Given that Elon Musk, the founder of Tesla, is now the richest man in the world (Forbes, 18 July 2022), it’s fair to say that Electric Vehicles (EVs) appear to be a compelling sector for wealth creation. But scratch below the surface, and it’s clear that not all EV investment opportunities are created equal.
There are many ways to gain exposure to the EV thematic, from investing in lithium producers who help to power EV batteries, through to the manufacturers of the vehicles themselves. However, we see the ‘E’ in EV as a significant opportunity. This article explains how investors can support the EV revolution by investing in the charging infrastructure that underpins the whole sector.
The opportunity
As the world moves to lower greenhouse gas emissions, transport is key to decarbonisation – road transport in particular, which accounts for around 75% of emissions in the transport sector.
EVs are set to be an important part of the solution. Already accounting for around 9% of vehicle sales globally, they are even more popular in countries like Germany, where 1 in every 4 vehicles sold is electric. In fact, global sales doubled between 2020 (3.2 million sold) and 2021 (6.6 million) according to BloombergNEF (BNEF).
Most governments around the world recognise the need to accelerate uptake of EVs to address the climate impacts of transport. European policies have been particularly supportive with the region’s largest car manufacturer Volkswagen Group expecting electric vehicles to represent 70% of sales by 2030 and to stop selling internal combustion engines by 2035.
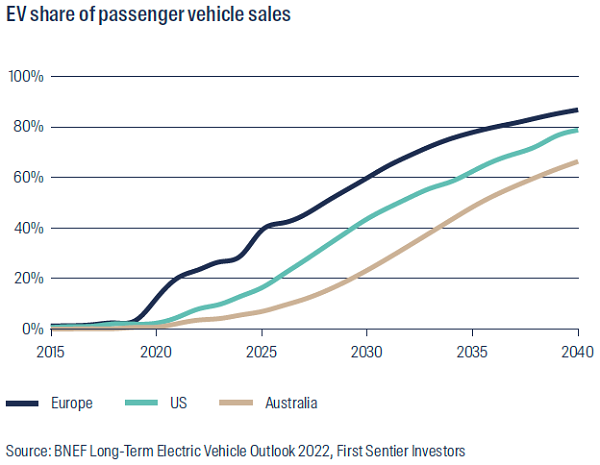
Data as at 31 March 2022
The infrastructure gap
As the new range of EVs hit the showroom floor, the real challenge begins. A Deloitte survey found that the number one barrier to EV adoption was a lack of charging infrastructure (33% of participants). If we add driving range (22%) and charging time (16%), then it could be argued more than 70% of the problem is about charging infrastructure.
As the fleet of passenger EVs expands, so too will the need for charging. BNEF estimates this investment opportunity could represent $US1.0–1.4 trillion over the next 20 years, roughly split evenly between private, public and commercial uses.
There are a number of ways to invest in this theme, including EV vehicle and battery manufacturers like TSLA, BYD or CATL, or gaining exposure to key minerals like lithium, cobalt or nickel. However, manufacturers are likely to face significant competition over time, while commodities could be a wild ride.
A number of EV charging infrastructure companies listed in recent years – ChargePoint, EVgo, Allego, Wallbox, Blink Charging and Volta. The business models vary, but may include the manufacture and sale of charging hardware, installation and maintenance of the hardware, a margin on electricity sales, and software for subscription-based access to charging networks.
Initial excitement in this growth opportunity has been overwhelmed by the reality of heavy losses. Our analysis indicates that these business models deliver low gross margins, there are few barriers to entry, supply chain issues have delayed rollouts, and the “land-grab” for charging sites is expensive. As a result, stock price performance has been disappointing.
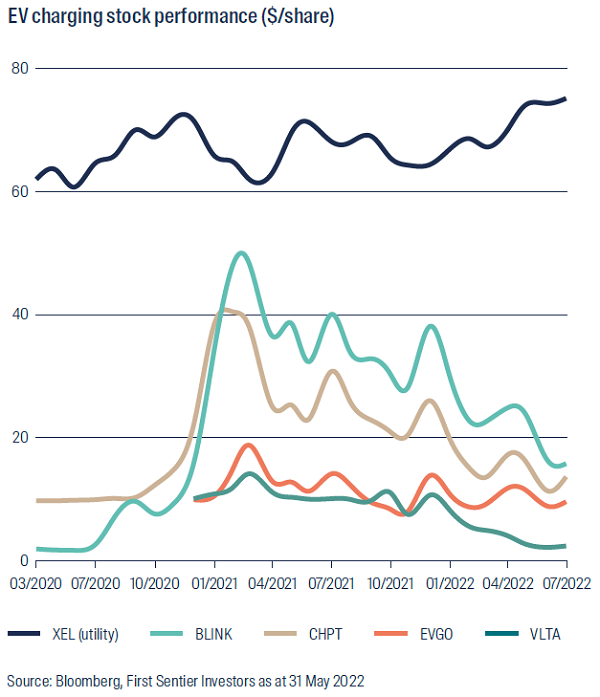
Utilities as an EV play
In our view, regulated utilities with electricity distribution networks represent a more compelling exposure to EV charging infrastructure. With the right policy and regulatory settings in place, utilities are well placed to deliver a coordinated rollout of a consistent product at a reasonable cost.
By including the EV charging infrastructure rollout costs in the regulated rate base, along with the required distribution and transmission network upgrades, costs can be shared across the customer base.
Xcel Energy provides a useful case study. Xcel owns electricity distribution networks in Minnesota, Colorado, Wisconsin and New Mexico with approved EV programs. The utilities intend to invest over $US2 billion over the next 10 years to enable 1.5 million EVs in their service territories. In current dollars that equates to around $US700 for charger equipment plus $US700 for installation for each customer.
Xcel is not alone. Across the US there are now 60 electric companies in 35 states or territories with regulatory approvals for EV programs, including: PG&E, Edison, Sempra in the west; ConEd, PSEG, Avangrid, Eversource in the north-east; and Duke, NextEra in the south-east.
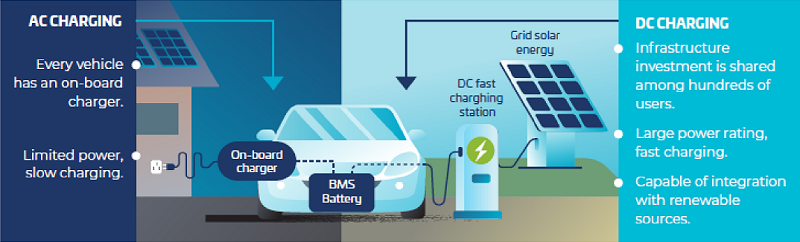
The investment opportunity could be materially higher if customers demand faster charging. While a home AC installation for overnight charging should price below $2,000, a fast DC charger that gets you back on the road in 20 minutes could cost more than $US100,000 (see table).
Types and cost of EV charging
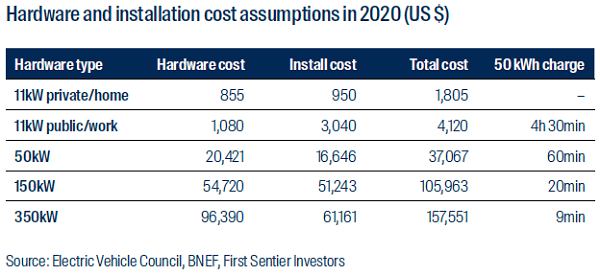
Data as at July 2022
Investor-led solutions
We believe EV charging is an enormous investment opportunity, despite the challenges. So, how can responsible investors contribute to accelerating the uptake of EVs? Below are a few ideas worth considering:
- Allocate investor capital towards electric utilities which have regulatory approval to rollout EV charging infrastructure
- Lobby energy regulators to include EV charging infrastructure plus associated electricity distribution and transmission network upgrades in the rate base to encourage investment. Multi stakeholder engagement with utilities, regulators and industry bodies could be a useful tool
- Real estate investors require minimum 1-in-5 vehicle parking spaces to be EV-ready for new or re-developed office, commercial, housing projects
- Explore opportunities for toll road companies to develop EV fast charging and recreation areas on vacant land along suburban or intercity roads
- Challenge integrated oil companies to transform retail fuel sites into EV fast charging centres
- Allocate higher risk capital to supply chain solutions including rare metals mining, semi-conductors and battery manufacturing. Allocate capital to the manufacture of component parts such as semiconductors
- Allocate your personal capital to an EV
Peter Meany is Head of Global Listed Infrastructure and Kate Turner is Deputy Head of Responsible Investment at First Sentier Investors, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This material contains general information only. It is not intended to provide you with financial product advice and does not take into account your objectives, financial situation or needs.
For a more detailed look at the EV industry, read the full report here.
For more articles and papers from First Sentier Investors, please click here.