In the middle of 2024, my mantra was 'don’t overthink it': positive nominal growth and interest rate cuts were supportive of equity markets, even against the backdrop of stretched valuations in the US.
Moving into 2025, I maintain that stance as I expect corporate earnings to hold up and, for now, inflation is still moving in the right direction. But two risks weigh on my mind.
First, will higher bond yields imperil equities? Since 2020 we have been talking about a shift in the market regime. The 2010s were characterised by tight fiscal policy and zero interest rates. It was an era we might describe as “Adam Smith on steroids”, the theory being that individuals and businesses acting in their own self-interest would create positive outcomes for the economy. It was the invisible hand operating on a global scale.
However, this led to excessive income inequality and a feeling that the average person in the West wasn’t doing well enough out of the system. This, in turn, has led to political support for populist policies and a new consensus focused on looser fiscal policy, protectionism and higher interest rates.
Looser fiscal policy implies higher borrowing. Right now, the UK is under scrutiny with a significant rise in gilt yields since the Budget in October 2024. This volatility highlights how fiscal policy is a much more important driver of markets than was the case a decade ago. But while the UK may be feeling the heat today this is not a one-country problem.
In many regions, an ageing demographic plus the need to spend elsewhere, including on defence, will lead to higher debt levels. These will then become the ultimate speed limit to market returns.
This is because the ultimate constraint on populist policies will be their consequences for inflation and debt levels and the willingness of bondholders to accept this. Government spending has helped support economies, but this might be storing up problems for equities in the future with excesses in the system that would normally be addressed in a downturn.
Equity valuations can be sustained as long as bond yields don’t rise too far. With the US 10-year government bond yield now around 4.8%, we are starting to move into a more dangerous zone for equity valuations relative to bonds. Higher bond yields can draw money away from the stock market as well as increasing borrowing costs for corporates.
Tactically, I find it interesting that after a couple of years of predicting a US downturn or recession, most market commentators including us are predicting a positive outcome for the US economy. This could mean that, from a contrarian perspective, we get some relief on bond yields in the short term, especially as US interest rate cuts are almost priced out for 2025. But high bond yields are a risk we need to keep an eye on for the year.
The second challenge is the level of concentration in market-cap weighted indices. In recent years, when comparing the current environment with the late 1990s dotcom era, our view at Schroders was that the strong earnings growth delivered by the mega cap tech stocks in this cycle made it very different to the speculative bubble of 1999/2000.
Back then, valuations were impossible to justify. This time around, many of the large US tech companies are delivering earnings that support their valuations. However, a misstep by one of these companies would pose risk to overall market returns given their dominance of major indices.
Wall Street’s blue-chip benchmark has a high concentration in just a handful of stocks
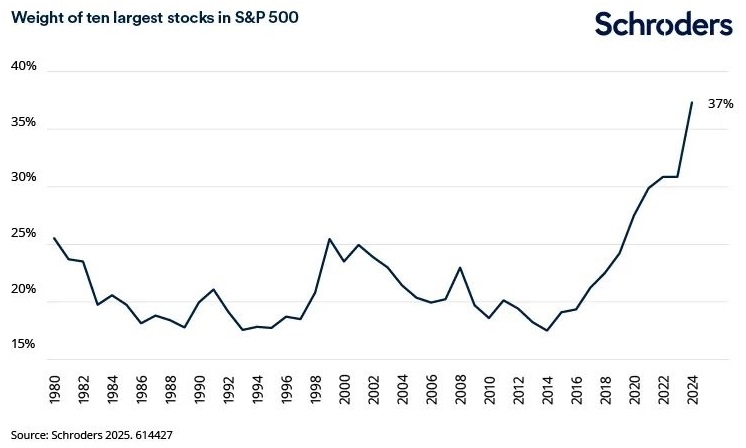
In fact, the level of index concentration far surpasses that of the late 1990s. From a portfolio standpoint, having such a high exposure to just a handful of stocks does not feel prudent. What’s more, the dynamics behind each of the ‘Magnificent 7’ vary. Treating them as a block underestimates the different business drivers between the individual companies. Given the concentrated nature of the market, this is not a time for unintentional bets.
These US risks are shared with other markets. Market concentration is similarly high in Europe and Japan. Investors relying on previous winners to drive performance are already starting to miss out. Since mid-2024, we have seen a much more interesting path for markets with different sectors performing at different times.
The full implications of DeepSeek’s technology still need to be understood. But it highlights that markets are vulnerable to a misstep by one of the large US megacaps, or by the emergence of new competition.
At a time when major equity indices do not offer the diversification they did in the past, and the shift in the political consensus is altering correlations across asset classes, investors will need to work harder to build resilient portfolios.
This article first appeared in The Financial Times on 15 January 2025.
Johanna Kyrklund is Group Chief Investment Officer (CIO) and Global Head of Multi-Asset Investments at Schroders, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This material is general information only and does not take into account your objectives, financial situation or needs. Schroders does not give any warranty as to the accuracy, reliability or completeness of information which is contained in this material. For important information and disclaimers, click here.
For more articles and papers from Schroders, click here.