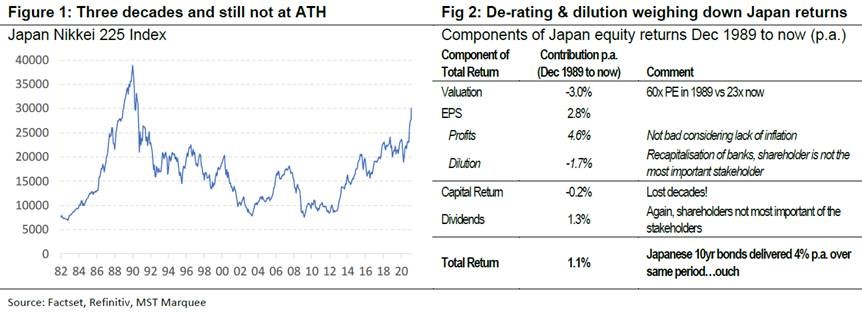
On 15 February 2021, the Japan Nikkei Index hit 30,000 for the first time since 1990. Media reports celebrated the milestone. However, we think it highlights the misery Japanese equity investors have endured for more than three decades. The Nikkei is still 23% below the all-time-high achieved in December 1989 at the peak of one the greatest equity bull markets in history. Since then the Japanese equity investor has endured an annualised capital loss of 0.2% and a paltry total return of 1.1% p.a. with dividends.
How did this happen? Can it happen in Australia?
Why Japan has performed poorly
Our analysis indicates the three main drivers of the dismal equity returns in Japan include:
1. High starting valuations
2. Dilutive equity issuance, and
3. Mediocre profits growth.
First, the Japanese equity market traded on Price/Earnings ratio of 60x in 1989. At the time it was the most expensive market in the world, by far, and it is a valuation level US tech stocks achieved in the late 1990s bull market. Now the Japanese equity market trades on 23x and the derating over the last 31 years has been a 3% per annum drag on equity market returns.
The second largest contributor to poor returns has been dilution. While Japanese profits have grown by around 4.6% p.a. since the peak in the bull market, Earnings Per Share (EPS) growth has been a puny 2.8%. Much of this dilution has come from recapitalising the overly-leveraged banks. However, Japan Inc’s unwillingness to put equity investors first as stakeholders has led to an erosion of equity returns if it means not sacking employees or restructuring businesses.
Third, mediocre profit growth has contributed to poor returns, but we think this should not be over emphasised. Profit growth of 4.6% p.a. is only 2% lower than what we have enjoyed in Australia over the same period. We think much of the difference has been due to the less forgiving inflationary backdrop in Japan.
So it is de-rating and dilution which have been the biggest culprits of the lost decades for Japanese equity investors. It has been less about deflation and an aging of the population, in our view.
Watch the ridiculous prices and equity diluters
To avoid future lost decades, our work suggests equity investors will need to avoid stocks which are ludicrously priced and are also likely to be big shareholder diluters (that is, issue large amounts of capital when not required) in the years to come.
While we don’t see either for the entire Australian equity market (but we are still early into the current bull cycle), we can see parts of the market which could deliver painful shareholder returns over the long-term.
The buy-now, pay-later (BNPL) sector could be one area. The stocks here are exorbitantly priced with Afterpay trading on 250x EV/EBIT. Potentially dragging shareholder returns further could be the capital intensity of these businesses. Credit providers have an insatiable appetite for new equity if they would like to grow. Afterpay, for example, has grown its share count by 20% over the last two years. Shareholders should expect further issuance to come. Afterpay just raised $1.5 billion in a convertible debt issue.
Another potential lost decade sector could be the infrastructure stocks. These companies are highly valued and are benefitting from low bond yields which keeps down their cost of capital. However, shareholders may have to endure dilution and de-rating in a world where bond yields push higher on a sustained basis.
While the potential for a lost decade should not weigh on short-term investor willingness to buy into these stocks, longer-term investors should avoid areas of the market that are turning Japanese. This is a sorry chart and set of numbers (ATH=All Time High).
Hasan Tevfik is a Senior Research Analyst at MST Marquee. This article is for general informational purposes only and is not a solicitation of any offer to buy or sell any financial instrument or to participate in any trading strategy.