The best available data on the SMSF sector as a whole comes from the latest ATO statistics. The report released in December 2016 is based on 2014/15 SMSF tax returns, with the time lag due to the tax return process.
Largest sector but slower growth
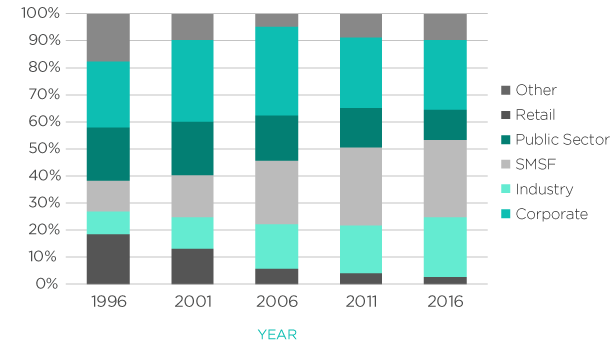
SMSFs remained the largest sector of the Australian superannuation industry, with 29% of the $2.1 trillion total super assets as at 30 June 2015. However, in the past five years, SMSFs are no longer the fastest-growing sector due to increased growth of institutional funds. During this period, total super assets grew by 59%, while SMSF assets grew by 55%, and non-SMSF funds by about 61%. The SMSF net cash flow, based on contributions and rollovers minus benefit payments, fell from $16 billion in 2011 to $7.8 billion in 2015.
Superannuation assets by industry sector, as at 30 June 2015 (Source: ATO)
Larger SMSFs share rising quickly
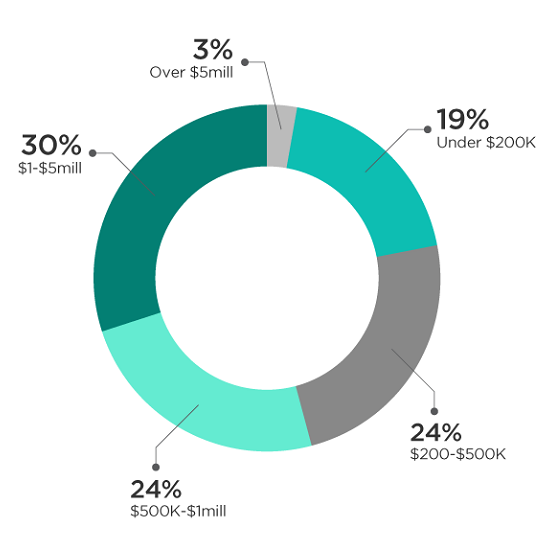
The average balance per SMSF was about $1.1 million as at 30 June 2015. Referring to the chart below, the number of SMSFs with more than $1 million of assets grew from 27.5% in 2011 to 33.0% in 2015, with 3% over $5 million. Conversely, the number of SMSFs under $200,000 fell from 24.7% in 2011 to 19.1% in 2015.
SMSF member balances and ages
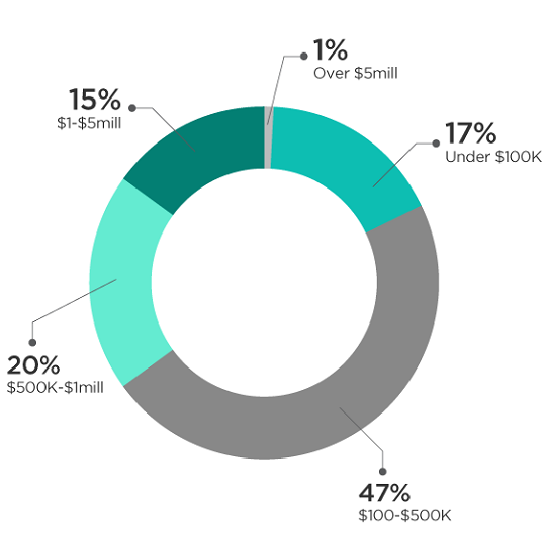
The average member balance was $589,636 compared with the average non-SMSF member balance of $46,000. The largest group of members (47.5% of the total) have balances between $100,000 and $500,000. Almost 17% of members have balances below $100,000 while 15.9% of members have individual balances in excess of $1 million.
About 38% of SMSF members also had entitlements in other superannuation funds, presumably to maintain insurance.
About 71% of SMSF members were over 50 years of age. This contrasts with non-SMSFs where 71% of members are under age 50. However, there are signs of increasing SMSF uptake among a younger age band. The 2015 year shows members below age 35 representing slightly over 10% of the newly established funds, compared with 5.7% for the whole SMSF member population.
Contribution levels
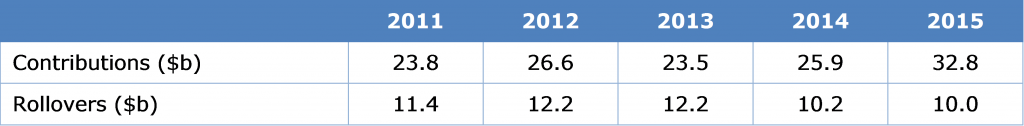
In the five-year period to 30 June 2015, contributions to the SMSF sector averaged $26.6 billion a year (member contributions $20.0 billion, employer contributions $6.6 billion). Member contributions to SMSFs increased by 54% over this period, while employer contributions decreased by 0.5%. In comparison, both member and employer contributions to all super funds increased by approximately 48% and 24% respectively. This discrepancy is driven by age differences between members of SMSFs and other super funds, with non-SMSFs having fewer retired members and thus receiving more compulsory employer contributions.
Form of benefits heavily skewed to pensions
94% of all SMSF benefit payments now are pension payments, a significant increase from 74% in 2011. The proportion of benefits relating to transition-to-retirement pensions is 19% for SMSFs compared to 12% for superannuation overall.
Despite the higher average age demographics of SMSFs, only 48% were paying pensions to at least one member, while 52% of SMSFs reported they were solely in the accumulation phase.
Philip La Greca is Executive Manager of SMSF Technical and Strategic Solutions at SuperConcepts, a leading provider of SMSF services. SuperConcepts is a sponsor of Cuffelinks.