[Editor’s note: The author is not a licensed financial advisor, and opinions are given as a personal conviction and as a futurist, not advice to investors.]
It is getting very tricky for Australian investors with over $3.7 trillion in super and other financial assets to know which asset classes are the best in terms of short or long term yield and capital appreciation. Or safest, regardless of yield.
The choices at the asset class level are:
- liquids (cash, short term, long bonds)
- shares (local or foreign).
- property (owner-occupied and investment dwellings, commercial)
- commodities and collectables (gold, other metals, collectables)
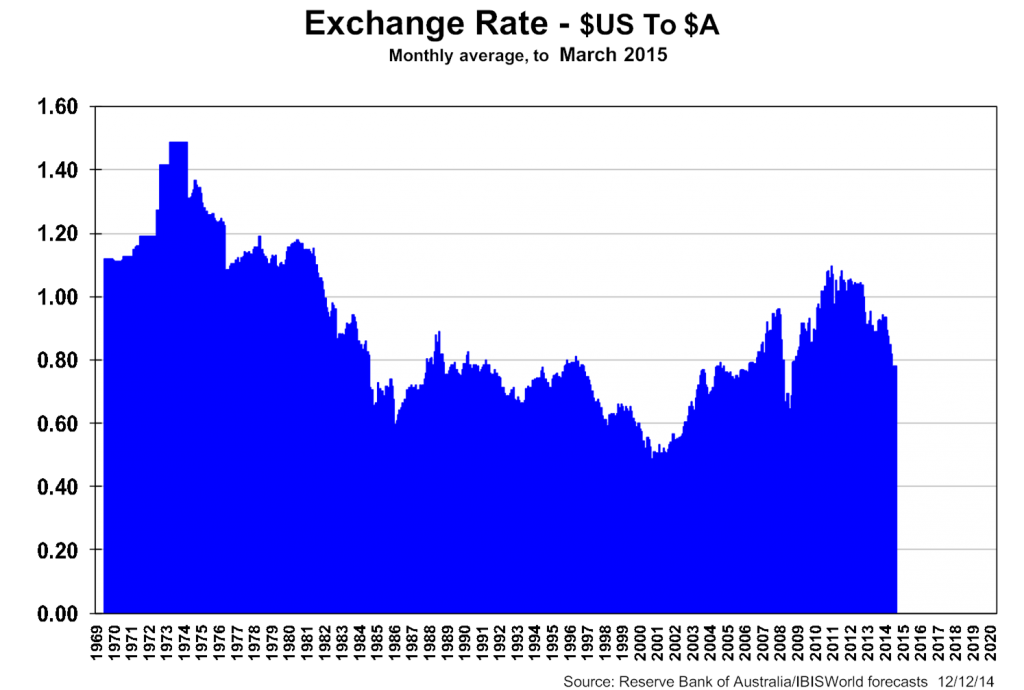
The offshore options on any of the above classes of investment introduce the exchange rate variable, further clouding the choices. As the chart below reminds us, the exchange rate is a very difficult variable to predict with any accuracy. And buying offshore assets is not as easy with a US76¢ exchange rate versus the US$1.10 of mid-2011.
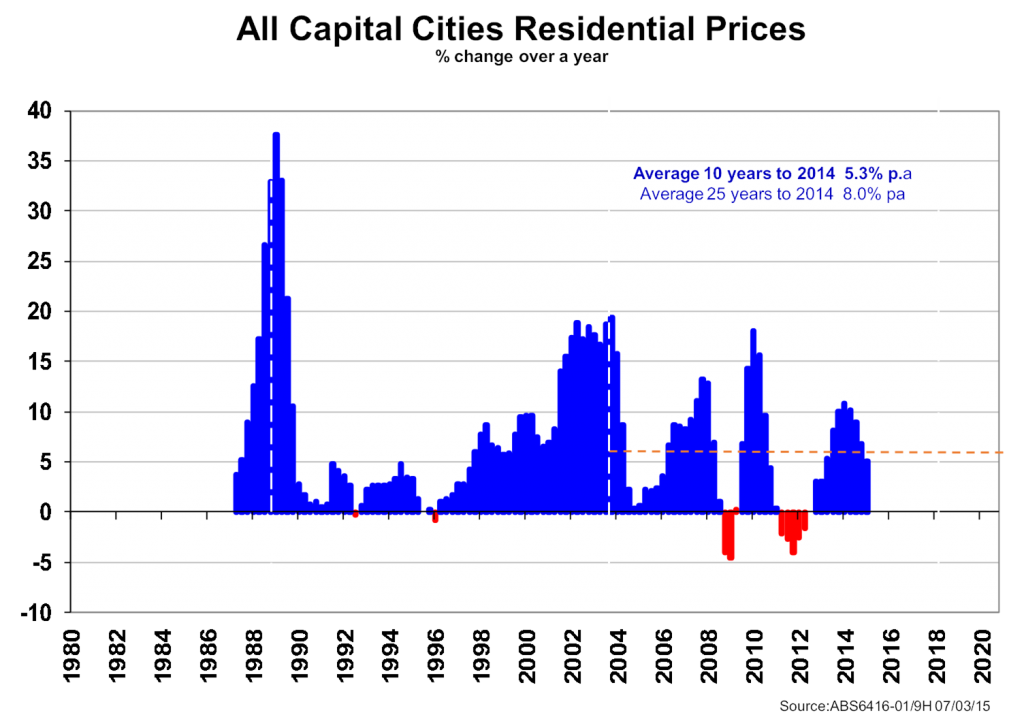
Residential property values also move around, but over the medium to longer term provided capital growth of a fairly safe 5¼% pa. However prices can go negative, as seen in the second exhibit. Australia already has some of the world’s most over-valued residential prices (over 3½ times average household income), kept high by record low mortgage rates at under 5% compared with the very long term average of nearer 7½%. So considerable care is needed as we head into the third decade of this 21st Century when it comes to looking for a lot of capital gain as distinct from low net rental returns in investment residential property.
Is gold ready for another of its spectacular leaps? As we know, gold is no longer used for currency backing, the gold standard having gone almost half a century ago when President Nixon abandoned it. These days it serves two purposes: use in jewellery and industry; and as a panic metal during financial crises.
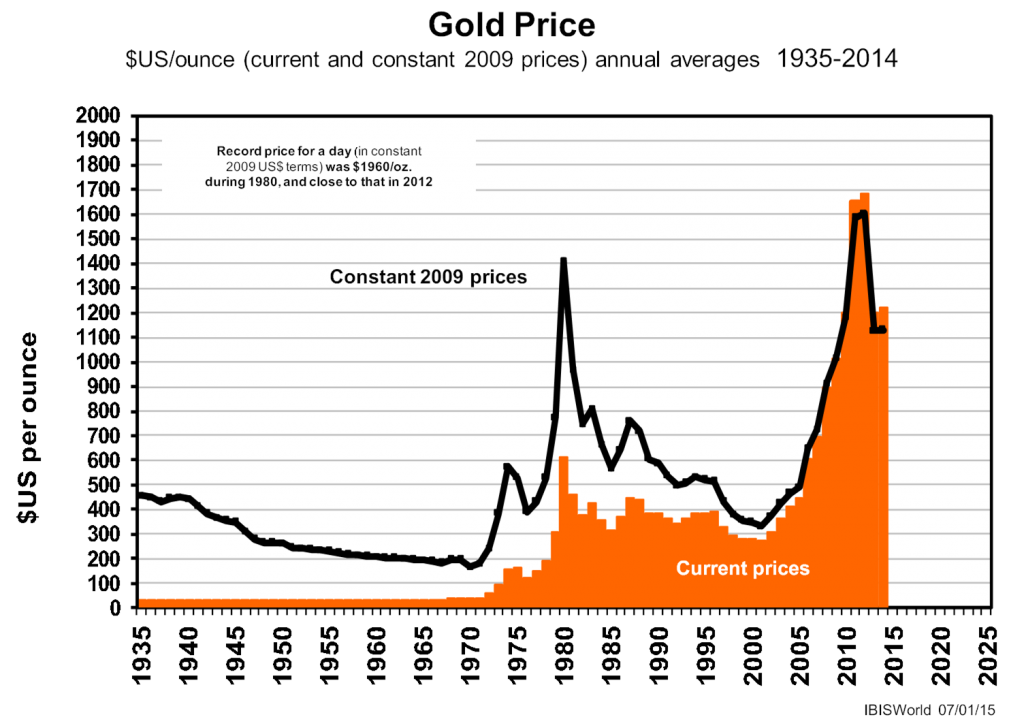
It doesn’t look like the price is going to spike again in the short term, but maybe in the much longer term.
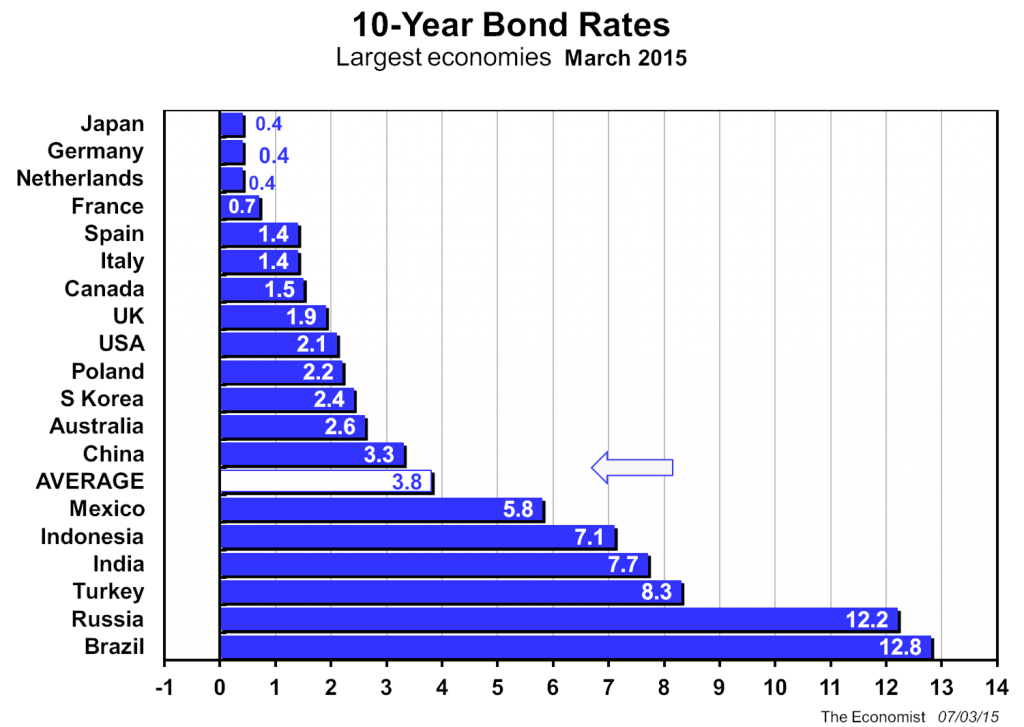
Are government bonds better? Hardly, when one looks at the fourth exhibit and its record low yield in March 2015 of 2.6%.
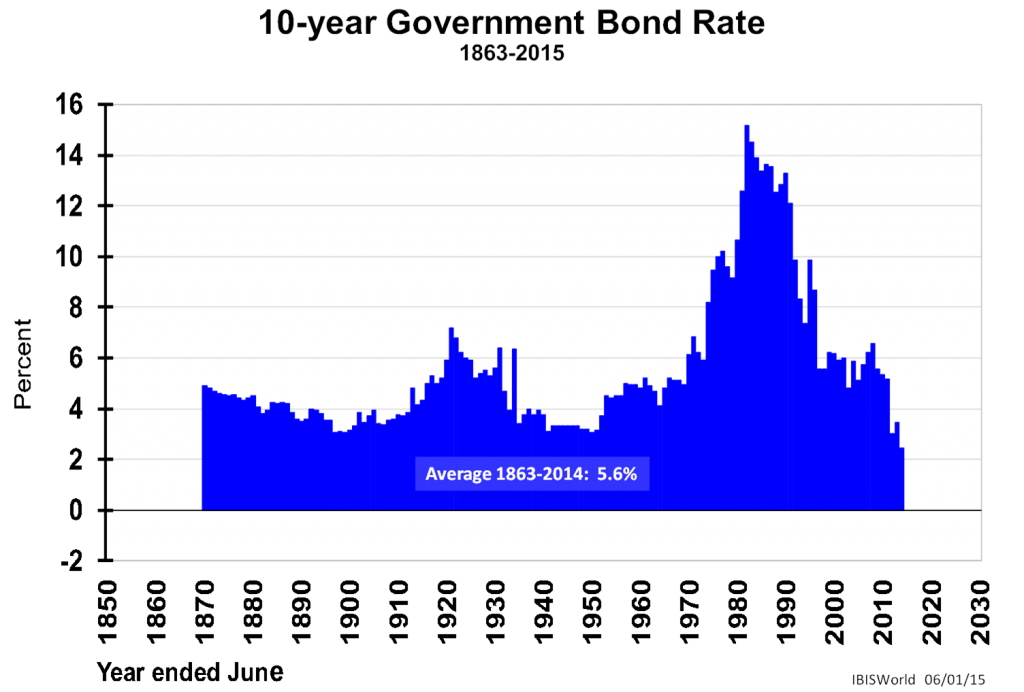
If we think that level of yield is unacceptably low to an investor, we could spare some compassion for investors in other large economies as seen in the fifth exhibit below.
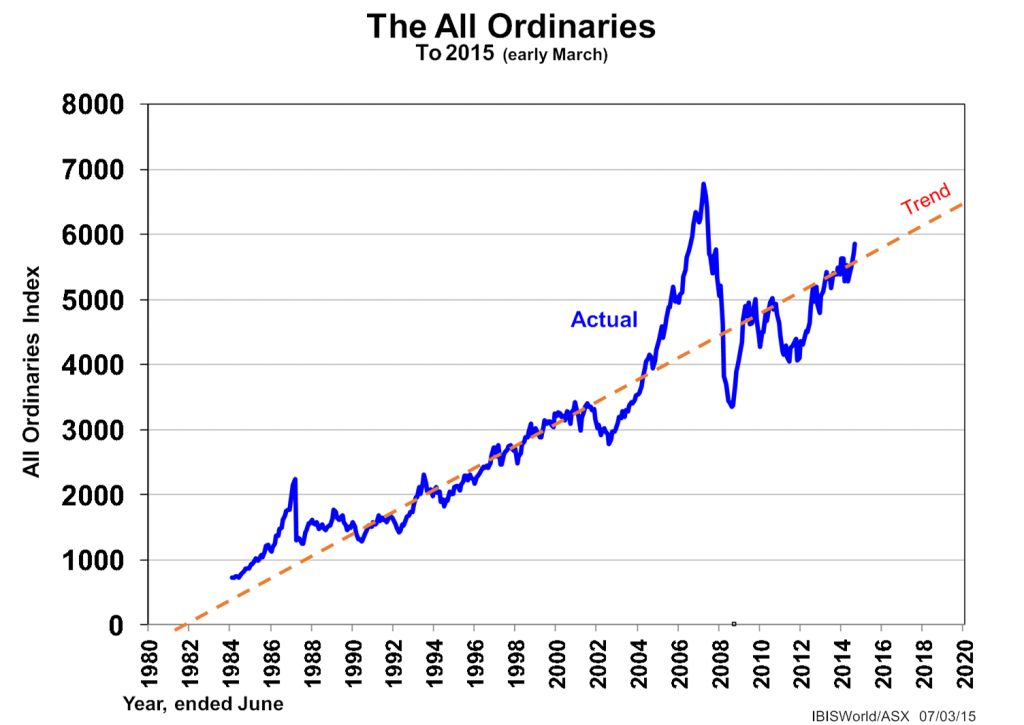
Which leads to shares. They are rising lately as much by default (unattractive yields in other classes of investment) as due to other fundamentals (rising profitability and dividends) as we see below in the sixth exhibit. So far into 2015, the All Ordinaries Index does not appear to be wildly over-trend.
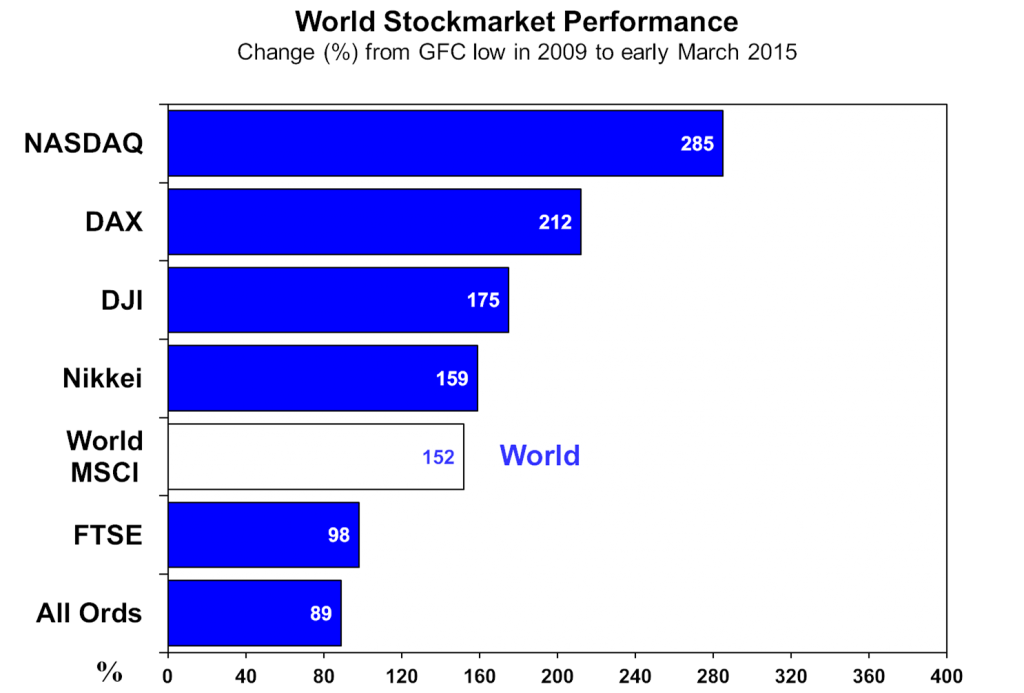
The final exhibit suggests that we can over-react to steep falls such as occasioned by the GFC. The recovery across the world’s major indices ranges from the mind-boggling (NASDAQ and DAX) to sort of reasonable (All Ordinaries).
So what does all this mean going forward from 2015?
Basically, that returns are not as good as they have been over recent decades, whether they be liquids, property, commodities or shares, where rising P/E ratios are lowering yields in response to record low interest rates. Then again we aren’t experiencing another GFC either which would be a much greater worry. Inflation is very low in most developed economies, and some are experiencing deflation, not seen since the Great Depression. This points to slightly better real returns than the nominal rates might suggest.
It is also very encouraging to see the USA and UK climbing out of their six-year long GFC, although we could be less sanguine by the almost motionless Japanese economy and the slowing Chinese economy – both big export destinations for Australia, accounting for well over half our trade.
Some forecasters are predicting apocalyptic troubles arising from world debt levels, but not this author, as yet. Government indebtedness is not yet back to the immediate post WWII levels (with some exceptions such as Greece and Japan). Yes, household debt is huge in many countries, especially Australia, but still manageable in terms of debt servicing costs as our RBA reminds us from time to time, while warning us of stupid dwelling prices and the long term dangers involved.
And business debt in terms of debt/equity ratios are generally prudent.
If all this tells us anything, it is don’t retire too early! Supplement any low investment returns with working income, be it on a part-time or casual basis if you can. We will probably live longer anyway by doing that.
Phil Ruthven is Chairman, IBISWorld and Australia’s leading futurist. Repeating, he is not a licensed financial advisor, and opinions are given as personal conviction and as a futurist, not advice to investors. The article is written for general information and investors should seek their own professional advice.