Markets perform well when the key indicators behind economic growth are strong. But when those foundations are rocked, things can get a bit scary.
And that’s where we are now.
How effective will the stimulus packages be?
Since the start of the year Australia’s economy has been hammered by a series of events, including horrific bushfires, the spread of the COVID-19 virus and a resumption of falling interest rates to try to stimulate a sluggish economy suffering from a lack of consumer spending.
It has led us to reduce this year’s forecast economic growth for Australia from an already sluggish 1.7% to an anaemic 1%. The risk of Australia going into recession is real, despite the massive stimulus packages from the federal government. The third package of $130 billion takes fiscal expenditure to a level never seen before, with this one decision costing more than the total annual health and social security budget.
But we are also at the mercy of global and unpredictable events, sometimes known as ‘VUCA’ (volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity).
Take interest rates in the US, for example. In December, markets were talking up the expectation for rates to rise. Weeks later the US Federal Reserve cut rates by 0.5%, and following the dramatic realisation of the terrble impact of coronavirus, it was lowered effectively to zero, a range of 0% to 0.25%, on 15 March 2020.
You cannot predict events like COVID-19 or Russia erupting into an oil production war with Saudi Arabia, but your portfolio will have to be prepared for such events.
Investing with VUCA
You also cannot predict how long such events will impact markets. Coronavirus will remain an overwhelming issue for many months, and the impact on government budgets will play out for years. It was the same with the trade wars, something that initially seemed a matter for diplomacy to resolve, but it continued to escalate throughout last year with rising market impacts.
For now, that’s yesterday’s news as coronavirus and oil shock fears have combined to create fears of global recession.
The shockwaves from those fears have created a series of record market movements, the type of volatility in prices not seen since the peaks of other crashes such as during the GFC and, indeed, the Great Depression. Heavy falls one day are followed by market bounces as investors scramble to take advantage of what were perceive to be low share prices.
The investors selling into the market were panicking, which is never a good time to make investment decisions. But were the people buying making a better decision? Buyers look like heroes one day, then late to the party the next.
Don’t try to time the market
Investors deciding how they want their portfolio to perform should not only think about returns. A major consideration is the ability to be able to withstand unexpected impacts. We have seen many examples of market-moving events over the past decade and each has one thing in common – unpredictability, as you can see in the timeline below.
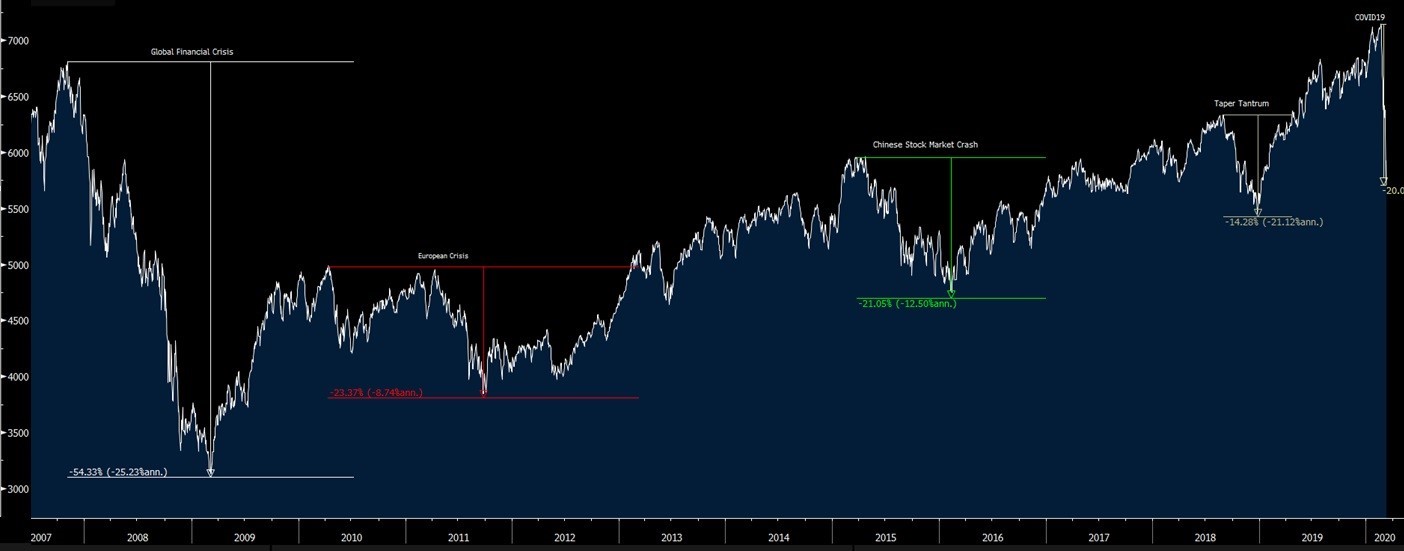
At Citi, from the early part of 2020, we noticed an increase in clients wanting to lock in returns and reduce risk. ‘VUCA’ is driving a renewed focus on income options such as corporate bonds and tailored investments that can give investors access to equities in a structure that can reduce risk. Even before the full impact of coronavirus was appreciated, investors were moving into instruments that allow individual shares to drop between 30-40% without an impact on their capital and return.
We have also seen a significant increase in foreign exchange transactions as investors shift into US dollars to take advantage of the USD’s safe-haven status. We have long been an advocate that a portfolio needs to be diversified not just by asset class but also geographically.
What should you do in these unprecedented times, and in fact, at all times?
- Stress-test your portfolio regularly to understand how it performs during market uncertainty.
- Ask yourself if the income from your investments is sufficient for your needs in a low interest environment over the long term.
- Diversify smartly by combining asset allocation with instruments which can earn a positive return, even if the market drops. For example, Citi offers a tailored investment which pays clients an income of 5% per annum if the equity market goes up but it also pays a positive return of 5% even if the market drops by less than 25%.
- Consider buying another currency - you buy many products from overseas, should you take the same approach for currency?
Gofran Chowdhury is Head of Investment Specialists at Citi Australia, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.
For other articles by Citi, see here.