The appeal of companies that can deliver sustainable and attractive earnings growth in difficult economic conditions seems obvious. But has this appeal pushed their valuations to unsustainable levels?
Broadening the definition of ‘quality’
Many global consumer stocks have outperformed the market and now appear expensive. Companies such as Colgate Palmolive and Unilever, for example, are trading at historically high valuation multiples. To find value in quality stocks today, investors need to broaden the definition of what makes a quality company beyond just a brand.
Our definition of quality refers to what we call ‘economic franchises’. These are companies with characteristics such as market-leading positions, a long history of stable financial returns, relatively low leverage, and large, sustainable competitive advantages.
Franchises in the past built their competitive advantages (or ‘moats’) from intangible, industry- or product-related features such as brands, intellectual property, network effects, or high customer switching costs.
These companies are by definition rare, and we believe there are roughly 250 of them globally. This includes consumer staples companies, but also many businesses operating in sectors such as information technology, consumer discretionary, health care, materials, infrastructure, and industrials.
Quality stocks can be cheap or expensive
All stocks in our franchise universe are ranked according to our estimation of their potential upside, with reference to the differential between their ascribed ‘intrinsic value’, as determined by our fundamental analysis, and the current prevailing market price. In the table below, each of the lines represents a particular company in our universe. The red lines are consumer staples, and based on our analysis, they look expensive, with expected returns below zero. However, many IT franchises, the green lines in the table, offer high expected returns and look attractive.
IT vs Consumer Staples, Expected Return
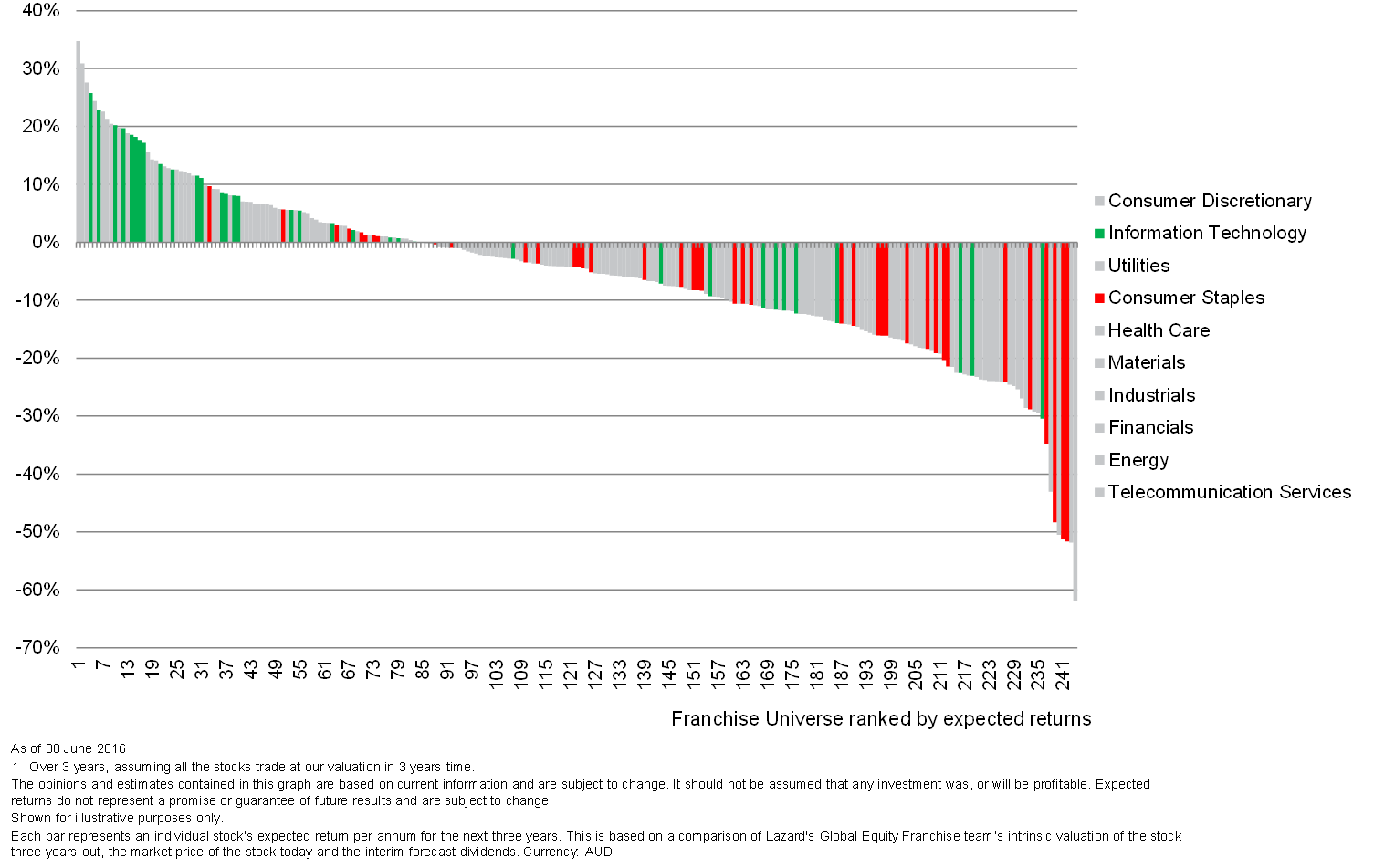
Compared with the consumer staples sector, certain IT companies offer higher returns on capital and higher growth at materially lower earnings multiples (see table below).
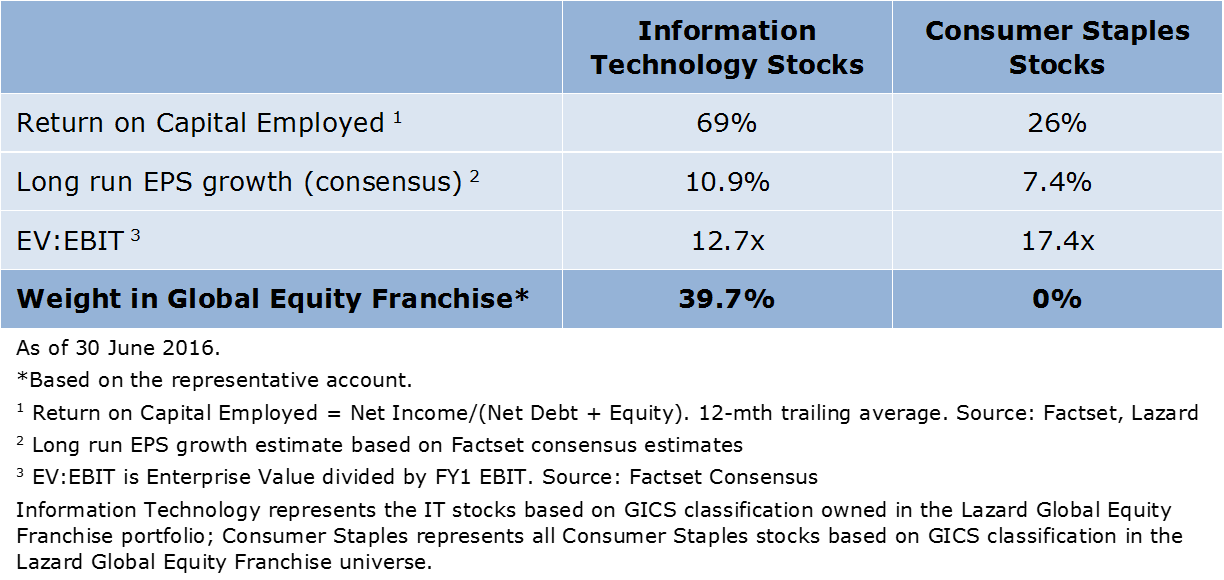
The appeal of technology
Start-ups would not qualify for our franchise universe, but within the IT space there are long-established companies with leading market positions that do. In the software sector, Microsoft, SAP, and Oracle have dominant market shares with products that make it difficult or costly to switch to an alternative vendor. In addition, the marginal cost of production for a software product is close to zero, underpinning operating margins of 35–45%, returns on tangible capital of 300–400%, and huge amounts of free cash flow every year. As a result, software companies are currently some of the most profitable businesses in our franchise universe.
Many dominant software companies now appear cheap, partly due to market fears that cloud computing will erode their economic moats. In most cases, we believe the reverse is actually more likely. The value proposition to customers is primarily the cost savings and flexibility they can achieve through replacing on-site servers, IT staff, and ongoing maintenance, with off-site cloud hosting. Importantly, that will typically enable the software vendor to charge more for their cloud-based products while still saving their customers money.
Since cloud-based software (often called ‘software as a service’) is sold by subscription rather than periodic licence renewals, software vendors’ total revenue over time increases by effectively compressing traditional renewal cycles of 3–5 years into much shorter periods. Customers can no longer defer upgrades, as non-renewal means no more software.
It is true that the transition to the cloud may give new entrants a foot in the door in some market niches. However, overall we see the revenue upside far outweighing any market share losses for incumbent software vendors with their vast installed customer bases, strong brands, and proven technology. Moreover, the switching costs that underpin their competitive advantage appear at least as high in the cloud, since the upgrade events which traditionally trigger tenders become a thing of the past.
It’s still early days, but the evidence to date indicates that the dominant software vendors are succeeding in their transition to the cloud.
Investors face a quandary at the moment. Global bonds offer close to zero yield, and some equity markets have hit multi-year highs. Developed economies appear fragile and political uncertainty continues to shake confidence. The appeal of quality companies is clear, but only at the right price and the right multiple. When shopping for quality, you may want to update your software while avoiding the toothpaste aisle.
Warryn Robertson is a Portfolio Manager at Lazard Asset Management. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual. Disclosure: Graham Hand is Editor of Cuffelinks and participates on a Lazard committee.