The recent inclusion in global bond indexes of China, the second largest bond market in the world, will be a tectonic shift for fixed income markets. It follows similar changes in equity markets. Global investors ranging from sovereign wealth funds, central banks, pension funds and even retail investors will dramatically increase their exposure to renminbi assets in coming years.
Key parts of China's onshore bond market – government and policy bank bonds – have been incrementally added to the Bloomberg Barclays Global Aggregate Bond Index and are expected to account for approximately 6% of the total index, forcing investors to revise their allocations. It will be a major adjustment in the construction of portfolios.
There has never been a change of this size for global indexes, coinciding with the growing importance of China as a major economic power. Demand for Chinese onshore bonds will come not only from index changes but also the wider desire for Chinese assets, with some central banks allocating as much as 25% of their fixed income assets to China.
In a world of low and negative interest rates, investors chasing yield will see China's current 10-year government bond yield of around 3.1% as attractive compared with 1.6% for US Treasuries and around 1% in Australia.
Five reasons Chinese bonds are worth considering
China offers a compelling opportunity to complement returns from traditional bond markets and help diversify investors' fixed income exposure. Here are some important reasons investors should take notice:
1. Yield. China government bonds offer positive nominal and real yields compared with developed markets. That's been a standout feature for the past three-to-four years, as shown below.
Real yields by country (%), August 2009 to August 2019
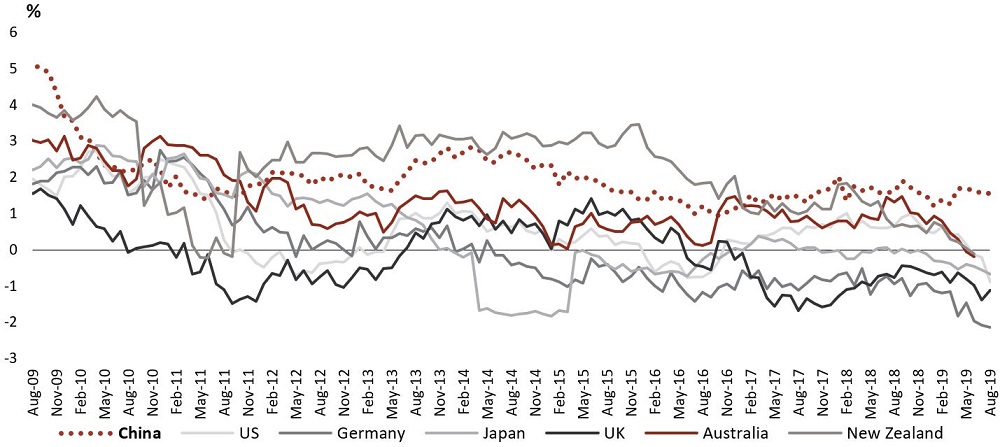
Source: Bloomberg. Real yields based on Core CPI. New Zealand based on Headline CPI, August 2019. Australia and NZ June 2019.
2. Liquidity. China's bond markets overtook Japan as the world's second largest in late 2018. As China reforms its financial sector and continues to develop bond financing channels, the market is expected to continue growing in the coming years.
3. Correlation. China bonds have a low correlation to global bond markets, giving a strong diversification benefit. Historically, China has had a 0.05 correlation to European bond markets, which has a 0.6 correlation with the US and 0.55 correlation with Japan (as at 27 September 2019, based on fortnightly returns of government bond markets since 3 October 2014, calculated by JPMorgan).
4. Downside protection. Given the higher relative yields and shorter duration profile of the China government bond universe, investors can expect smaller drawdowns (losses) during periods of rising bond yields compared with other developed markets.
5. Safe haven. Chinese government bonds show the traits of safe haven assets, with falls in yields during recent bouts of broader market volatility. China remains a net creditor nation and has the world's largest FX reserves, so no one will be calling China on its debt.
But despite all these points, investing in China can be a leap for more traditional investors. In part, that's because China is always in the news cycle and much of the coverage is sensationalist.
Four common concerns (or myths) around investing in China
#1 – China's economy is slowing. Yes, it is slowing – and that's a good thing. China's rapid growth of the past was fueled by unsustainable growth in debt and fixed asset investment. Now, China is committed to deleveraging and has shifted the economy toward the more sustainable growth drivers of consumer demand and services-led growth. This means slower but more sustainable growth for the long-term.
#2 – China has a debt problem. Debt is certainly high, but we don't see it as a source of an impending crisis, for three main reasons. Firstly, China's debt is drawn from one of the world's largest savings pools, so it is domestically financed rather than externally, giving little risk of a balance-of-payments crisis. Secondly, more than half of China's debt is concentrated within state-owned enterprises (SOEs), i.e. within the government and not the private sector. Finally, China still has a lot of growth potential. Unlike the Japan situation in the 1990s, China has many productivity gains ahead of it, so it has the room to grow its way out of the debt to some extent.
#3 – Investors can't get in or out of China's markets. Not true. Recent index inclusion and the opening of the China Interbank Bond Market Direct and Bond Connect channels means full access to onshore China bond markets, with ready access to investment capital via these channels. We see it as unlikely that China will implement capital controls for foreign investors given its commitment to becoming one of the world's major developed bond markets and in integrating with the global financial system.
#4 – International investors aren't convinced by China. Also not true. Official data shows sustained growth in international investors' holdings of onshore China fixed income. In fact, total holdings have tripled since January 2016, and recent trends have seen acceleration, as shown below.
Overseas investors' holding of onshore fixed income in China (RMB trillions), Jan 2016-Jun 2019
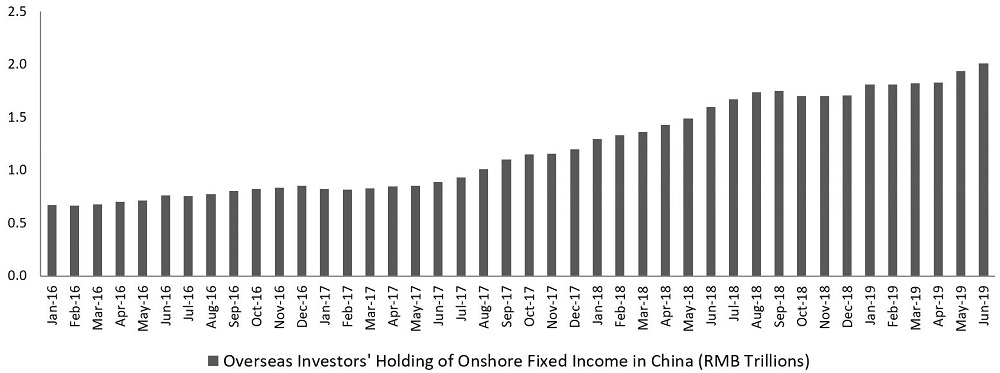
Source: People's Bank of China, August 2019
The most fundamental shift
The inclusion of China's onshore bond market into major global bond indices started with Bloomberg in April 2019, and this has now broadened with JP Morgan recently announcing index inclusion plans. This impacts a wide range of global bond investors as passive (i.e. index) funds that follow these major indices must now invest in China bonds, and active managers must take a view given the major benchmarks will include parts of the China onshore bond market.
This shift is expected to lead to as much US$500 billion of inflows into China's markets from Bloomberg bond index inclusion alone, and this has three important implications.
- It is happening because the world's biggest index providers have seen China's recent reform efforts and now deem China as 'safe-to-swim'.
- Allocation to China will become a mandatory, not optional, allocation for millions of investors worldwide.
- The massive influx of global investor capital will put downward pressure on yields, and that means it is time for investors to take the opportunity now.
This phenomenon is occurring across more asset classes than fixed income. MSCI included China equities in its emerging markets index in 2018. FTSE Russell and S&P Dow Jones have since followed, a reflection of China's increased efforts to integrate its capital markets into the global financial system.
The compelling case for China fixed income is one of many opportunities uncovered by actively exploring the global fixed income opportunity set and why it pays to employ a truly global and diversified approach to investing, particularly in a world of lower – and increasingly more negative – bond yields.
Hayden Briscoe is Head of Asia-Pacific Fixed Income, UBS Asset Management, a sponsor of Firstlinks. Learn more about UBS Diversified Fixed Income (DFI) here. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.
More articles and papers from UBS can be found here.