Australia’s largest superannuation and pension funds recorded a compound growth rate of 11% per annum between 2009 and 2014, stronger than the growth rate of funds across the entire world of 6.4%. Yet despite this strong growth, a current challenge for all funds is how to diversify across return opportunities and risks in an environment of increasing asset market and interest rate uncertainty.
These are two of the findings in Towers Watson’s annual report of the top 300 global pension funds, available here. It contains analysis of growth rates, asset allocations, fund types, regions and countries.
Towers Watson said the key drivers behind Australian funds’ growth are:
“The net inflows resulting from the compulsory superannuation guarantee which continue to aid in growing Australia’s retirement savings and perhaps more importantly the fact that Australian superannuation is 84% defined contribution with a larger allocation to equities and other growth-orientated assets than other geographies. This last point, and the strong, positive returns over the five years since the global financial crisis in these growth-oriented assets, have held Australian funds in particularly good stead.”
Other points specific to Australian funds include:
- Australia had 16 funds in the top 300, as listed in Figure 1, the same as in 2013, with no new entrants in the last year
- Of these 16 funds, eight improved their ranking compared to 2013, one fund stayed the same and seven funds fell
- The number of Australian funds in the top 100 increased by one, with UniSuper joining the Future Fund, AustralianSuper, QSuper and First State Super
- Australia has no funds in the top 20 but two in the top 50, the Future Fund and AustralianSuper.
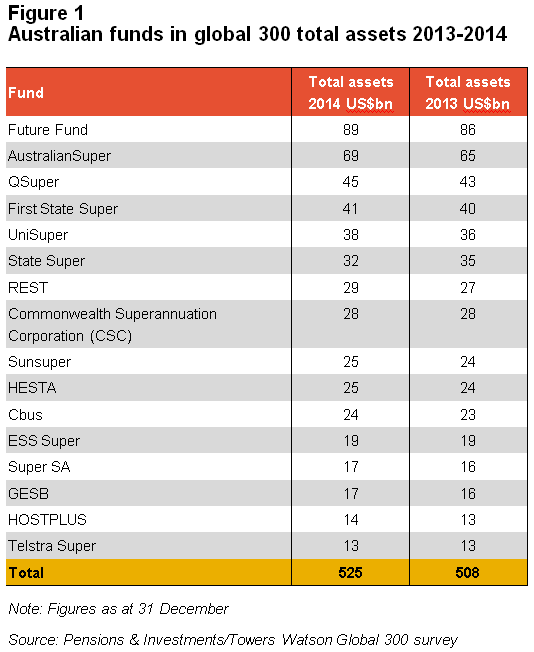
The Future Fund ranked ninth amongst sovereign pension funds in the survey with US$89 billion in assets. Established during an era of Federal budget surplus, the fund will help provide for the defined benefit entitlements of Government employees. The report notes the decrease globally in defined benefit funds’ share of pension assets from 75% five years ago to 67% in 2014. Defined benefit funds continue to grow but at a slower rate than newer defined contribution funds.
In the next 12 months a number of economic and market factors will impact Australian funds’ rankings and rates of growth relative to international peers. These include:
- The Australian dollar’s exchange rate against the US dollar, with a falling Australian dollar adversely impacting Australian funds’ rankings
- Global and Australian interest rate changes impacting rankings of funds with higher bond asset allocations
- Equity market returns, with rising markets generally improving rankings of Australian funds given their higher equity allocations.
The top 300 global pension funds combined had assets under management (AUM) of US$15 trillion in 2014, representing 43% of the estimated US$36 trillion total global pension asset pool. The total pool has doubled in the last decade, riding out the GFC and subsequent market recovery. North America remains the largest region accounting for 42% of AUM and 49% of funds, with 78% of their AUM in defined benefit funds.
While longer term growth has been strong, the annual growth for the top 300 decreased from 6.2% in 2013 to 3.4% in 2014, through lower global equity market and interest rate returns. Longer term asset mix and currency management will remain important in achieving strong and steady growth, with funds increasingly considering future sources of return value and adjusting their investment strategies accordingly.
Towers Watson says many funds are developing their product range, especially:
“ … in ‘added-value spaces’ to find the extra returns that no longer come from the market. In the process they are increasingly thinking about diversification in the context of all return drivers and adding the necessary governance or outsourcing to ensure success. This is likely to increasingly polarise winners and losers and could reshape the investment industry, completing the shift away from siloed - and indeed expensive - ‘asset class’ thinking and increasingly breaking down the distinction between ‘traditional’ and ‘alternative’ investments.”
While fund assets have doubled over 10 years, questions remain whether the funds management industry has focussed enough on the outcomes for members or reducing costs enough. In the past, most funds emphasised relative investment returns and less the value chain cost containment. This has allowed risk to build up in portfolios, and the cost gains for clients that should have come from such increases in fund size have been modest. There have been some margin reductions, especially in MySuper offers, and with greater scale, this should continue.
Iain Middlemiss was Executive Manager Strategy at Colonial First State and Head of Strategy at Superpartners. This article is for general educational purposes only.