I am as guilty as most market participants of using the phrase ‘active versus passive’, when strictly speaking, that is not what I mean. The problem with using those terms is it glosses over some important details. As a simple example, a highly active investor can use index funds and a highly passive investor can use traditional actively managed funds.
What should the debate focus? There are three comparisons that immediately spring to mind:
- Low cost versus high cost
- Low turnover versus high turnover
- Rules-based versus forecast-based.
Low cost versus high cost funds
We have written at length about the costs of funds and ETFs. Costs are closely associated with performance. Numerous studies have confirmed this, starting with the work of Nobel Laureate William Sharpe in ‘Mutual Fund Performance’ written in 1966. It is not as if the thought is new, rather the marketing of more expensive investment options has been very effective.
Why do costs matter so much? Fees are taken directly out of performance daily and investors never actually see them. The less paid in fees, the more that remains for the investor, but it's not as simple as active equals expensive and index equals cheap.
Not all index funds are cheap nor active funds expensive
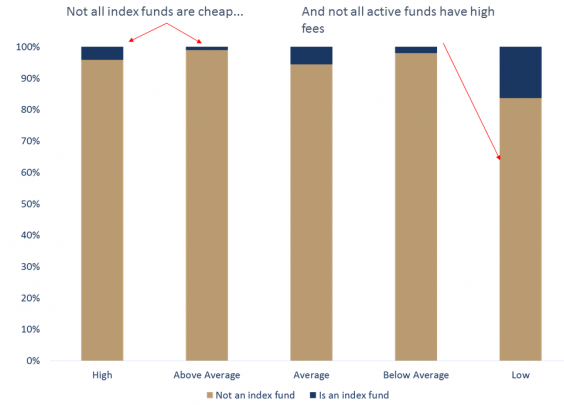
Source: Morningstar, Owners Advisory, May 2017
Low turnover versus high turnover
One metric that is often overlooked, but is extremely important particularly to after-tax returns, is turnover. Turnover measures the frequency in which securities are traded over a 12-month period and serves as a proxy for trading costs. Trading costs directly impact a fund’s performance (and again, like fees, are taken out prior to performance is calculated, making it difficult to see). In addition, capital gains can be locked in and then passed through to the investor. Traditional active managers and indeed some rules-based approaches have very high turnover, which investors pay for, and again impacts directly the returns realised.
Not all index funds have low turnover
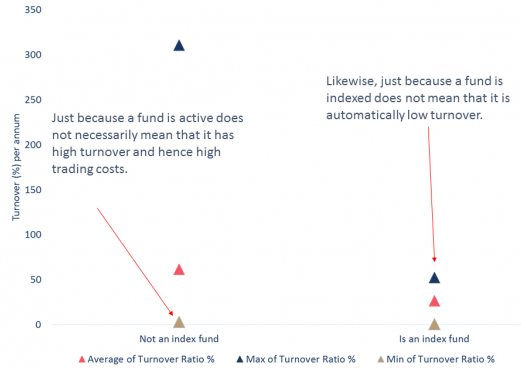
Source: Morningstar, Owners Advisory, May 2017
Rules-based versus forecast-based
Rules-based investment strategies are what underpin nearly every smart beta offering or factor tilt investment strategy. Typically, rules-based approaches are based on academic research. Value, for example, is such a factor. Researched endlessly, in the early work by Fama and French, companies with low price-to-book ratios were identified as providing excess returns to the market over the long -term. Indeed, straight cap-weighted index funds, such as an investment that tracks the S&P/ASX 200 is another factor investment, but here the factor is beta or the market as a whole. These rule-based strategies do not care about the direction of the market. They simple follow the rules.
On the other hand, forecast-based approaches are typically seen in the traditional active management strategies. Analysts work to identify the ‘true’ or ‘fair’ value of a security using some valuation method and then look to see where mispriced securities may be lurking. This is a tough gig, particularly as technology improves. A well-designed algorithm can identify mispricings much faster than a human can. The impact is to push prices to their ‘fair’ value faster than was once the case.
Using the phrase ‘active versus passive’ is an oversimplification of the problem investors face when thinking about how to implement their asset allocation. Really, what ultimately matters is returns individual investment vehicles deliver, not whether they are index investments or not.
Leah Kelly is Portfolio Manager at Owners Advisory. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any individual.