In a quest to diversify portfolios from the concentration biases found in the large cap Australian equities market, investors often allocate a defined (and usually static) weight to Australian small cap investments. This intuitively makes sense, because we expect to achieve superior diversification by investing outside the large cap stocks, and because of the belief smaller companies will have stronger earnings growth opportunities.
But these views may be flawed.
The small cap index is a dud index
Over the long term, the small cap index has underperformed the large cap index by around 2.8% p.a. (since 1990) and has done so with 25% higher risk. That’s not to say there are not significant opportunities in small caps from time to time, with the performance differentials between small and large cap significant over the short term. Actively managing the rotation in and out of the small cap market should be a consideration, and timing is important.
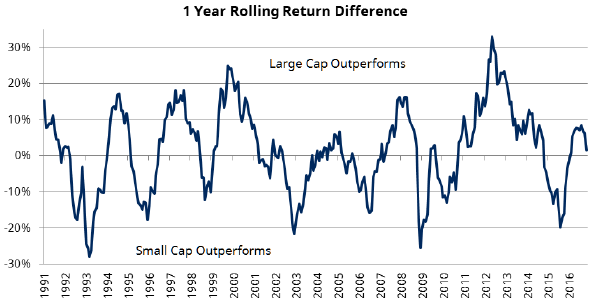
Source: Schroders, Global Financial Data. Returns from 1 Jan 1990 for S&P/ASX Small Ords and S&P/ASX 200 (All Ords before 1/4/2000).
The index construction that provides risks and opportunities
In Australia, the lack of a mature venture capital industry results in listing rules that do not consider a business’s profitability or financial viability, unlike in other global markets. There are times where our market is built around a large number of no-revenue or no-profit generating mining companies. For small cap equity managers, when one of the most effective portfolio construction methods is to avoid the losers, is it reasonable to pay an active or performance fee based on this market anomaly?
Our belief is that while the average active manager in Australian small caps has been able to outperform the index, this is due in a large part to the inefficiencies in the index construction. On average, small cap managers earn a fee 60% higher than that for large cap portfolios. While at a base fee level there is some justification for this given the relative size of assets that can be managed in each market cap segment, we would suggest investors should be wary of the potential for large performance fees to be accrued versus the poorly-constructed small cap index.
A broad-cap flexible approach should be adopted
Valuation is a strong indicator of future returns and this belief is supported by analysis of starting point Price to Earnings ratios (P/E) and the subsequent 3-year performance, as shown below.
There is a distinctive trend towards higher valuations in small caps leading to subsequent underperformance relative to large cap. Interestingly, higher valuations in large caps don’t necessarily lead to underperformance of small caps. At present, small cap P/Es are relatively high compared to history (at 18.7x) and higher than the large cap market.
It makes sense for investors to explicitly consider the valuation differences between small and large cap stocks in making their investment allocations. Not all investors have the skill and tools to either monitor the timing of asset allocations or the ability to change the investments. We believe the decision and implementation for actively managing Australian equities is best made by a broad-cap investment manager with skills to understand when the opportunity is right across the full market cap spectrum (large, mid, small and micro-cap sectors). This ensures stock specific ideas can be prioritised rather than esoteric ideas coming from a specific cut off point in a benchmark.
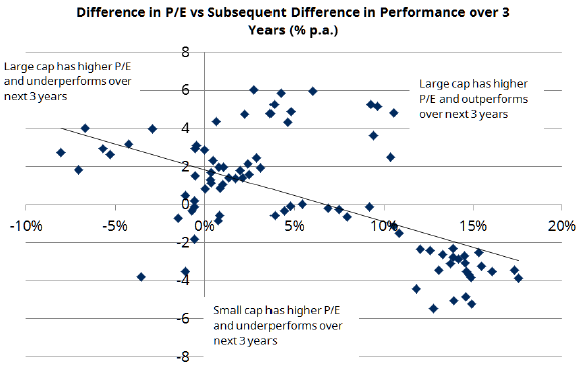
Source: Thomson Reuters Datastream, Global Financial Data, Schroders Analysis
Benchmarks and active management
An objective look at the opportunities presented across the small and large cap markets suggests that segmenting the allocation by market cap (as defined by some arbitrary stock number) isn’t necessarily the best way for investors to manage their portfolio. Investors may wish to consider a bias toward smaller caps to take account of the greater economic diversity from this part of the market. However, an alternative broad-cap exposure is a different way to structure a client’s aggregate equities exposure versus separate small and large cap portfolios.
We conclude that:
- The small cap index is poorly constructed and suffers from significant structurally lower long-term performance, higher risk, and poorer earnings growth characteristics.
- Active management of this part of any Australian equity exposure is both essential and rewarding.
- The appropriate benchmark against which performance should be measured and fees calculated is a broader market index or the large cap index, rather than a specifically small cap index as this is more representative of the opportunity set and removes the bias created by an arbitrary index cut-off.
- The performance differentials between small and large cap stocks, while biased in favour of large cap, have shown significant historical variability and this represents a greater opportunity for investors with broad-cap research capabilities to add value.
Greg Cooper is Chief Executive Officer at Schroders Australia. This article is in the nature of general information that does not consider the circumstances of any individual.