Millennials recently became the largest demographic cohort, and now 29% of the Australian population was born between 1980 and 2000. By 2030, they will represent the largest source of income and consumer spending, earning two out of every three dollars in Australia. While much has been written about how the shift in spending patterns will change the retail landscape (online over brick and mortar and experiences over materialism) relatively little research has focused on the changes to investing and asset management. Over the next two decades millennials will not only become the largest earners but are also set to inherit significant wealth, further increasing their importance to the investment industry.
Tech savvy and socially responsible
Much of the focus on the investments of millennials has to date revolved around the growth of passive/ETF investing (according to Commsec, millennials now account for 25% of ETF trades) and the use of ‘robo-advice’. Both have largely been driven by lower minimum investments and perceived low fees, making them attractive entry level propositions. While these trends are likely to continue, millennial investors are also likely to move into more traditional investment products as they build wealth over their lifetimes. Indeed, we are already beginning to see this, with Commsec finding that 50% of all new customers are under 35 years of age while millennial customers have increased by 51% over the last five years and now represent 28% of all active members.
With 87% of millennials believing that business success should be measured by more than just financial performance, one of the largest changes is likely to be the continued growth in responsible, sustainable or ‘impact’ investing. Growth in these strategies is accelerating in Australia, with rise in funds invested in ‘core responsible investments’ from $11.9 billion in 2006 to $64.9 billion in 2016 and reaching 4.5% of total assets, as shown below. Market share remained under 2% for the majority of the last decade, but have surged in the last few years.
Core responsible investment strategies as a percentage of assets under management
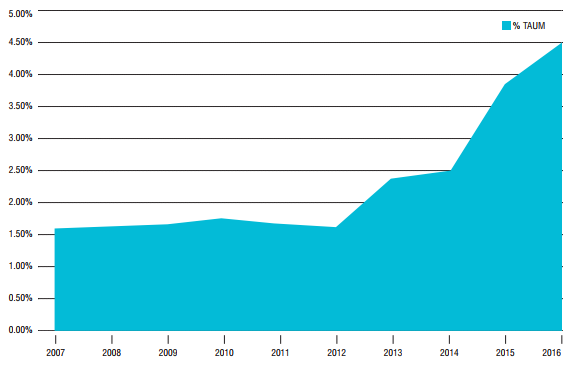
Source: RIAA, Responsible Investment Benchmark Report 2017 Australia.
With 85% of millennials interested in or currently using social impact investments, this trend is likely to accelerate further as they make up a larger proportion of the market. Additionally, 85% of millennials now consider investment decisions as a way to express their values. Financial investments will become more aligned with social, political and environmental factors.
At CFSGAM, we recently conducted a survey of our own staff (30% of whom are millennials) on the extent of their individual beliefs on responsible investment. The survey found that:
- 80% of staff believe considering ESG issues leads to more complete analyses and better-informed investment decisions.
- 85% supported the view that asset owners should, as part of their duties, consider both the direct and indirect ESG impacts of their investments.
- 75% believed that the risks and opportunities associated with ESG factors are not being captured in market values.
This tells us that millennials are ahead of the curve when thinking about the impact and implications of responsible investment strategies. Further, they are more likely to favour responsible investment strategies and are also more likely to believe that investing responsibly does not negatively impact performance. Indeed, there is strong evidence that utilising ESG factors improves performance, with a recent BofAML Report finding that they could have helped investors avoid 90% of bankruptcies.
The funds management industry will need to adapt and responsible investing will become increasingly mainstream and less of a niche or nice to have addition to traditional offerings.
Harry Moore is Head of Business Development for Australia and New Zealand at Colonial First State Global Asset Management, a sponsor of Cuffelinks.