When the Hawke Government came into power in 1983 one of its first decisions was to float the Australian dollar (AUD), assuming that this action would cause the AUD to fall and improve our international competitiveness. Before 1983, the value of the AUD had been set each day by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) and the Federal Government. Since then, rises in the Australian dollar are often presented in the press as a vote of confidence in Australia as a nation. A falling Australian dollar is viewed as a negative event, raising the cost of online purchases, imported flat screen TVs and skiing holidays in Colorado.
Since 30 June 2014, the AUD has fallen 7% against the USD, as the ‘carry trade’ (borrow cheaply in USD and invest the proceeds in higher yielding AUD securities) quickly unwound and foreign speculators fled back to USD. The AUD was sold off more than almost every other developed and emerging market currency, just like it was in the May-June 2013 ‘QE taper’ scare and also in the 2008-2009 GFC. Whilst this move is negative for a government wanting to buy F-35 Joint Strike Fighter jets, the falling AUD can help investors, as both asset allocation into unhedged international equities and Australian equity portfolios can be designed to benefit from a falling AUD.
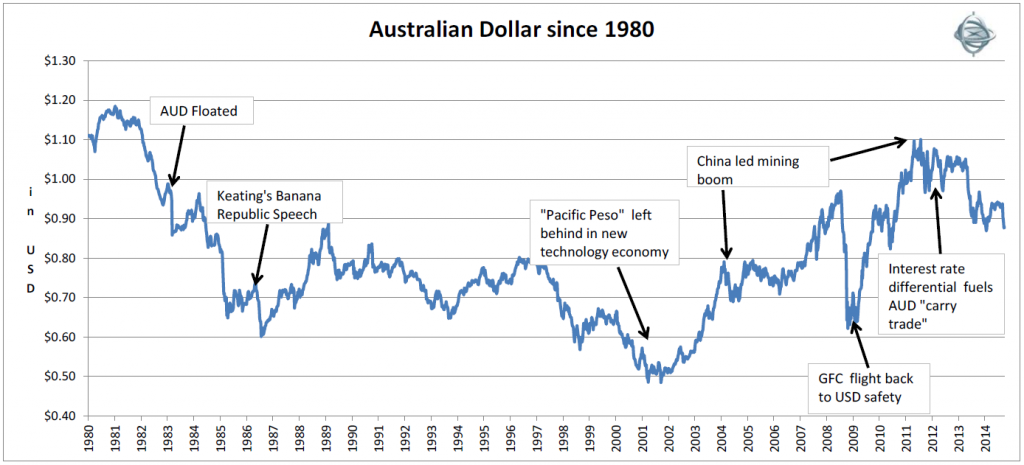
Since floating, the AUD/USD has averaged 76 cents, however as one can see from the above chart the AUD was in a downward trajectory from 1983 to 2002. This was broadly due to Australia’s higher relative inflation rate. The strength in the AUD over the past 10 years has been a result of China’s industrialisation and its associated unprecedented explosion in demand for Australian minerals since China joined the World Trade Organization in 2001. As the impact of this one-off event diminishes, we would expect the AUD to move towards fair value based on purchasing power parity, which we estimate is approximately USD66 cents.
Winners
Broadly speaking the companies that are likely to benefit from a weaker AUD fall into four categories:
- Companies that manufacture or provide a service in Australia and compete with the now more expensive imports such as steel (BlueScope), fertiliser (Incitec Pivot) or tourism (Crown).
- When a falling AUD results in inflation, companies like Woolworths and Transurban should see an expanding profit margin. Their product prices from cans of tuna to road tolls will increase with inflation, whilst a proportion of these companies’ costs remain fixed, thus resulting in higher profits.
- Companies that have production costs in AUD but export products like natural gas (Woodside) and iron ore (Rio Tinto) which are priced in USD. A falling AUD translates into higher AUD revenue from the same USD level of goods sold. For example, every 1c fall in the AUD increases BHP’s profit by USD100 million and Rio by USD57 million.
- The falling AUD also benefits companies with substantial offshore operations such as CSL and Orica, as their USD- or Euro-denominated earnings when translated back into AUD for Australian investors are now worth more.
Losers
The companies that are typically hurt by a falling AUD are those that buy goods offshore for resale to Australian consumers such as retailers Myer and JB Hi-Fi. Over the last 12 months, the 8% fall in the AUD/Korean Won effectively results in a price increase for that new 140cm Samsung LED TV that some may have their eyes on for the upcoming Cricket World Cup.
Similarly, a falling AUD presents a challenge for companies like Qantas that earn revenue in AUD from domestic consumers, but have significant USD-denominated costs such as aviation gas. Further companies that have significant un-hedged USD borrowings such as Boral will see their interest costs increase, especially when the company does not have USD earnings to service their debt. For example Boral’s US building materials businesses last generated a profit in 2007.
How to position a portfolio
Investors who view the AUD as overvalued on fundamentals can position both Australian equity portfolios and unhedged global equity portfolios to benefit from a falling AUD. Favoured companies might be those with significant offshore earnings and strong franchises (CSL, Orica or Sonic Healthcare), rather than structurally-challenged companies that need a declining AUD to compete with imports (BlueScope Steel or CSR). Additionally, mining and energy holdings such as BHP, Rio Tinto and Woodside will benefit from a rising price per tonne of ore or a barrel of oil sold in AUD terms.
Hugh Dive is Head of Listed Securities at Philo Capital Advisors. These comments are general in nature and readers should seek their own professional advice before making any financial decisions.