As has been well canvassed, those who withdraw money from superannuation under the COVID-19 early access scheme will reduce the savings available to them and hence weaken their prospects of an adequate retirement.
But what of the other, broader, impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on retirement savings?
Four factors drive retirement income variations
To demonstrate the possible impacts, Willis Towers Watson created 12 examples of people (we'll call them 'cameos') aged between 30 and 60 years and with various earning levels. We assume all 'cameos' work to age 67 with no career breaks, receive contributions at the legislated superannuation guarantee (SG) rates, invest in a balanced investment option throughout their working lifetime and retirement, and are married with a superannuation account balance equal to their spouse throughout retirement (for the purpose of Government Age Pension).
We consider four factors to show how retirement outcomes might be affected by the pandemic:
1. Investment returns
2. Switching behaviour
3. Early release payments
4. Periods of unemployment.
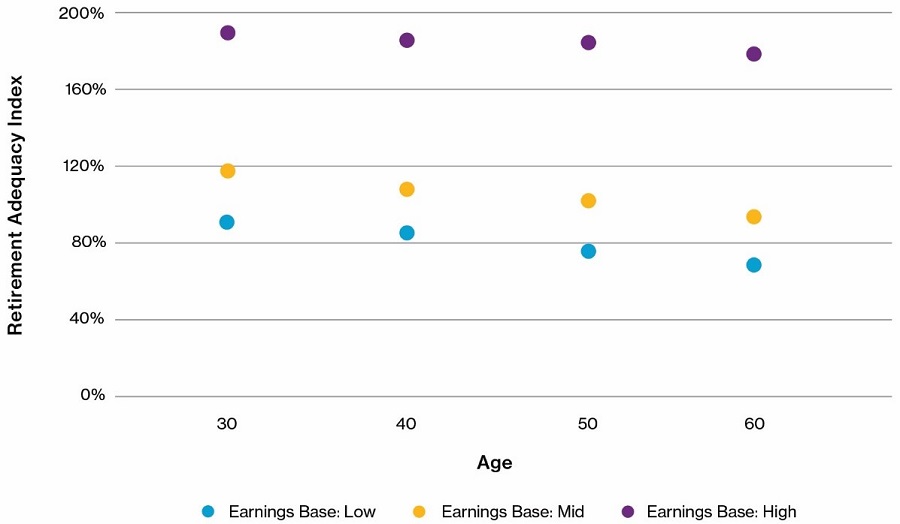
Before we can quantify the pandemic’s impact, we need to establish a baseline. We have determined the retirement adequacy for the 12 cameos on a pre-COVID-19 outlook as at 31 December 2019. We measure retirement adequacy using an index calculated as the ratio of prospective retirement income (including age pension) to the ASFA Comfortable Standard.
As expected, younger members benefiting from a full working lifetime of SG contributions are projected to achieve a higher Retirement Adequacy Index (RAI) than older members.
For each cameo, the RAI has been redetermined after allowing for each of the pandemic-related stresses.
Pre COVID-19 Retirement Adequacy
1. Investment returns
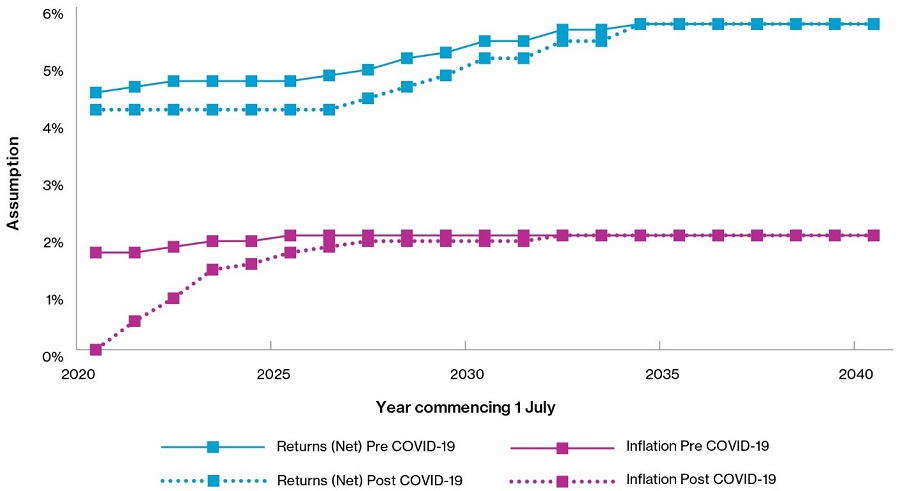
COVID-19 saw markets tumble globally in the March 2020 quarter. While markets partially recovered over the ensuing months, Balanced options still recorded losses for the six months ending 30 June 2020, with a median return (SuperRatings) of -4.9%.
While acknowledging the unpredictability of markets, the investment return stress comprises both the impact of the (lower than anticipated) returns to 30 June 2020 and assumptions reflecting lower expected inflation and investment returns in the medium term due to the ongoing effects of the pandemic.
Key Financial Assumptions
2. Switching behaviour
Throughout March and April 2020, many funds reported members shifting to cash and low growth investment options in response to the market downturn. Similar patterns were observed during the GFC in 2008-09, after which many members did not return to their previous investment options for some time, if at all.
The ‘switching’ stress assumes a switch to cash at 31 March 2020, following the most significant COVID-19 related investment losses, returning to a Balanced investment option after 10 years, to illustrate the impact of a long delay before reinvesting.
3. Early release
The special provision allowing the release of up to $20,000 (two payments tranches of up to $10,000) from superannuation accounts was introduced as a pandemic stimulus measure. Over $30 billion had been released by 16 August by over a million individuals.
Our ‘early release’ stress allows for two early release payments of $10,000, up to the value of the current account balance. We have allowed for the timing of many tranche one payments, which occurred immediately following the poor investment returns of the first quarter of the year, and hence reduced the exposure to the subsequent market recovery.
4. Periods of unemployment
The shutdown imposed to restrict the spread of COVID-19 in Australia has resulted in a significant spike in unemployment, with Treasury forecasting an unemployment rate of up to 9.25% in the December quarter 2020. Large numbers of Australians will see little to no contributions coming into their superannuation accounts over the next few years.
Our ‘unemployment’ stress allows for a three-year period of unemployment to illustrate the potential impact of a period of sustained unemployment, after which time the individual is assumed to return to their previous level of earnings.
Impact of COVID-19 on retirement adequacy
The reduction in Retirement Adequacy as a result of each stress, both in isolation and collectively, is shown below.
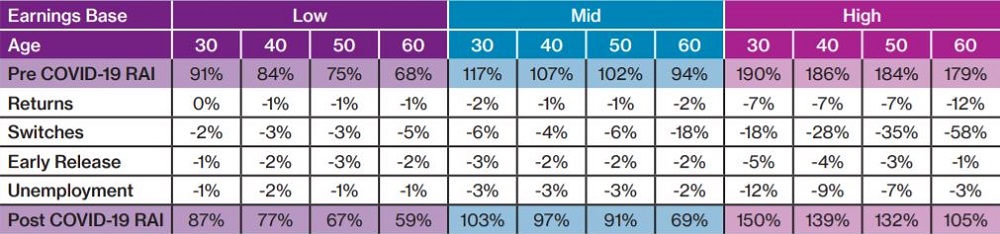
Those in the low earnings band incur the smallest reduction in adequacy across the board, due to retirement income being buttressed by the age pension.
The greatest adverse impact comes from switching. While the proportion of members that switch to cash is still reasonably small across the industry, the analysis demonstrates that it can be very damaging and is particularly acute for older members, reflecting the importance of investment returns in the ‘retirement risk zone’ (the years immediately preceding and after retirement date).
The impact of early release is greater for younger members. The exception is those with a low earnings base and account balance, where withdrawals are significantly less than the maximum $20,000. And younger members are most affected by periods of unemployment, with lost income in the early years leading to the largest impact at retirement through the power of compound interest.
So, what can individuals do to offset these impacts? Some, particularly higher earners, may choose to retire with a slightly lower retirement income if they are able to maintain their desired lifestyle with the funds available.
For others, the most obvious action is to contribute more by way of voluntary member contributions. However, at a time where unemployment is projected to reach its highest since the great depression, many will not have the ability or inclination to do this.
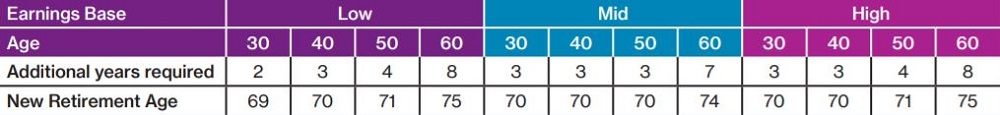
Those unable or unwilling to make additional contributions may be forced to work past their preferred retirement age – if such an option is available to them. The below table illustrates the additional number of years an individual would need to work to achieve their pre COVID-19 adequacy. Clearly, for those approaching retirement for whom additional work for up to eight years is required, this approach may not be feasible.
Additional working years required to restore Pre COVID-19 Retirement Adequacy
By using this analysis to understand how different cohorts have been affected by the pandemic, investors and service providers can better understand the impact of policies, unemployment and investment returns and how to respond sensibly.
The full report is available here.
Nick Callil is the Head of Retirement Solutions and Erinn Cullinane is Associate Director, Retirement at Willis Towers Watson Australia.