In mandatory retirement savings systems like Australia’s Superannuation Guarantee, default options are critical. A ‘default’ is where the investment is chosen on behalf of the investor, such as by their employer. In other words, the investor accepts the default option. International research and experience show that ‘passive’ regulatory settings like defaults are far more important than those relying on active decisions like tax concessions. Super fund members face two key defaults: the fund itself and then the investment strategy.
The recent introduction of MySuper gave the superannuation sector a reason to review and renew default settings. And with the support of the Centre for International Finance and Regulation, the research paper, Delegation, trust and defaulting in retirement savings: Perspectives from plan executives and members, was commissioned to find out how well the refurbished MySuper defaults fit the people they are designed for. We interviewed superannuation fund executives and collected their impressions of member needs and characteristics, and the goals of MySuper defaults. Then we surveyed over 1000 members on their default behaviour, reasons for defaulting or opting out, and their superannuation goals.
More active choices than expected
More members described themselves as active choosers than we expected. The diagram below shows the proportion of members who stayed with the default fund and default investment option. Only 36% of our sample defaulted at both stages, meaning that 64% made at least one active choice. Also, around one-quarter of members in the default fund and 9% of investment defaulters chose the default options deliberately. So the proportion of completely passive defaulters in our sample is probably below one-third. Clearly, not all defaulters are completely disengaged or uninformed, and conversely non-default choices are not a simple proxy for member interest and engagement.
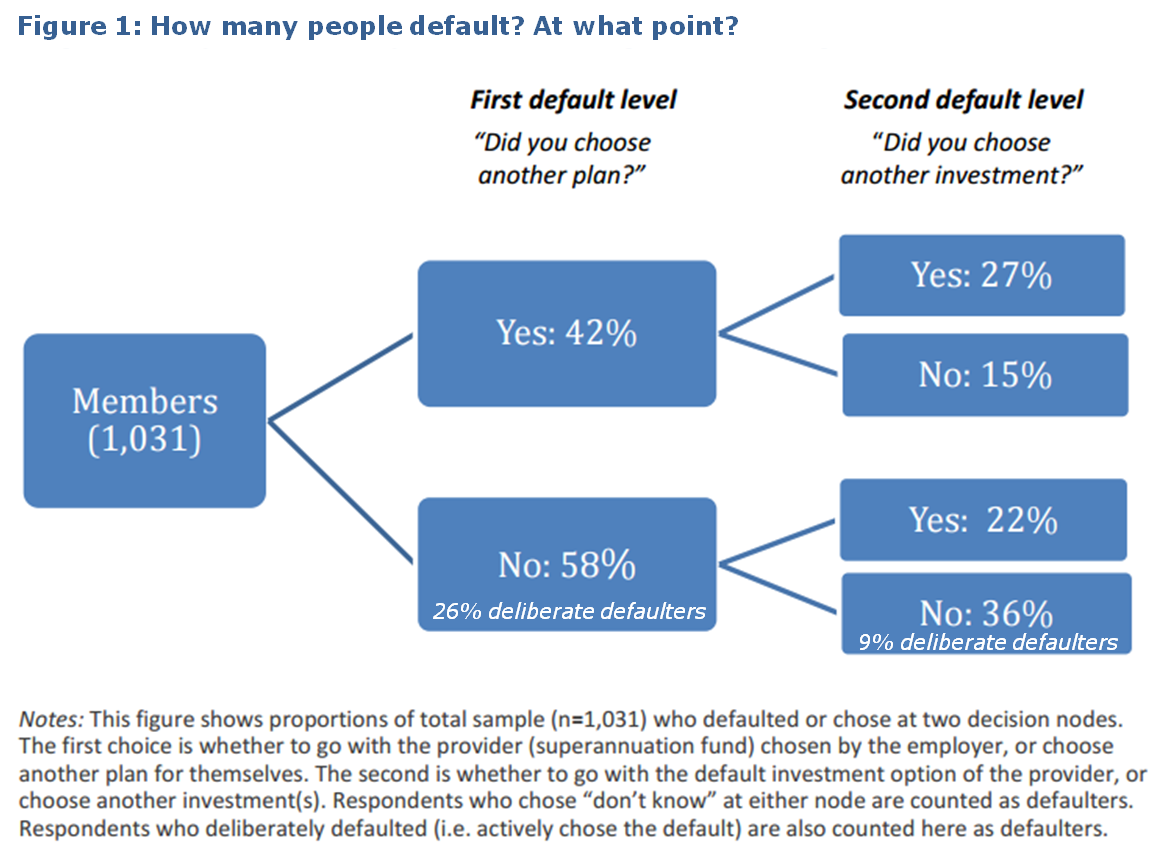
Defaulters are more likely to be younger, female and have lower incomes than non-defaulters. As account balances rise and retirement approaches, the costs of a non-optimal default become larger and are likely to prompt more members to make another choice. Interestingly the financial literacy of defaulters was only a little lower than that of choosers and the difference was not statistically significant.
Interest, trust and defaulting
We also asked members about their reasons for defaulting versus choosing. Most people said they do not want to relinquish control over their retirement savings, but they found the products suitable, and viewed the fund as trustworthy and accountable. Respondents in the default investment option emphasised more than others their own low skill and knowledge. Respondents in the default fund expressed more trust and belief that the system is well monitored. Time costs of active decision-making were rated high more often than money costs. These results are at odds with some industry commentary that characterises default members as uninterested in superannuation.
A lack of interest was not the main reason for delegating investment to the fund according to the survey (although it did have some impact), and neither is relinquishing control. However, interviews with fund executives suggested that trust is sometimes mistaken for disengagement. Trust, when combined with a self-conscious lack of financial skill, underlies both a low level of active choice and a low level of direct interaction with the fund.
Goals for superannuation
In terms of goals, members emphasised achieving a basic amount of wealth for retirement. This lines up with comments from interviews where executives framed default design in terms of retirement outcomes rather than short-term performance. However there is little agreement in the sector about what are the best strategies to reach this goal.
Members thought low fees were an important, but not the most important, aspect of a fund’s goals. This also seems broadly consistent with executives, who acknowledge that fees matter but view them as constraints rather than objectives.
A noticeable area of difference between executives and surveyed members relates to risk tolerance. The clear skew towards low risk tolerance among default members stands in contrast with relative aggressive investment strategies, where growth asset exposure averages over 70%. While life cycle funds are designed to de-risk near retirement, many executives express the view that default members need strategies with high growth asset exposure in order to generate higher balances and retirement incomes.
Regulators and industry might improve member outcomes by developing smart defaults that allow for a variety of risk preferences and demographics. The study emphasises the dangers of misconstruing super fund members as uninterested: instead, many see themselves as low in skill but high in trust.
Susan Thorp of the University of Sydney co-authored the research paper with Adam Butt of the Australian National University, Scott Donald of University of NSW, Doug Foster of the University of Sydney, and Geoff Warren of the Centre for International Finance and Regulation.