Buying food from a shop is so simple that it’s something we take for granted. If it were the same experience as investing, it would be far more complex.
Instead of taking, say, a carton of eggs to the checkout, imagine having to first ask the farmer if they’re free-range or caged, the grader for the size and quality, the Food Standards Board for nutritional information, and (finally) the shop for the price.
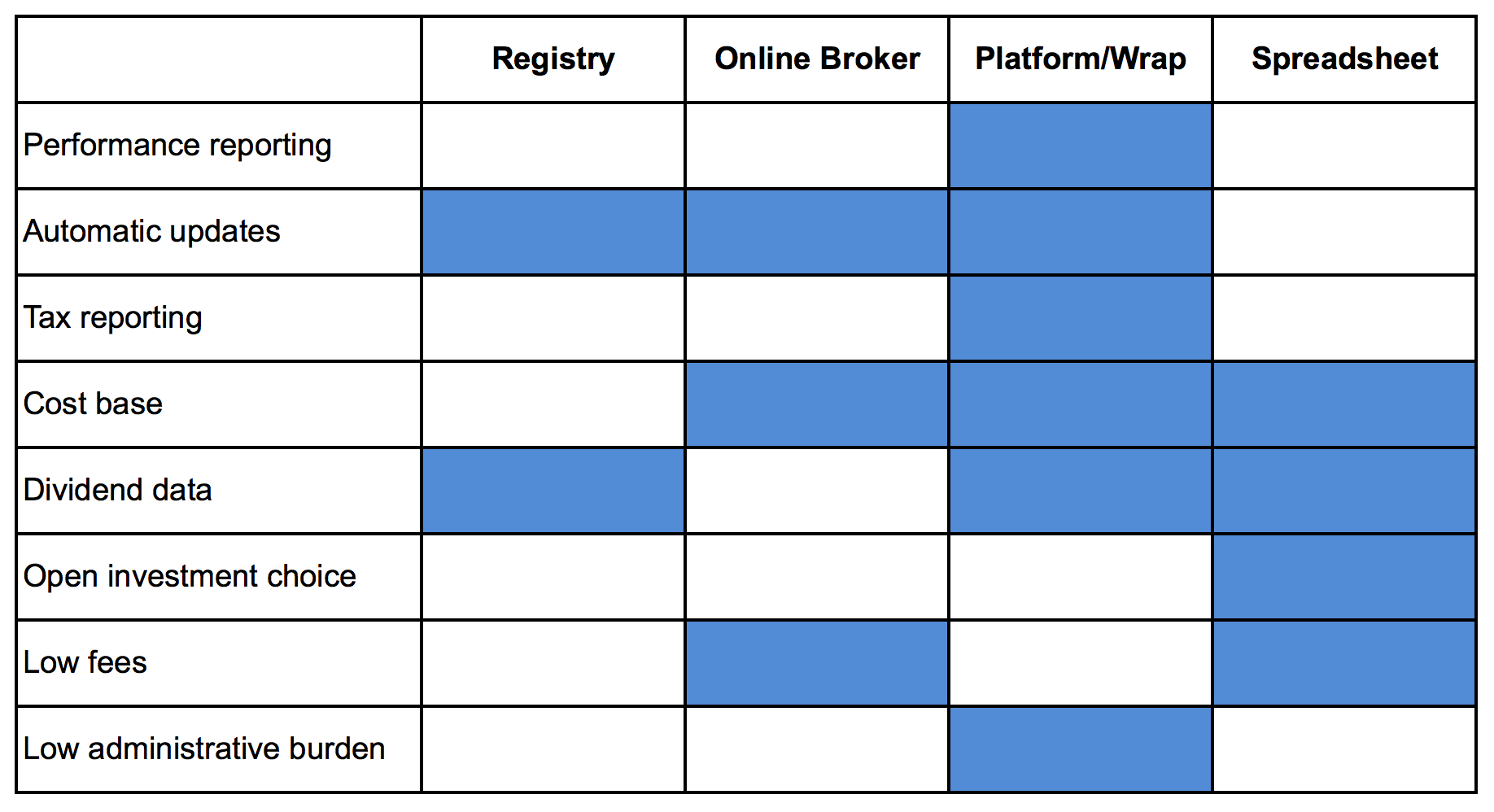
Investors face a similar proposition every day. Crucial information such as performance data, tax reporting, share dividends, corporate actions, and cost bases are spread across online brokers, share registrars, investment platforms, wraps, and even old-fashioned spreadsheets.
Bringing these pieces together can leave investors with a heavy administrative burden which may ultimately weigh down performance.
It is not a new problem, but many previous solutions have forced investors to pay excess fees for bundled, inflexible products or lumped them with simplistic performance methodologies which leave much to be desired.
Investors need to understand each provider’s strengths, and ultimately sidestep their weaknesses, if they want to solve this puzzle.
Missing pieces in a broken chain of service
Consider what each traditional service provider delivers.
1. Online brokers: the transaction hub
Online brokers play a key role for investors: they represent a direct window into the world of listed securities. They democratised share trading in the 1990s by slashing trading costs and, over the years, have expanded their offering with greater volumes of research and trading ideas.
Today, almost 6 million Australians own shares directly, according to the ASX, and 635,000 investors placed at least one share trade through an online broker in the 12 months to November 2015, according to Investment Trends. Online brokers make money when investors trade and maintain high cash balances. This is a key driver for the massive volumes of research and trading ideas they release and why they only offer minimal performance and tax reporting capabilities. One drives profits while the other drives costs.
Online brokers are a transaction hub rather than a performance and administrative hub. Typically, the profit/loss figures they provide fall down in two key areas: they don’t include dividends and they ignore how long investors have held their investment. These misleading performance measures can be hundreds of percentage points away from common benchmarks used to compare a portfolio.
2. Share registrars: tracking what you own
The main function of a share registry, such as Link Group and Computershare, is to keep account of who owns what shares.
This is a crucial function but one that is performed on behalf of listed companies, which pay for the service. Share registrars provide a range of functions to companies such as paying out declared dividends, as well as administering employee share schemes and annual general meetings.
A share registrar’s focus is on serving the needs of companies rather than those of share investors. Investors can typically see the number of shares they hold (but not the original purchase price), dividends paid, and set up a dividend reinvestment plan. However, their investor-facing websites leave much to be desired and lack critical information such as true performance data and tax reporting.
3. Wraps and platforms: the advice portal
Wraps and platforms dominated the advice industry for many years. They offered a simple way for financial planners to sell a restricted range of managed funds while bundling in a range of fees such as platform, advice and volume rebates.
Many of the funds management products on platforms were from related parties, raising conflicts of interest: were they sold because they were the most suitable investment or because they raised profits for the parent company?
Platforms and wraps remain popular although, with much conflicted remuneration now banned, the industry is slowly moving away from product-led advice towards goals-based advice.
With less certainty about the strength of future investment returns, fees have also attracted more attention. Many investors have realised that percentage-based platform fees may outweigh any administrative and reporting benefits and have looked for cheaper solutions.
4. Spreadsheets: the most basic solution
Investors often intuitively fall back on the most basic technology of all: spreadsheets. They spend substantial time manually updating trades, share prices, dividends, and costs from service providers (often including multiple online brokers and share registrars). They then attempt to calculate performance and tax data, which is a process prone to error.
Many investors remain trapped in the past and identifying effective solutions remains a key challenge for them.
The rise of technology
Each provider in the investment chain has an important role to play but it is only now, with the rise of low-cost, cloud-based technology, that investors have an opportunity to use each to its full potential.
New service providers acting as a hub can automatically receive useful data from each service provider, make complex performance and tax calculations, and send it to others, such as accountants and advisers.
The most effective technology-based service providers also share a range of other attributes not commonly seen in the financial services industry. They are highly flexible and easily accommodate investors’ widely varying assets and choice of service provider. They provide value for money by charging a flat dollar amount rather than a percentage of funds.
Investors who can intelligently employ this type of fintech can build stronger portfolios by cutting their administrative burden and revealing a true picture of investment performance.
Doug Morris is the CEO of Sharesight, an online portfolio tracking system used by self-directed investors and advisers. Sharesight is an alliance partner of Cuffelinks.