The S&P/ASX Emerging Companies Index has underperformed the S&P/ASX 200 Index by 12% over the last 12 months. What does this say about the future of active investment in small companies?
“Past performance is not always indicative of future performance”
Historical performance can often act as a double-edged sword. While the outperformance of large cap indices has drawn investors en masse, the past is not always indicative of the future. What works today, driven by a confluence of factors—be it economic conditions, regulatory environments, or global events—might not necessarily hold its ground tomorrow.
Strong performances by the major, large cap-focused equities indices have outdone active small cap investors for a number of years and lulled passive investors into the false security that their hands-off approach is not only easier but superior.
Average % price change over last 12 months (to Aug 18, 2023)
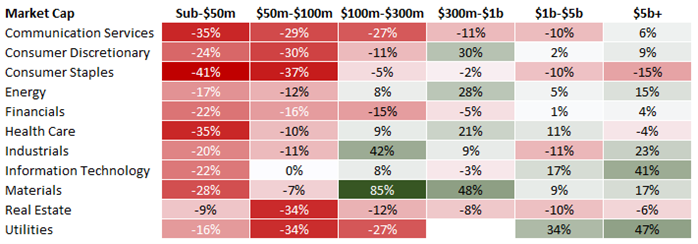
Source: Koyfin, H&G Investment Management Limited
Concentration
Passive investing in the index was originally pitched as a simple diversification strategy but thanks to its own success, is now shaping up as a form of concentration risk itself.
Index-tracking investors are placing all their eggs in one large cap ‘basket’ that has no fundamental reason to outperform other portfolios in the long-run and is currently priced with far less margin for error than many alternatives - and with more concentration in a small number of securities.
In theory, the passive index should not outperform in the long run. The differences between the index and the average portfolio performance should be limited to fees and other costs.
Does anyone believe that the committee at Standard & Poor’s that selects stocks based on their ‘free float’ has a special and sustainable edge over other investors?
If not, the conclusion that follows is that these large indexes are outperforming because, in their respective markets, a disproportionate amount of capital has been flowing to the index portfolio only.
Passive index investing has become momentum investing - buying equity in businesses without reference to fundamentals and buying more of a stock at higher prices simply because it has already experienced demand that outstrips supply.
When momentum is working for the investor, it makes markets look simple. But when momentum crashes it can get ugly. If a large percentage of investments in the market concentrate on an index, the entire market becomes vulnerable to systemic shocks.
Two strategies to de-risk from the index are: (1) to weight a pool of investments differently to the index; and/or (2) selectively invest in smaller companies that don’t have material (if any) index weightings.
Buying better
Today we look at the Australian equities market and see the market cap weighted average Price/Earnings (PE) ratio of the top 200 stocks is just under 22x earnings reported for the last 12 months.
Unless investors are willing to accept low returns, these companies need to have growth baked in for investors to justify buying ‘the market’ index rather than sticking to the safety of government bonds.
The current ten-year government bond yield of about 4.3% has been closing in on the ASX 200 Index’s market cap-weighted earnings yield, which is the PE ratio inverted, and equates to 4.6%.
While the S&P data on mainstream equities funds has been disheartening for active investors, the evidence does suggest that investors have found greater success relative to the large indexes when focusing on smaller companies.
This market-cap weighted PE multiple for large caps is currently a 24% premium to the median for micro-to-mid caps of 17.5x (excluding the resources sector). If we look at EV/EBITDA multiples, which take into account the total capital structure, the premium is 32%.
Another way of seeing the current opportunity for small caps relative to large caps is the historical relationship between their valuations. The S&P/ASX Small Ordinaries Index, which consists of the companies ranked between 100 and 300, has historically traded on a PE multiple 12% lower than the S&P/ASX 100 heavyweights, looking back to June 2002.
Before COVID-19 hit in early 2020, smaller stocks were actually trading on a premium PE multiple to the top 100. Today that discount is hovering at 26%.
One thing the historical data shows us is that when these extreme valuation gaps emerge, they are always closed again within several years.
There are a number of reasons why such gaps emerge. Small firms are neglected by analysts and investors, leading to a lack of awareness and information flow. Their shares are generally less liquid, meaning investors do not have the luxury of being able to change their minds and sell stocks on a whim. They can suffer from a lack of resources or poor governance.
Neglect
There are nearly 1,800 ASX listings with market caps below $1 billion - and only ~240 valued above that level. Most of the latter make up the S&P/ASX 200 Index.
Analyst coverage is focused on the larger stocks. Around 340 stocks are covered by at least three analysts. Another 260-odd have at least one analyst setting a price target (often from an obscure firm or with the conflict of receiving fees from the researched company). The majority are left with no formal research, adding another barrier for investors who do not have the time or ability to do the work themselves.
Media coverage follows a similar pattern, with a focus on the big end of town and very little insightful or investigative coverage of smaller listed companies.
Yet the great juxtaposition is that studies have shown less researched stocks deliver greater risk-adjusted returns than stocks receiving greater focus from analysts.
Liquidity and exits
The lack of liquidity may be one explanation of the greater risk-adjusted returns from under researched stocks. It is harder to buy meaningful positions in these companies and once a position has been accumulated a decision to sell could be difficult to execute without driving down the price.
To H&G High Conviction Limited (HCF), illiquidity represents opportunity. As managers of permanent capital, there is no pressure to realise investments at a time that doesn’t suit.
A feature of smaller companies is that they don’t necessarily have to rely on increasing investor interest to convert their operating performance into market value. In time, if investors do not appreciate the value creation, larger corporates and financial buyers (like private equity) will seize the opportunity for themselves.
We have seen this play out time and time again - most recently with Ensurance (ASX:ENA), a small ASX-listed insurance agency. Last month, Ensurance agreed to be acquired by leading insurance broker PSC Insurance for ~$25 million and at a 40% premium to the previous closing share price.
A patient, long-term view is necessary to be able to see an investment through from its purchase to the optimal exit. Our investment approach takes that a step further though - we actively work to solicit such opportunities to maximise value.
Active engagement
HCF has found that rolling up our sleeves and working constructively with shareholders, boards and management teams can help maximise shareholder value. This is possible by sitting on company boards directly, sharing previous business experience, identifying stand-out talent, and helping to deploy capital management strategies and M&A.
Successful investment in small companies requires intensive due diligence and active engagement with companies. At HCF, we believe the recent sell-off means there is considerable value in this segment of the market for diligent, long-term investors.
Joseph Constable is the Portfolio Manager of H&G High Conviction Limited (HCF) and an executive director of Hancock & Gore Limited (H&G). H&G is the investment manager of and owns shares in HCF. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.