'Fake news' has been dominating the media since the Trump Presidential win. Financial markets have a parallel concept we will call 'fake crises'.
A fake crisis is a major sell-off of one or more asset classes brought on by widely-held expectations of an impending disaster, but one that fails to eventuate or has been massively exaggerated.
Unnecessary losses from a fake crisis
A fake crisis can inflict heavy losses on an investor who dumps quality assets at depressed prices during the panic but provides the opportunity for an investor to acquire good assets cheaply.
An outstanding example of a fake crisis in investment markets – the cause célèbre – occurred in the early weeks of 2016. The dominant view then was China’s economy was 'contracting' and would soon cause a global recession. Commodity prices, share markets and the Australian dollar plunged.
As things turned out, retail sales continued at almost double-digit growth, industrial production expanded strongly, and China boosted demand on a scale the doomsayers had not allowed for. Shares, commodities, confidence and the Australian dollar all rebounded.
Other fake crises in investment markets during recent years
Many examples of fake crises have unnecessarily worried investors, including:
- The initial (but very brief) collapse in share prices following Donald Trump’s win in the US presidential election.
- The loss in market sentiment following the Brexit vote in June 2016.
- The 'taper tantrum' in 2013, when bond markets sold off aggressively on the expectation the Fed would mismanage the phasing out of its huge programme of bond purchases.
- The 'sovereign debt crises' in Europe in 2012 and 2013, which were exaggerated and were followed by record low bond yields.
- The widely held fears in the second half of 2011 that the US economy was sliding back into recession.
Fake crises generally follow the same pattern. Investors always have a lot of things to watch and to worry about. From time to time, concerns develop, sometimes without justification. A momentum builds up. Many investors come to uncritically accept data or comments that support the majority view while ignoring the countervailing facts. Maybe some hedge funds will 'short' assets or asset classes, expecting to buy them back during the crunch at lower prices. Research reports may be released full of gloom and doom to support the portfolio positions the hedge funds have taken up.
Managing reactions to a fake crisis
The best way I know of working out whether a crisis will create prolonged pain or be short-lived is for the investor (perhaps through his or her adviser) to create two lists on the outlook for the relevant market or markets. One list would show the worries. The other list would set out the positive or counter-balancing influences. The investor can then take an on-balance view appropriate to their risk tolerance.
This approach can be applied to any or all investment markets. Let us try it on the current outlook for the Chinese economy.
List of China negatives and positives
Negatives:
- The huge build-up in indebtedness by Chinese governments (at the national and regional levels) and by property developers.
- The potential for bad debts of banks to blow out.
- The excess capacity in heavy industry.
- The risk of a surge in capital outflow causing a run on the Renminbi.
- The slow pace of reform among state-owned enterprises.
Positives:
- China has a high level of saving.
- The increased debts are mostly owed domestically and not to lenders abroad.
- International reserves still stand at US$3 trillion.
- For many years there will be a high level of building construction for the urbanisation program.
- To date, the move to a more market-determined exchange rate mechanism is working well.
Buy, sell, do nothing?
A reasonable on-balance assessment is that the pace of expansion in the Chinese economy will slow a little, both cyclically and in trend terms, in the next couple of years. The risks of recession are low but there will be recurring big swings in investors’ confidence in China’s economic conditions and prospects.
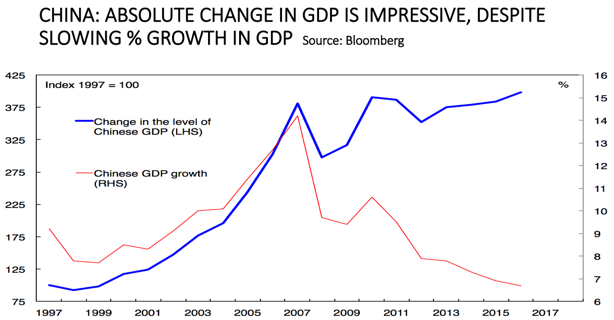
China’s growth has moderated from a rate of 14% in 2007 to 7% in 2016. But in absolute terms, the year-by-year expansion in the Chinese economy has remained impressively large, and that is what matters for both global growth and the Australian economy.
Fake crises can materially impact investor returns if it leads to panic selling, so a calmer and more systematic approach is called for to avoid overreacting to the noise.
Don Stammer has been investing for over 50 years, including long periods with Deutsche Bank and ING. He writes a fortnightly column on investments for The Australian and has advisory roles with Altius Asset Management and Stanford Brown Financial Advisers.