[Editor’s Note: For background, CEPAR is the ARC Centre of Excellence in Population and Ageing Research. ARC stands for Australian Research Council, an Australian Government entity whose mission is to deliver policy and programmes that advance Australian research and innovation globally and benefit the community].
Understanding the changes in our population and its demographics are vital inputs when planning our retirement systems. On 8 September 2016, ARC awarded CEPAR $27.25 million in funding to finance a second research term of seven years. This is a significant achievement and the many people involved, notably Professor John Piggott (Centre Director) and Marc de Cure (Chair of CEPAR’s Advisory Board), deserve congratulations.
To put this win into context, consider the other eight winners of ARC funding:
- ARC Centre of Excellence for All Sky Astrophysics in 3 Dimensions
- ARC Centre of Excellence of Australian Biodiversity and Heritage
- ARC Centre of Excellence for Climate Extremes
- ARC Centre of Excellence for Engineered Quantum Systems
- ARC Centre of Excellence for Gravitational Wave Discovery
- ARC Centre of Excellence in Exciton Science
- ARC Centre of Excellence in Future Low Energy Electronics Technologies
- ARC Centre of Excellence for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology
Reactions may include awe at the complexity of some of the topics and the breadth of research areas supported by government funding. A large number of top quality applications were unsuccessful, and I agree wholeheartedly with Piggott’s comment that “population ageing is an issue of paramount importance to all; this is truly the ageing century”.
CEPAR is a good example of collaboration:
- From a research perspective, while based at UNSW Australia, it applies a best practice model and has research members from the Australian National University, the University of Sydney, the University of Melbourne, the University of Western Australia, the University of Manchester, the University of Pennsylvania and the Wharton School.
- CEPAR has a collaborative funding model, receiving additional funding from industry and government partners including the major Commonwealth policy departments, large corporates, and the NSW Government. CEPAR also has strong support and engagement with the World Bank, OECD and COTA.
CEPAR’s multidisciplinary approach draws on expertise in actuarial studies, demography, economics, epidemiology, organisational behaviour, psychology and sociology. Piggott explains, “CEPAR’s research programmes are assembled into four interconnected streams, that cover demographic modelling; decision making, expectations and cognitive ageing; work design and successful ageing in the workforce; and sustainable wellbeing in later life. The latter including not only physical but financial wellbeing as well.”
Sometimes it may be difficult to identify the output of a research body. Some of CEPAR’s statistics shed light on the breadth and quantity of output (for the period 2011 to 2015):
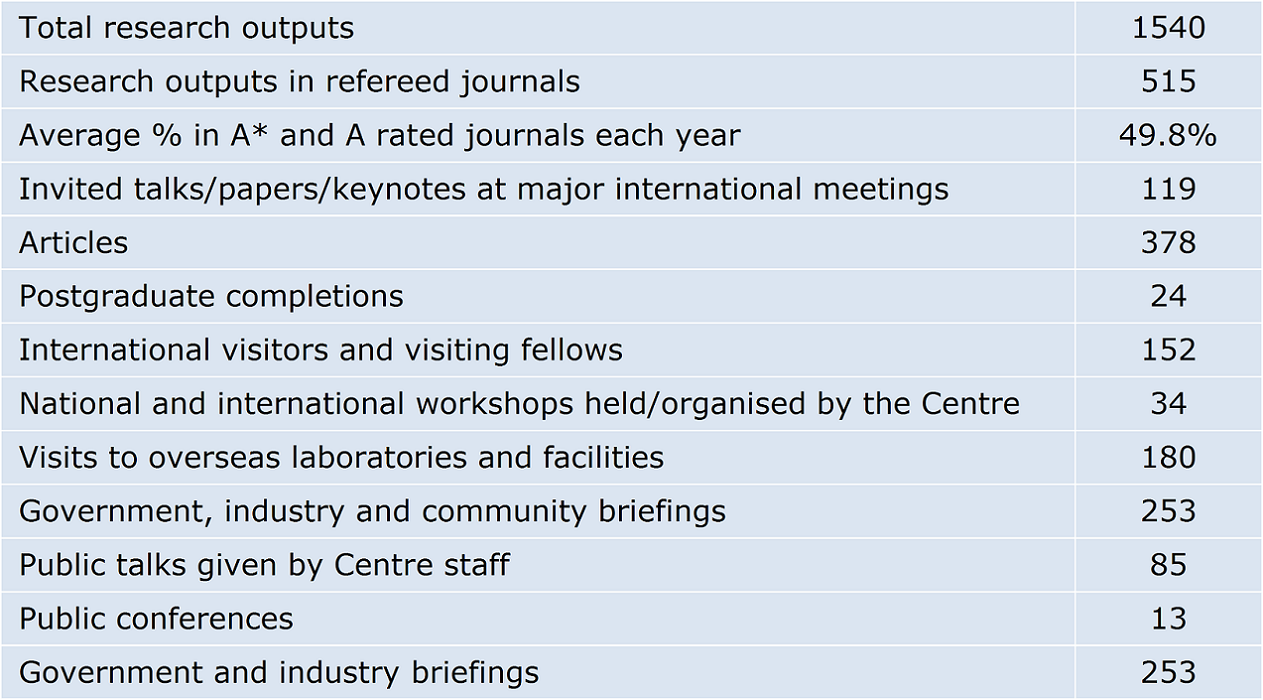
Why does this matter for industry and individuals?
People will ask questions such as “How does this all flow down to the real world?” or “How does society benefit from academic research?” The table above demonstrates how research centres are increasingly focusing on more than publication in academic journals (though that will always be important). Modern day research in practice recognises engagement and collaboration are drivers of success.
If research groups engage well, then their research is better positioned and reaches a larger audience. By engaging and collaborating, academic researchers are better informed of research needs and barriers to implementation.
The first draft of this article received strong editorial feedback. It was going to finish with the following paragraph.
Perhaps it is important for industry to ask themselves “Are we sufficiently engaging with the research community?” If you haven’t heard of CEPAR or aren’t aware of the work CEPAR is doing, then it is worth learning more about, especially if you are affected by population ageing (in my case, for instance, superannuation).
However, the alternative paragraph is as thought-provoking.
How many people in industry have heard of CEPAR? Are the metrics tabled above ones which best measure effective engagement? How highly does CEPAR value the benefits of engagement with industry and is it sufficiently core to their culture and philosophy? And how can we more clearly see how the benefits work for the ageing public who pay for their research?
Personally, I feel there will always be the potential for greater levels of collaboration between industry and researchers such as CEPAR. All parties are stepping in the right direction, and there is more to come. In CEPAR’s case, at least seven years and hopefully a lot more.
David Bell is Chief Investment Officer at Mine Wealth + Wellbeing. He is working towards a PhD at University of New South Wales.