Like their peers around the world, Australians have enthusiastically embraced passively managed index tracking funds in recent years. Active funds are of course still significantly larger than their passive counterparts making up roughly $2 in every $3 of equity assets under management in this country, about the same as in the UK.
Change happens more slowly than we think
This is simply because net flows of new cash into funds are orders of magnitude smaller than the hundreds of billions of dollars already under management, so change tends to happen rather slowly. What’s more, having steadily lost market share in the past, active funds have recently fought for new investment dollars more successfully here in Australia than they have in in comparable countries.
The Calastone network handles hundreds of millions of fund transactions around the world each year. We have good coverage in Australia, so we get a great overview. It is not our role to say one kind of fund is better than another. This is a job for financial advisers and investors themselves. But we are well positioned to observe the behavioural trends and pick up turning points long before anyone else can, and in real time.
What's happening with fund flows?
First a bit of context. 2020 saw a huge increase in overall transaction volumes across our network globally (+45% compared to 2019). The year started with net outflows from equity funds as the coronavirus infection took hold in China. Investors in Asia were first out of the blocks. Australians and Europeans jumped ship next, selling down heavily in February, while those in the UK took longer to respond.
From April onwards, however, the global policy response to the pandemic prompted investors everywhere to pump cash into equity funds. Australian investors were among the most bullish, adding $6.8 billion to their holdings by the end of the year. Three fifths of this was in November and December alone as vaccine approvals raised hopes for an end to the pandemic. Our index of funds flows for the year scored a very positive 54.9 in Australia compared to those outside Australia of 51.3 (a reading of 50 means inflows equal outflows).
More than a third of the money Australians added to equity funds in 2020 went into funds that only invest in Australian equities. In Europe, the UK, and most of Asia, investors preferred to take a more global approach. While there are good reasons to have a portion of savings in domestic assets, it is surprising to see Australia-only funds take such a big slice of the inflows. Perhaps the successful suppression of the pandemic here in Australia encouraged investors to stay local.
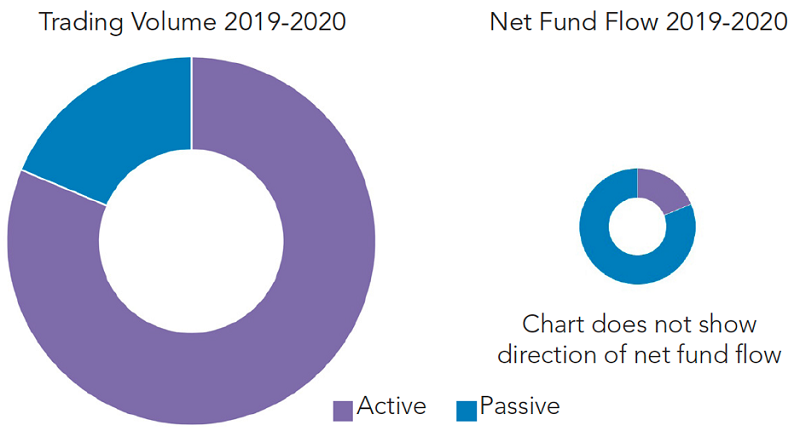
When it comes to active and index funds, investors behave rather like fund managers. Flows into index funds are relatively stable, reflecting a simple ‘buy and hold’ strategy that accumulates savings over time. Net inflows are large by comparison due to total trading volumes – steady buying, not much turnover.
By contrast, investors trade their active funds much more often, picking favoured funds, adding money more opportunistically in response to news flow on economic, political or world events. Investors re-allocate around the world by switching between funds with a particular regional focus or favoured strategy. For active funds, total trading activity is very large, and the resulting net inflow or outflow is extremely small by comparison to overall volumes.
Net fund flows are small relative to huge trading volumes
Overseas, index funds are comfortable winners
Outside Australia, index trackers comfortably beat active funds in the race to attract new capital in the last two years. Across Calastone’s global network, index funds garnered inflows of $12.2 billion in 2019 and a further $18.2 billion in 2020. By contrast, active funds saw net outflows of $16.7 billion in 2019 and would have shed cash again in 2020 were it not for a dramatic turnaround in the final quarter. By the end of the year, investors added a net $3.3 billion to their holdings (not enough to make up for 2019 outflows).
Net inflows for index tracking equity funds were US$23.5 billion (A$31 billion) in 2019 and 2020.
Australians still focus on active funds
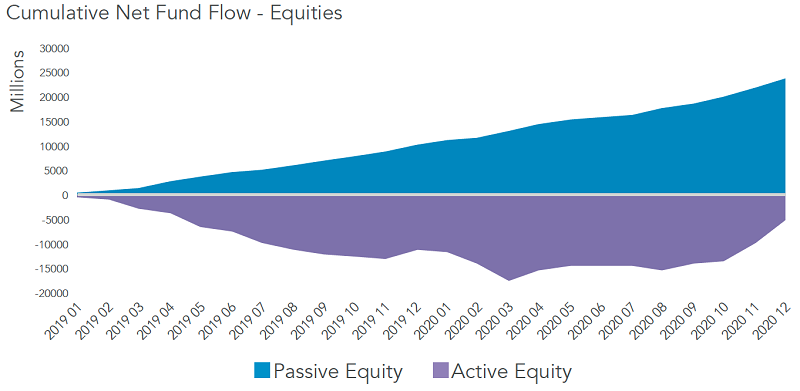
In Australia, the preference for passive funds has been less clear in the last couple of years. Australians actually added modestly to their active fund holdings in 2019 and significantly in 2020, in contrast to investors in the rest of the world. Over the two-year period, these inflows totalled A$5.7 billion.
Unlike investors elsewhere, Australians added less to index funds - A$3.6 billion. However, there was relatively little two-way trading associated with the index-fund flows. Activity was characterised by steadier buying while active fund inflows were on the back of volumes four times greater.
The long bull market has favoured passive funds. Savers are happy to ride a rising index and take the simple market return. But passive investors are all-in on market bubbles and market crashes alike. Moreover, the rise of mega-caps like Apple and Amazon has increased absolute risk for passive investors, even if a fund continues to mirror the market perfectly. This is a sort of hidden risk.
Active funds winning in ESG globally
There is one area where the active fund management industry outside Australia is mounting a hugely successful defence against the rise of index trackers – ESG funds. They are the undisputed success story of the last two years. From a near standing start, they have captured investor imagination to such an extent that in 2019 and 2020 they took an astonishing $84 in every net $100 flowing over our network into equity funds of any kind. Net inflows rose seven-fold between 2019 and 2020, even though overall turnover in ESG funds only doubled. Three quarters of this new ESG capital ($16.3 billion) flowed into active funds.
Globally, three quarters of new ESG capital (US$11.3 billion) flowed into active funds. If we strip out ESG funds altogether then traditional active funds have shed US$16.8 billion over last two years.
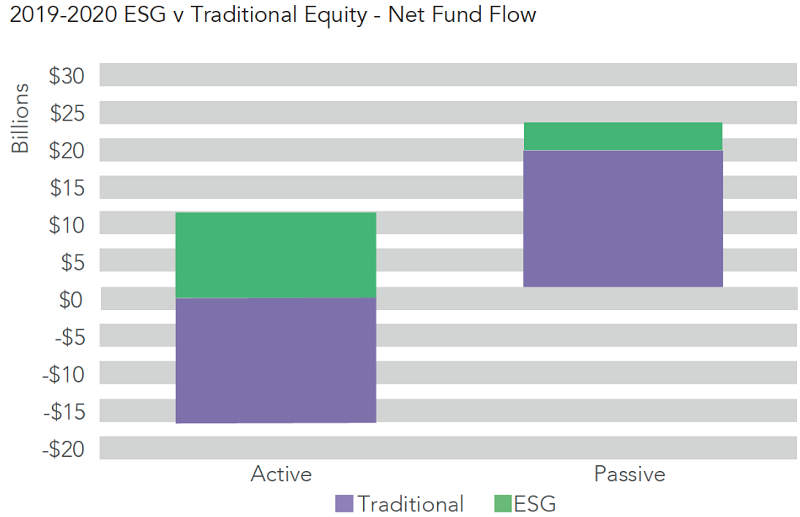
UK and European investors have been the keenest buyers. Based on fund flows, Australian and Asian investors appear to be about two and three years behind the curve respectively. In 2019 and 2020, Australian investors added just $1.2 billion to ESG equity funds, only $1 for every $13 that flowed into equity funds of any kind – a fraction of the global average.
Appetite is growing, however. November and December saw larger inflows to ESG funds in Australia than in the previous two years combined. Active managers like them because it’s much easier to differentiate their funds from vanilla index trackers. In Australia they are pushing at an open door.
Investors have shown they are still open to buying active funds. Structurally, index funds are likely to take more market share over time, but ESG has given active managers a new string to their bow and a good reason to fight back.
Edward Glyn is Head of Global Markets at Calastone. The full report, “Tidal Forces – Can Active Funds Fight the Passive Flows?” can be downloaded here.