The highly variable and diverse nature of the emerging markets equity asset class makes it well-suited to active management. By remaining benchmark-aware without being benchmark-guided, active managers are free to enhance value by investing in attractive regions, industries and individual companies.
The popularity of ETFs in emerging markets equity
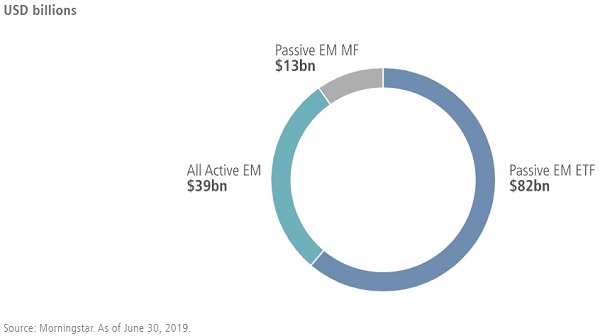
Despite the benefits of active management, investments in emerging markets equity often flow by default to Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) and other passive vehicles. Over the last five years, passive strategies have attracted almost 2.5 times more capital flows than active strategies into US-domiciled funds, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Five-year cumulative flows to US-listed active and passive emerging market equity
Emerging markets equity ETFs lagging their benchmarks
In the broader capital markets, the rising popularity of ETFs sometimes may reflect an increased focus on fees. However, ETFs for emerging markets equities are far less capable of delivering benchmark returns than ETFs tracking large capitalisation U.S. equities.
As shown in Figure 2 below, the largest US equity ETF (SPY) has managed to track the S&P 500 over the last 10 years. The two lines replicate each other almost exactly.
However, the median emerging market passive ETF has underperformed the MSCI Emerging Markets benchmark. The following example shows the iShares emerging markets ETFs, and the same is true for Vanguard. They have trailed their benchmarks by a substantial margin since their respective inception dates.
Figure 2. iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF has lagged its benchmark since inception
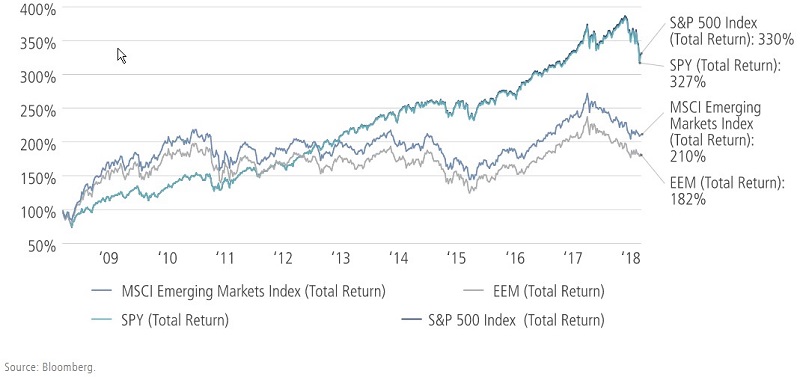
Over the last 10 years, iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF (EEM) and Vanguard FTSE Emerging Markets ETF (VWO) have finished in the 79th and 58th percentile respectively among all U.S.-listed emerging markets equity funds. (The variance in performance between the two is a function of iShares targeting the MSCI benchmark while Vanguard is based on the FTSE Russell, which excludes Korea.)
Why is this happening?
The sources of physical ETF tracking error
ETFs attempt to track their target indexes by holding all, or a representative sample, of the underlying securities that make up the index. Generally, higher tracking error in physical ETFs tied to the MSCI Emerging Markets index stems from a combination of factors, including:
Transaction pricing: Due to a lack of liquidity in certain securities, the stock price observed in the calculation of the index is not available to a tracking portfolio. Supply-demand dynamics can push the actual price at which a tracking portfolio can transact to buy or sell to a less favourable level.
Optimised sampling: Physical emerging markets ETFs typically use optimised sampling techniques, whereby they hold a basket of securities designed to match the characteristics of the benchmark, but not exactly the same securities, in the same weightings. Optimised sampling is typically employed where the index has fairly illiquid constituents, a large number of index members or where there exist legal and regulatory barriers to owning certain securities. The nature of the sampling technique is imprecise, which can lead to higher tracking error. The same holds true for ETFs aiming to replicate the MSCI World index, which have lagged that index by 19 basis points (0.19%) on average, relative to synthetic, derivative-based counterparts.
Depositary receipts: many physical ETFs tracking the emerging markets index trade American Depositary Receipts (ADRs) or Global Depositary Receipts (GDRs), instead of buying and selling the underlying local securities. Listed on large U.S. or European exchanges, ADRs and GDRs are designed to mirror the ownership of a company’s domestic stock listing. Deviations between these proxies and their local parents contributes to tracking error in ETFs.
Fees: ETFs, like traditional mutual funds, charge management fees that detract from the products’ net asset value and, in many instances, prevent an ETF from matching the performance of the index it tracks. ETFs also incur shareholder transaction costs through brokerage commissions and bid-ask spreads, which are costs that take away from an investor’s actual return even if not captured in an ETF’s reported performance.
Benchmark inefficiencies provide active opportunities
Setting aside the tracking issues confronting emerging markets equity ETFs, we believe the MSCI emerging markets benchmark itself remains inefficient for the following reasons:
- Weighting by market capitalisation implies a backward-looking bias toward stocks that have performed well in the past
- Holdings of state-owned enterprises, whose interests are not necessarily aligned with minority shareholders, can lead to unproductive capital allocation decisions
- Minimal exposure to small capitalisation stocks hampers access to some of the fastest growing companies in emerging markets
- Lack of a financial viability requirement for entry of indices may detract from performance
- The MSCI benchmark is also limited to 1,193 constituents, when there are over 10,000 public companies in the broader emerging markets universe.
Active opportunities in emerging markets
By focusing on company profitability and taking a broader view of the emerging markets stock universe, active managers have the potential to positively differentiate their returns relative to passive strategies and their index benchmarks.
Emerging markets equity is a particularly supportive asset class for active management. The ETFs designed to track emerging markets equity indexes are challenged by illiquidity and sampling issues, while the indexes themselves can be inefficient due to the inclusion of less attractive companies and state-run enterprises, for example. Investors should carefully consider their investment options in order to maximise the capital appreciation potential of this growth asset class.
Conrad Saldanha is a Senior Portfolio Manager at Neuberger Berman, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This material is provided for information purposes only and nothing herein constitutes investment, legal, accounting or tax advice, or a recommendation to buy, sell or hold a security. It does not consider the circumstances of any investor.
For more articles and papers by Neuberger Berman, please click here.