deductible contributions.
Given that we are in the last quarter of the financial year 2017/18 (FY18), let’s have a look at those changes that apply now and others that will start from next financial year. With only a couple of months until 30 June, it’s time to review the basic rules in case these opportunities apply to you.
Concessional contributions
For FY18, the concessional contribution cap is $25,000 for everyone who is eligible to make these contributions. There is no longer a higher cap for anyone 50 or over. Anyone who has a salary sacrifice arrangement in place and has previously contributed more than $25,000 of concessional contributions in an income year should now make adjustments to these arrangements to ensure they don’t exceed the lower $25,000 concessional contribution cap.
Tax deduction for personal contributions
The change allows a tax deduction claim for personal contributions, but there is a bit of a catch as personal super contributions claimed as an income tax deduction count towards the concessional contribution cap of $25,000 for FY18. The cap also includes contributions made by your employer such as employer contributions for super guarantee purposes or under salary sacrifice agreements.
Don’t forget to tell the fund if you are claiming a deduction for super contributions by completing a notice and keeping it with the fund records. If you do make deductible contributions, the amount you claim cannot create or add to a loss that you may have made in your personal tax return. Any personal contributions which are not claimed as a tax deduction (or the deduction is disallowed) count towards your non-concessional contribution cap.
Remember what it was like before 1 July 2017. If you were an employee you could only claim a personal tax deduction for superannuation contributions if you qualified under the ‘10% test’. This meant that nearly all employees missed out on claiming a tax deduction for personal super contributions, but things have changed since 1 July last year.
Non-concessional contribution cap linked to total super balance
The annual non-concessional contribution (NCC) cap for FY18 is $100,000 (reduced from $180,000 in FY 2016/17). However, if the total amount you have in super on 30 June in the previous financial year is not less than $1.6 million, you won’t be able to make a NCC for that financial year.
For example, if we look at FY18 and the balances of the following two individuals, we can see what a difference a small amount either side of each person’s total superannuation balance (TSB) can have on their respective NCC cap.
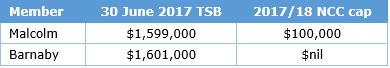
A person’s TSB also determines how many years of the standard NCC cap a person can ‘bring forward’ where they qualify under the bring forward rule. This means that there are now ‘trigger points’ for the NCC cap, as follows:
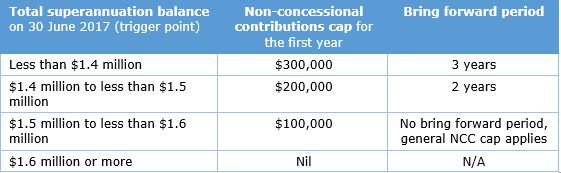
The TSB test for NCCs is also important where a person qualifies for the bring forward rule but does not fully use the maximum bring forward amount in the first year.
For example, Cynthia, aged 60, at 30 June 2017 has $1.48 million TSB and has not previously triggered the bring forward rule. Consequently, for FY18, her NCC cap is $200,000 (refer to the table above). If Cynthia makes the maximum NCC of $200,000 in FY18, her NCC cap in FY 2018/19 is zero. Further, her TSB is likely to exceed $1.6 million after the NCC and fund earnings are allocated. However, the test is based on her TSB on the previous 30 June, not what her TSB is after the contribution is made.
Let’s say, however, that Cynthia does not make her maximum allowable NCC in FY18 but makes an NCC of $160,000. Based on the above table, Cynthia may think that she can make a further NCC of $40,000 in FY 2018/19, being year two of the two-year bring forward period.
This is only true if Cynthia’s TSB at 30 June 2018 is less than $1.6 million. If, however, her TSB at 30 June 2018 is more than $1.6 million, which it could be once you allocate fund earnings, then even though she has not fully utilised her bring forward amount, her NCC cap is zero for FY 2018/19, and she is unable to make a NCC without it being treated as excessive.
The ‘work test’ lives
The work test still applies for those 65 and above when they make a contribution to super (no personal contributions after age 75). This requires a person to be ‘gainfully employed’ for at least 40 hours in 30 consecutive days in the financial year the personal contribution is made. This test should be satisfied before the contribution is made.
Downsizer contributions
For those aged at least 65 (no age 75 cut off for this one), from 1 July 2018, there is a new type of personal contribution which allows those who qualify to contribute up to $300,000 to superannuation from the sale of their family home that has been owned for at least 10 years on a once-only basis. This only applies where a contract for the sale of a qualifying home has been made on or after 1 July 2018.
The eligibility criteria and more details are on the ATO’s website.
Changes were not all bad
So, if you think the super changes shut the door on concessional and non-concessional contributions you may need to think again. For some, it may have opened the door a little to claim personal tax deduction for super contributions and, if you sell your family home, it may let you to make non-deductible contributions to super after you have reached 65.
Mark Ellem is Executive Manager, SMSF Technical Services at SuperConcepts, a sponsor of Cuffelinks and a leading provider of innovative SMSF services, training, and administration. This article is general information only and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.