The Chinese economy is transitioning from a dependence on investment spending and infrastructure projects towards consumption and services. This provides many new opportunities for Australia in areas such as food, wine, education and tourism. These ‘newer’ exports are likely to continue to grow strongly and take over some of our recent reliance on commodity exports.
The Chinese Government has expressed concern about the nation’s high dependence on capital investment. They appear reluctant to continue to use fiscal spending on infrastructure projects to keep economic growth ticking over. At the same time, the growing wealth of many Chinese is leading to an increased focus on consumption. Consumption as a percentage of GDP in China is much lower than in most developed economies like Australia. The emerging middle class want to spend their wealth on areas such as tourism, clean foods and overseas education for their children.
Don’t underestimate Chinese domestic wealth
According to the latest Credit Suisse Global Wealth Report, China now has 5% of the world’s millionaires. More importantly, China accounts for 33% of those the Report defines as ‘mid-range wealth’ (between US$10,000 and US$100,000), double the proportion in 2000. By way of contrast, India – often touted as the next growth story – only has 3% of the global ‘middle class’, and that number has not changed much in the last decade.
Australia has benefited greatly from the growth in the Chinese economy over the past 20 years by supplying the growing demand for commodities such as iron ore and coal. We now have an opportunity to take advantage of the next stage of growth by supplying the middle and upper income earners in China with food, wine, health related-products, education for their children and a destination for their holidays.
In tourism, Chinese visitors to Australia have overtaken New Zealand as our most numerous short-term visitors. Sydney airport now has six Chinese airlines providing regular scheduled flights between Australia and China. Some of these Chinese airlines are also offering Australians very competitive deals on flights to Europe. According to ABS data, visitors to Australia (from all countries) delivered almost $45 billion to the economy in 2015-16. This compares to around $48 billion in iron ore exports and $35 billion in coal in the same year. Exports of beef have overtaken aluminium and copper in value.
Wine is the big mover
The growing Chinese demand for our food, wine and related products has been most evident recently in the Australian wine industry. Total Australian wine sales to China in 2016 jumped 40% to $520 million. To put this in context, however, total wine exports are currently only 5% of the value of iron ore exports and less than 1% of our total exports. Nonetheless, the Australian Bureau of Agricultural & Resource Economics (ABARE) estimates that total agricultural exports will reach $48 billion in 2017-18, the same value as iron ore exports in 2015-16. The growth story is also backed up by ABARE estimates of a 5% growth in wine exports in 2017-18 (together with a 14% growth rate for cheese – perhaps a related commodity!).
For example, Australian Vintage, which sells wine brands including McGuigan and Tempus Two, has joined forces with COFCO, China’s largest online wine retailer, receiving an equity injection as part of the deal. Swan Wine Group last year exported a reported 250,000 bottles of Australian wine to China. It’s latest rather unique marketing move was to market an ‘Ambassador’ label wine, complete with a sketch on the label of former Australian Ambassador to China, Geoff Raby. The visit of President Xi Jin Ping to Tasmania helped to showcase that state’s ‘clean, green’ food products to the Chinese market.
The other sector with potential is professional and financial services. The Australia-China free trade agreement offers some longer-term hope for growth here. Professional service firms such as lawyers, accountants and engineers are developing a significant market in China for their expertise. Australian knowledge in areas such as investment management, banking and insurance all offer potential.
Demand for iron ore, coal and other commodities will always be a staple of Australia’s exports, although the value will vary as commodity prices fluctuate. However, the growth export sectors of the next 5–10 years will be food, wine, health products and tourism.
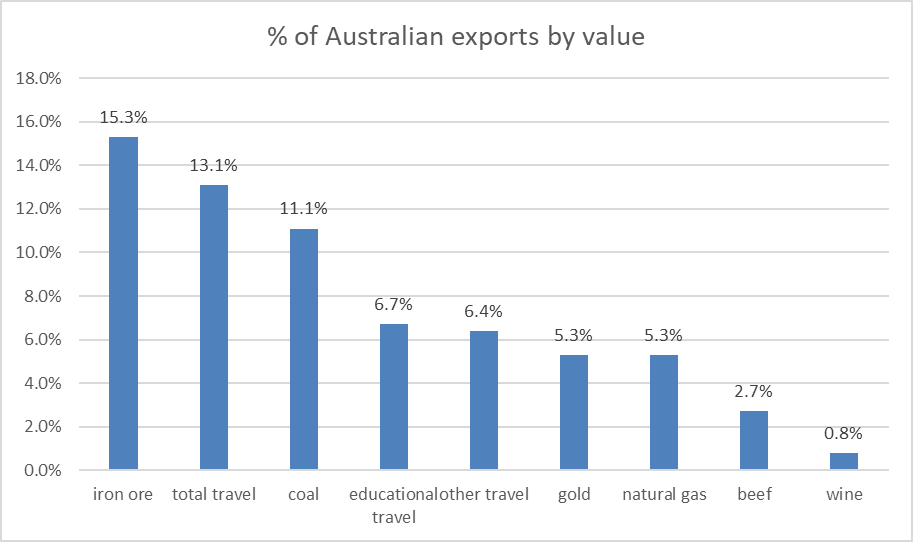
Source: ABS, ABARE. Data for FY2015-16
David McDonald is an experienced investment professional who has spent several decades in the Australian wealth management industry. He was previously Chief Investment Strategist in Australia for Credit Suisse Private Banking.