A thorough understanding of how sub-investment grade bonds work, and the reasons for their high yield, can help investors discard the ‘junk’ label, and potentially replace it with ‘juicy’.
Interest rates might be predicted to rise in the US but for many months they have been kept notoriously low globally as governments use monetary policy to stimulate economies out of COVID-19 induced lulls. As a result, the return on investment grade bonds has also been low, and not much better than cash. But it is possible to generate equity-like returns from bonds, with a lower risk than previously thought.
What is junk?
Whether going by the name of speculative, junk or high-yield, any bond with a rating less than BBB is sub-investment grade. These bonds are given lower ratings because the issuer is deemed to be less likely to pay the bond back (in other words, they are more likely to default), therefore the investor is compensated for the increased risk with the higher return.
The US high-yield bond market accounts for $US1.5 trillion in issuance, with more than 1,000 issuers that include Netflix, Tesla, Ford American Airlines and MGM.
The Bloomberg Barclays Global Aggregate Bond Index includes almost all investment grade bonds and accounts for $US60 trillion in debt. Its average yield is around 1%. The smaller Global High Yield Index has a market value of $US2.3 trillion but an average yield of 5.8%. Despite its smaller size, this index generates $130 billion in annual income.
To put that in perspective, the global high-yield market is just 4% the size of the investment-grade market but generates 20% of the income.
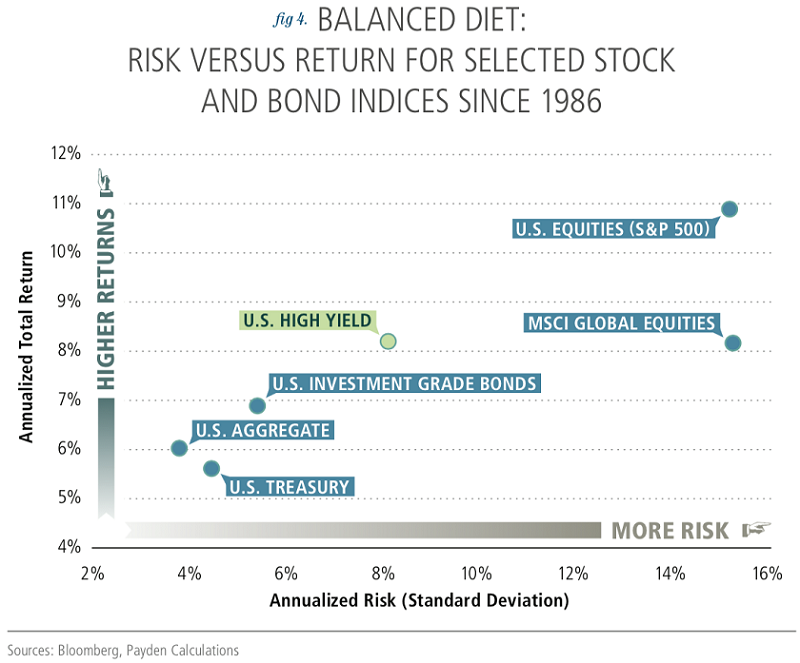
Risk versus return
Of course, investing in high-yield bonds is not all smooth sailing, and when the aggregate index is broken down, a negative price return can be observed. That is because over time some of the bonds in the index do default or fall in price when investors start to get nervous about an issuer’s credit standing.
But there are enough bonds in the index – potentially hundreds - to compensate if any one company defaults. And even if a bond falls in value, the yield, or coupon, is fixed and the investor will continue to receive that income.
Since 1996, the US High Yield Index had an average return of 7.8% from coupons and -1.1% from price, resulting in a total return of 6.6%. Since 1986, the US High Yield Index has had an annualised total return of 8.2%. The S&P 500 returned an annualized 10.6% over the same period. Not bad for bonds!
Bonds versus equity
The elephant in the room here, of course, is that while an annualised total return of 8.2% for high-yield bonds is attractive, it’s not as good as an annualised return of 10.6% which is what the S&P 500 has returned since 1986.
But we’re not arguing that high-yield bonds are a substitute for equities here. Rather, as a yield-producing investment, they can play a role in a portfolio alongside equities, traditional fixed income and other asset classes.
The income-producing features of high-yield bonds are also attractive to investors at certain life stages. Retirees, for example, are much more interested in income returns than capital returns and do not like volatility.
When comparing the standard deviations of the high-yield bond index and equities, high-yield bonds have far less volatility than equities but higher returns than other bond classes, as per the table below.
Another factor working in high-yield bonds’ favour is their lack of sensitivity to interest rate changes, compared to other bonds. Traditionally when interest rates rise, as is expected to happen in the US in the not-too-faraway future, bond prices fall as there is an inverse relationship between interest rates and bond prices.
However, high-yield bonds offer investors higher interest rates over and above official cash rates, and the differential between the cash rate and the bond’s higher coupon is likely to be a much bigger influence on high-yield bond prices.
Furthermore, cash rates usually increase during periods of economic growth, which are positive environments for high-yield bond issuers, as their creditworthiness improves.
A place for everything
It’s time to shake off the traditional idea of high-return, high-risk equities and low-risk, low-return bonds. Every asset class has value in its own right.
High-yield bonds carry more risk than investment grade bonds, but they also offer higher income returns, less volatility and less sensitivity to cash rate movements. All factors which make an allocation to high-yield bonds in an investment portfolio - alongside traditional equities and bond allocations – worth considering.
Damien McIntyre is CEO of GSFM, a sponsor of Firstlinks and distributor of the Payden Global Income Opportunities Fund in Australia and New Zealand. This article contains general information only. Please consider financial advice for your personal circumstances.
For more papers and articles from GSFM and partners, click here.