Investing success is not just about picking the right asset class or securities, but also avoiding the poor investments. In the current global economic environment, out of the world’s major asset classes, global fixed rate bonds appear to have the lowest likely return over the next year or so.
Global bond yields are incredibly low
The rally in risk markets since the GFC has benefited from a major tailwind. Central bankers have delivered extraordinary monetary stimulus, despite the recovery in global economic growth and employment. They have remained resolutely accommodating to lift still unusually low rates of inflation.
As seen in the chart below, this has led to a decline in global bond yields – as represented by the prevailing yield on the Bloomberg Barclays Global Aggregate Bond Index – through the post-crisis global equity rally. The yield is now only around 1.6% p.a. This reflects very low bond yields around the world, with the yield on US, German and Japanese 10-year government bonds presently around 2.3%, 0.4% and 0% respectively. These bonds are an important component of most diversified investment portfolios around the world.
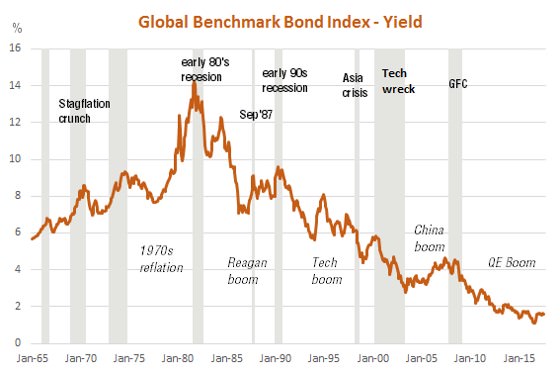
Source: Bloomberg. ‘Yield-to-worst’ for Bloomberg Barclays Global Aggregate Bond Index. Shaded areas represent periods of significant equity market decline. Past performance is not an indicator of future performance.
Given this bond index is comprised of fixed rate bonds (both government and corporate), the low yield means that even if interest rates don’t change further, the best annual return available from this Index is around 1.6% p.a. That’s not much compensation for the rate of inflation or for the volatility in capital returns on fixed rate bonds as interest rates fluctuate over time.
What’s more, depending on the period over which this Index is held and the speed of the change in market interest rates, returns may be even lower should, as seems likely, global bond yields eventually return to more normal levels.
Global bond values at risk of higher rates
As many investors know, the capital value or ‘price’ of fixed rate bonds moves inversely with movements in the level of interest rates. This sensitivity is greater, moreover, the longer the duration of the bonds in question. In the case of the Bloomberg Barclays Global Aggregate Bond Index, the average term-to-maturity of the bonds it contains is relatively long at around seven years. A 1% general rise in interest rates is estimated to produce a 7% decline in capital values.
Indeed, the ongoing decline in bond yields since the bottom of global equity markets in early 2009 has delivered investors, up until end-September 2017, a handy 7% p.a. return as measured by the global benchmark bond index. But while global central banks have been a boon to bond holders over recent years, the reverse is likely to be case over the next few years. Already the US Federal Reserve has started lifting official interest rates and will begin net reductions in its substantial bond holdings this month. The European Central Bank is also inching toward policy tightening, and is likely to announce in the next month or so a reduction in its bond buying programme for 2018.
By way of example, should the yield on the benchmark global bond index rise from say 1.6% p.a. to 2.6% p.a. over a given year, the implied total return from the Index (ignoring hedging costs) would be negative 5.4% (1.6% income return less 7% loss in capital value). Even if such a rise in yields were to take place over two years, it would still imply negative annual returns over this period of around 2% p.a.
In short, when and if global bond yields start to rise, investors in the global bonds benchmark index should expect negative returns for a time. At the very least, given the ongoing recovery in global economic growth and corporate earnings, global bonds may well underperform other major asset classes such as local bonds, global and local equities and even many commodities over the next year or so.
Accordingly, at least in terms of major asset classes, in my view, longer-term fixed rate global bonds are currently potentially one of world’s worst investments.
Rising rates favour floating over fixed rate bonds
Given that local bond yields also tend to closely track global rates, rising bond yields would not be great news for the Australian fixed rate benchmark bond index, even if the Reserve Bank initially resists following other central banks in tightening policy. While the local Bloomberg AusBond Composite Bond Index might outperform the global benchmark, returns would still likely be low, and even potentially negative for a time. Indeed, in the year to end-September already, this Index produced a negative 0.7% return due to a rise in its average yield from 2% to 2.6%.
In this environment, Australian floating rate bonds should deliver a potentially better risk-return outcome than funds which aim to track the AusBond Composite. The floating rate exposure not only benefits from higher interest payments, it should not suffer the capital losses of fixed rate bonds if bond yields rise.
David Bassanese is Chief Economist at BetaShares, which offers exchange traded products listed on the ASX. BetaShares is a sponsor of Cuffelinks. This article contains general information only and does not consider the investment circumstances of any individual. Floating Rate Bond ETFs are now available on the ASX, with BetaShares’ QPON being the largest.