Diversifying investment portfolios is known to provide a rare ‘free lunch’ to investors. The value of portfolio diversification was demonstrated by Harry Markowitz, who also gave investment professionals one of their most beloved acronyms, ‘MPT’, when he established Modern Portfolio Theory in 1952. MPT demonstrates how diversification removes unrewarded risks in a portfolio without sacrificing return expectations.
Measuring risk factors
How effectively diversified a portfolio is can be measured a number of ways. Simple ways cover the number and variety of assets, managers, sectors and industries in the portfolio. More sophisticated measures capture how correlated the portfolio’s assets are to each other (how closely their values move up and down together) and how much the performance of these assets can be explained by underlying common ‘factor risks’.
Factor risks are attributes like size, value (for example, low price to book value), growth, momentum and volatility. A diversified portfolio spreads exposures across a range of factor risks, rather than loading up on one or two factor bets. Of course, an investor deliberately loading up on assets with particular-factor attributes (such as value stocks) is not necessarily being unwise. But the investor must recognise that this becomes more like a high-conviction, concentrated portfolio than a well-diversified one.
Portfolio diversification has benefitted investors since the advent of MPT, especially for large investors with billion-dollar portfolios at stake. However, there is a kind of ‘indigestion’ to this free lunch which we uncovered last year while analysing the Australian equity portfolio of one such large superannuation fund.
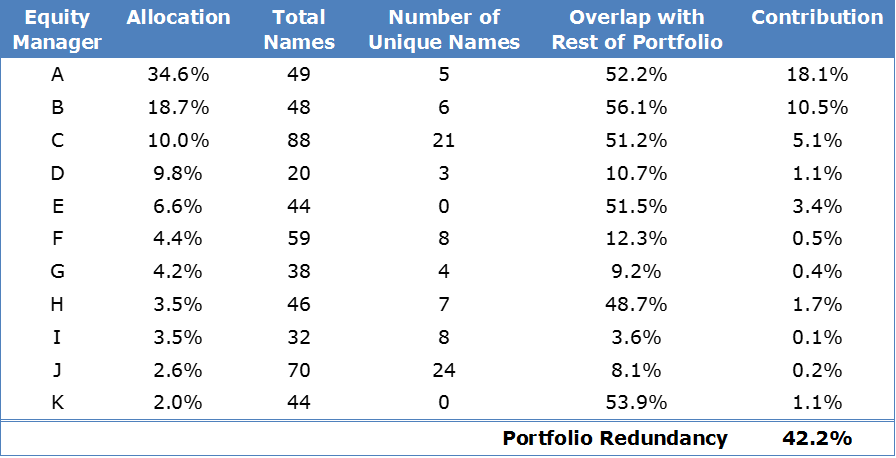
Superficially, the portfolio showed the qualities of a well-diversified equity portfolio, which was the objective of the fund:
- 11 discrete managers and styles
- 538 holdings of ASX-listed stocks
- a spread of between 20-88 ASX-listed stocks per manager
- exposures to five of the factor risks (size, value, growth, momentum and volatility).
Putting the jigsaw together
However, we discovered that this diversification was working against the fund in three critical areas.
First, it was hard for the fund to think about and analyse the portfolio as a whole. The complete picture could only be assembled by putting together the jigsaw of separately managed portfolio pieces. We did this by reconstructing the multi-manager portfolio in a centralised portfolio management (CPM) structure.
Second, we created a measure of ‘portfolio redundancy’, or the extent to which the 11 managers were holding very similar positions. We measured portfolio redundancy by calculating, per manager portfolio, the minimum of each stock’s value held in both the specific manager’s portfolio and the wider portfolio (ex-manager) – overlapping stock positions – and then summing these per-manager overlap figures on a weighted basis (reflecting manager weights within the total portfolio) as follows:
Too many similarities diminish diversification
Our portfolio redundancy calculation of 42.2% showed that the 11 managers were creating similar positions to each other over nearly half of the portfolio by value, or 452 of the total 538 stocks. Only 57.8% of the portfolio, across 86 stocks, was doing the heavy lifting to diversify the portfolio away from this common core.
This problem can arise in multi-manager portfolios which benchmark the underlying managers to similar indexes such as the S&P/ASX 300. ‘Tracking error’ to benchmark is a form of risk which these managers will not take on unless they expect to be rewarded. A large investor may think it is diversifying by spreading its portfolio over a number of managers, but if all the manager portfolios are tightly tracking a similar benchmark, there can be less diversification, and more portfolio redundancy, than the investor thinks.
Third, we classed each stock holding as a type of factor risk exposure to consider the level of factor risk diversification at the whole-of-portfolio level. Each of the 11 manager portfolios was expressed as a bundle of factor risks to detect how true to label each manager was (for example: was a value manager long the value factor? Was a defensive manager long the low volatility factor?). We identified two managers who were virtually identical to each other and another three who were very similar when profiled according to factor risks. Hence, three managers were adding nothing to the factor risk diversification of the portfolio.
False sense of security
This exercise shows how the free lunch of diversification can cause indigestion when it gives a false sense of security, complicating the portfolio and muddying the bigger picture, rather than reducing the risks of the portfolio.
There is another danger of using a wide suite of active managers with a seemingly diversified set of risks which can directly hit the investor’s bottom line. If the collective risks, from a whole-of-portfolio perspective, look just like the market, then the investor is paying active management fees for a portfolio that could have been provided much more cheaply by an index manager or ETF provider.
Raewyn Williams is Managing Director of Research at Parametric Australia, a US-based investment advisor. This information is intended for wholesale use only. Parametric is not a licensed tax agent or advisor in Australia and this does not represent tax advice. Additional information is available at www.parametricportfolio.com/au.