Simon Mawhinney has experienced a takeover or two in his time. Allan Gray, the investment firm he joined as an analyst in 2006 and now heads up, has built its track record on taking a contrarian stance and buying cheap equities. Because low valuations often attract buyers, takeouts are a common exit for Allan Gray investments whether they like it or not.
Unfortunately, Mawhinney often lacks confidence in those deciding whether a takeover should happen, and at what price. “I’m not saying this is the norm”, he starts, “but there are instances where boards have a completely distorted view as to what a company is worth”.
You might expect Mawhinney’s main gripe to be with directors letting buyers steal companies for too little. But he’s just as scathing about boards that expect too much from buyers. He sees Ramsay Healthcare (RHC) – which saw a deal with Kohlberg Kravis Roberts (KKR) collapse in September 2022 – as a prime example.
“You can't expect someone to take over a company without accounting for potential downside risks in the price somehow. Ramsay wanted to extract every single last dollar from the would-be buyer. By the time there was sort of some agreement, things had changed, and the deal fell over. Look at what's happened to the shares since.”
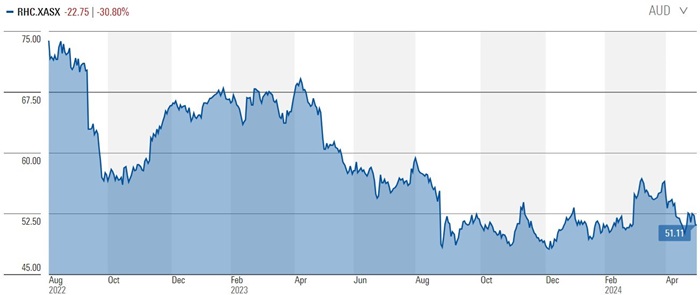
Source: Morningstar.com
Things can, of course, go the other way. A few years ago, Allan Gray were the biggest shareholder in construction group UGL. Mawhinney says the board’s expectations were “frighteningly low” here, no doubt influenced by a mining downturn and project write-offs that had battered the shares.
“CIMIC ended up buying that business for around four times earnings. At times like that, you would expect boards to take a long-term view of the world and not be preoccupied with short-termism.”
But Mawhinney thinks boards have strong incentives to do otherwise. Chief among these is the desire to avoid criticism – or a court case – from shareholders obsessed with getting a quick return. This can make lowball offers look more attractive than they really are, a situation Mawhinney sees written all over Nationwide Bank’s bid for Virgin Money in the UK.
“Nationwide’s offer valued Virgin Money at 0.65x net tangible assets. The cheapest major bank in Australia trades well above 1x, but the board probably felt they needed to recommend the offer because it was 40% above Virgin Money’s prevailing share price. But just because it's a 40% premium, does that make it cheap? We should be comparing the offer to the underlying value of the company, not to the share price”.
It's little wonder why Allan Gray don’t want boards to get carried away by pessimism or fall prey to short-term thinking. After all, they are the very same fallacies Allan Gray try to exploit by buying out of favour shares. If the company’s board fall prey to these biases, it can cap the pay-off from what Allan Gray see as a real behavioural edge.
When it comes to building better boards for shareholders, Mawhinney stresses the need for quality over quantity. “Boards have become a box ticking exercise more than anything else. We're getting to boards with ten, twelve people. I'd rather a board that's half the size, pay each member double and attract really good talent. People with fire in their belly and some energy.”
As well as boards, Mawhinney is cautious of another powerful group that usually fly much further under the radar – proxy advisors. These firms consult large passive shareholders like mutual and index funds on how to vote on matters like AGM resolutions and takeover proposals. This gives them a huge amount of power over corporate governance, even if they own zero shares.
“There are times when the proxy firms highlight things that other shareholders might miss, in which case there is definitely some good that comes from it. But recently, like is the case now with Woodside, I think the proxy firm’s influence is far in excess of what it should be.”
Mawhinney was referring here to Glass Lewis, which recently advised clients to reject Woodside Energy’s climate report and block the re-election of its chairman Rochard Goyder. Woodside was a major position for Allan Gray’s equity fund as of March 31st and they disagree with Glass Lewis’s recommendation.
Mawhinney’s caution on proxy advisors is partly down to the scale of Glass Lewis and its peer Institutional Shareholder Services, which hold an estimated 95%+ market share between them.
“They write these things on thousands of companies, thousands. There is no way that it can all be thoughtful and in-depth. A lot of it is quite superficial and I think the Glass Lewis report [on Woodside] was particularly poor.”
He also thinks their need to retain subscribers pushes proxy advisors to publish occasionally “off the wall” research to keep things interesting. It isn’t the first time Allan Gray have disagreed on the right direction for one of their portfolio companies, and it probably won’t be the last.
Joseph Taylor is an Associate Investment Specialist for Morningstar and Firstlinks.