When was the last time you saw a positive story about a mortgage fund in the financial press?
The only time a mortgage fund or its operator is mentioned in the press these days is to chronicle what went wrong in the wake of the GFC, detail the mismanagement that took place and update the public on the progress of the multitude of court cases being brought about by ASIC and others.
There is no denying that, post-GFC, some operators of mortgage funds have been shown to be foolish or greedy at best and, at worst, criminal. However, the GFC brought into focus a lack of corporate governance, excessively risky management decision-making and misleading marketing practices across a whole range of industries and asset classes.
Post-GFC, almost every other asset class has been allowed to reform itself and prove to the investing public that it has changed and is worthy of a second chance. Mortgage funds do not appear to have been afforded this same opportunity. Instead they seem to have been consigned to a purgatory of mistrust.
Contrast this situation with the burgeoning crowdfunding and P2P (peer-to-peer) lending industries. In the many newspaper columns dedicated to these industries, the coverage is almost universally positive. There are few questions being asked about whether these platforms are actually offering an acceptable risk-adjusted return to the investor. Interest in digital methods of raising capital seems to have reached the point where the mode of capital raising is of more interest than the investment itself.
Sometimes I joke that if I operated my fund through a fancy online presence and called myself a P2P lender, I would be hailed as one of the ‘entrepreneurs’, the ‘innovators’ seeking to ‘disrupt’ the banking industry, a modern day Robin Hood hell bent on ‘democratising’ property-related financing and bringing it to the masses. Instead, as my business only has a modest online presence and our fund is called a ‘mortgage fund’, it is largely disregarded. Am I the only one that sees this contradiction?
This article seeks to dispel the idea that all mortgage funds are bad news. Choosing to disregard all debt-based investments because of the historical bad behaviour of a few is throwing the baby out with the bathwater.
A common misconception about debt
People seem to find it difficult to differentiate between the risks of taking on too much debt as a borrower and making an investment that is backed by a debt.
Many people would have little hesitation in investing in either a commercial property syndication leveraged at 60% or buying a residential investment property leveraged at 70%. These investments would probably be considered relatively conservative. However, if the opportunity is presented to invest in a loan that is secured by a first registered mortgage over that same commercial property leveraged at 60% (or the residential property at 70%), many of those investors would consider it a very risky proposition. This attitude fails to appreciate that the debt position secured by a first registered mortgage within the capital stack is the lowest risk – it is actually the equity component that provides the debt investors with their first loss buffer.
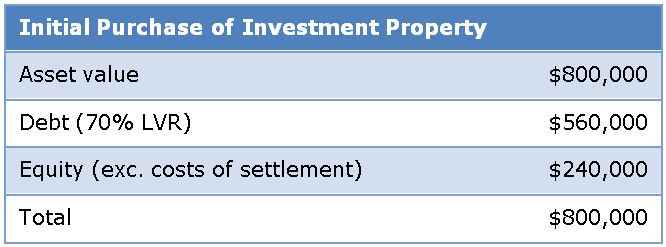
For example, consider a residential investment property purchased for $800,000 using 70% leverage:
Now consider the position if the value of the investment property falls by 15%:
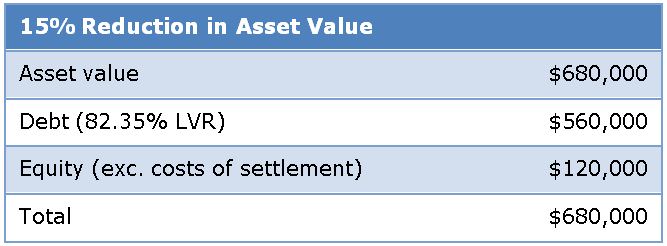
As you can see from this simple scenario, if you are an investor in the equity component of the capital stack you have lost 50% of your equity. However, if you are an investor in the debt component then 100% of your investment is preserved and there is further buffer to protect your investment from any further deterioration in the underlying asset value.
Not all mortgage funds are created equally
Although they are often thrown in the same bucket, there are actually three quite distinct structures that fall within the ‘mortgage fund’ moniker: debenture issuers, pooled mortgage funds and contributory mortgage funds. For example, a contributory mortgage fund gives the investor control over which mortgage funding opportunities they invest their money in. These different structures may bring about different investment experiences and outcomes.
The GFC highlighted the frailty of some debenture structures as well as the misleading claims used to promote pooled funds. Neither of these structures were able to deliver on the promises of their pre-GFC marketing flyers. In contrast, contributory mortgage funds emerged from the GFC relatively unscathed.
Moving forward, I believe contributory mortgage funds will become the preeminent structure within the mortgage fund industry, pooled mortgage funds will continue to have their place but will be accompanied by more modest claims as to their liquidity whilst debenture structures are unlikely to remain viable.
Changes in the banking landscape has created opportunities
The Australian banking landscape has undergone enormous change since the onset of the GFC. Consolidations have occurred within Australian banks, global banks have withdrawn or moved toward niche markets, and new macro prudential controls continue to be introduced.
These factors in combination have led to a situation where banks are highly selective in terms of the type of lending that they do, and have tended to favour residential home loans at the expense of commercial loans. Accordingly, well credentialed borrowers who would previously have been able to access bank finance are now turning to private finance or are unable to have their funding needs met at all.
This shift in the banking landscape has created a fertile environment for the mortgage fund industry and the providers of private finance.
Conclusion
Whilst P2P lenders may promise returns of 8 to 10% per annum, which sounds attractive as a headline, these loans are typically unsecured. By contrast, many mortgage funds also offer returns of 8 to 10% per annum but secured against a first registered mortgage over real property.
Lachlan Perks is the Co-Founder and Director of Keystone Capital, manager of a contributory mortgage fund designed for wholesale clients. Lachlan is also the Managing Director of property funds management business, PPI Funds Management.
This article does not constitute formal advice and contains general information only. It does not consider the individual needs of any investor.