Ten years since the global financial crisis, the recent spike in market volatility after a long lull stirred uncomfortable feelings for many investors. This makes it a perfect time to put in place a financial fire drill.
Of course, no one can reliably predict when the next bear market will arrive. But as someone who worked through the 1974, 1987, 1999 and 2008 downturns, I can confidently say that while down markets are always tough, they are even more so for the unprepared.
Advisers and other fiduciaries should reflect on whether they have adequately prepared and educated their staff, clients, and centres of influence for the next downturn. And investors should check if their portfolios are positioned with the risks in mind.
Lessons from history
In the early 1970s bear market, broking staff were laid off as there was no brokerage commission being generated. This was long before the fee-for-service model. Clients were frightened to buy, and the flood of doomsday news did a good job in scaring many into selling what they had.
After much pain, investors resumed buying. But we have seen repeatedly that the net result from selling on fear and buying on greed is that investors end up with significantly less than the market rate of return.
The looming 10-year anniversary of the collapse of investment bank Lehman Brothers on 15 September 2008 and the unsettling events of October 2008 mean there inevitably will be a flood of stories in the media about the past financial crisis and the possibility of another.
However, there is unlikely to be much mention of how those investors who kept their nerve and stayed with their plan were rewarded for their discipline, as shown below. That reward is the payoff for having an investment philosophy and a plan to stick with through extreme volatility and uncertainty.
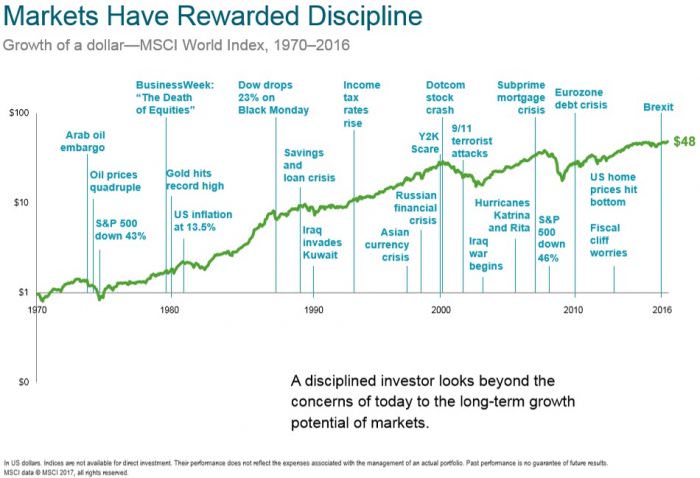
Do the drill before the fire
Messages about the possibility of further volatility and the need for discipline are more likely to be assimilated during the upswings, when emotions are settled and minds are clear, than during the unsettling mood generated by downswings.
Having been trained in firefighting at the age of 16, I learnt it is not the time to develop mastery when faced with an emergency. That’s why firemen regularly carry out drills in which they rehearse their responses to a major fire. Being operationally prepared with a concrete strategy makes everyone feel more confident.
It’s similar for advice firms. The time for preparing for a crisis is not during a crisis. Instead of trying to predict when a downturn will occur, the focus for advisers should be on preparing an agreed strategy for when it does.
In contrast, market timing is hazardous. The chart below shows that an investor who missed just the 25 best days on the Australian market from April 2000 to December 2016 would have been reduced to an annualised return of 1.7% against the market’s 8% return.
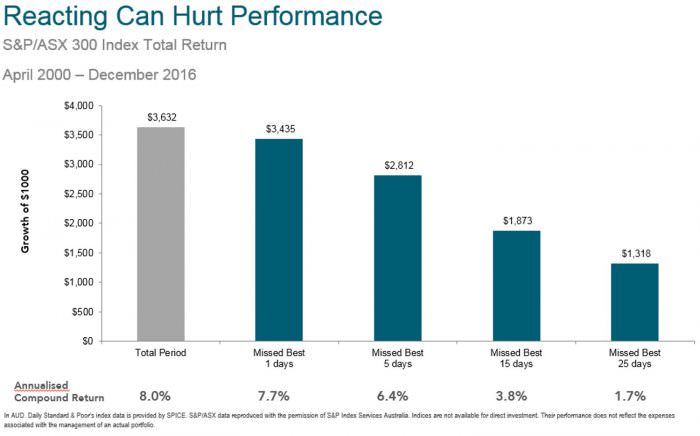
Fire drill checklist
Drawing on nearly four decades of experience in wealth management, here’s my financial fire drill checklist:
1. Cash flows
Ensure sufficient cash flow to see through a downturn, such as 2-3 years in accessible liquid assets to meet day-to-day expenses without the need to sell growth assets.
2. Different outcomes
Prepare for a range of possible outcomes and the manifestation of those outcomes. Consider what happened in past bear markets and stress-test asset allocations to demonstrate extreme scenarios. If you don’t think you can withstand the pain of a 30%-40% downturn, consider reducing exposure to growth assets.
3. Communication
The greater risk for advisers and fund managers is under-communicating to clients. In previous major down markets, the efforts of managers who kept advisers informed with timely bulletins were appreciated. These lessons were absorbed by many and used in the 2008 crash. The message to clients should be that markets are forward-looking and already reflect known information.
4. Diversification
Ensure portfolios are well diversified. If it makes sense for an investor’s age and circumstances, ensure portfolios include a risk-dampener, including cash and fixed interest. Focus communications and analysis on the total portfolio, including real estate. Otherwise, people can become preoccupied with individual securities or sectors in isolation, missing the forest for the trees. A balanced view is particularly important for those who have a Transfer Balance Cap (pension) which is mainly in growth securities.
Guidance for advisers
Advisers should be mindful of the tone of their communications. No one wants the fire fighter to panic. Be measured and reassuring, without seeking to downplay the natural anxiety brought about by difficult markets. It is easier for clients if the ground is prepared beforehand.
This means setting appropriate expectations and stress-testing asset allocations with each client, educating them about how markets work and reinforcing the benefits from your own experience of discipline, diversification and focusing on those elements within their control.
The payoff is that when the alarm does go off, you are calm and ready to offer reassurance and confidence to clients, so that they remain disciplined. If you succeed at this key task of stupidity prevention, your clients will be grateful and see your fee as a worthwhile investment.
Nigel Stewart is a 40-year veteran of the Australian financial markets, a professional financial adviser and an Executive Director of funds management firm, Dimensional Australia. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.