The COVID-19 bear market hit severely, with the 34% fall in the S&P500 from 19 February 2020 to 23 March 2020, making it the quickest collapse in history. A bear market is usually defined as a 20% fall in a market index, and in March 2020, this took only 20 days.
Compared with other bears, however, there are reasons this bear market could be shorter. There has already been a strong recovery, although clearly this could be a bear market rally.
This short article compares the latest falls with previous bear markets, noting the one thing they all have in common – they end.
Consider the following chart of bear markets in the Australian All Ords Accumulation Index.
- Every bear market is different in terms of its speed and duration of falls, and how long they last.
- In a bear market, panic selling of assets turns mark-to-market, or paper losses, into real losses.
- The nature of each bear market is determined by the initial shock that triggered them (demand or supply side) and the quality of the policy response (weak versus strong).
- The COVID-19 bear market was triggered by a supply side shock that quickly escalated into a profound demand side shock as health policies saw activity ‘stop’ during the lockdown phase of managing the rate of infection.
- The policy response to this biological shock has been swift, dynamic and comprehensive. Central banks are providing unbound liquidity and fiscal policy is helping economies ride through to when infection rates begin to fall or a vaccine is close.
- The nature of the COVID-19 biological shock helps explain the speed and depth of fall in the Australian share market compared to other bear markets.
- The vigorous policy response and finite nature of the event suggests that this bear market will have more of a ‘U’ shape and be shorter in duration than other bear markets.
All Ordinaries Accumulation Index (100=cycle peak) in previous bear markets
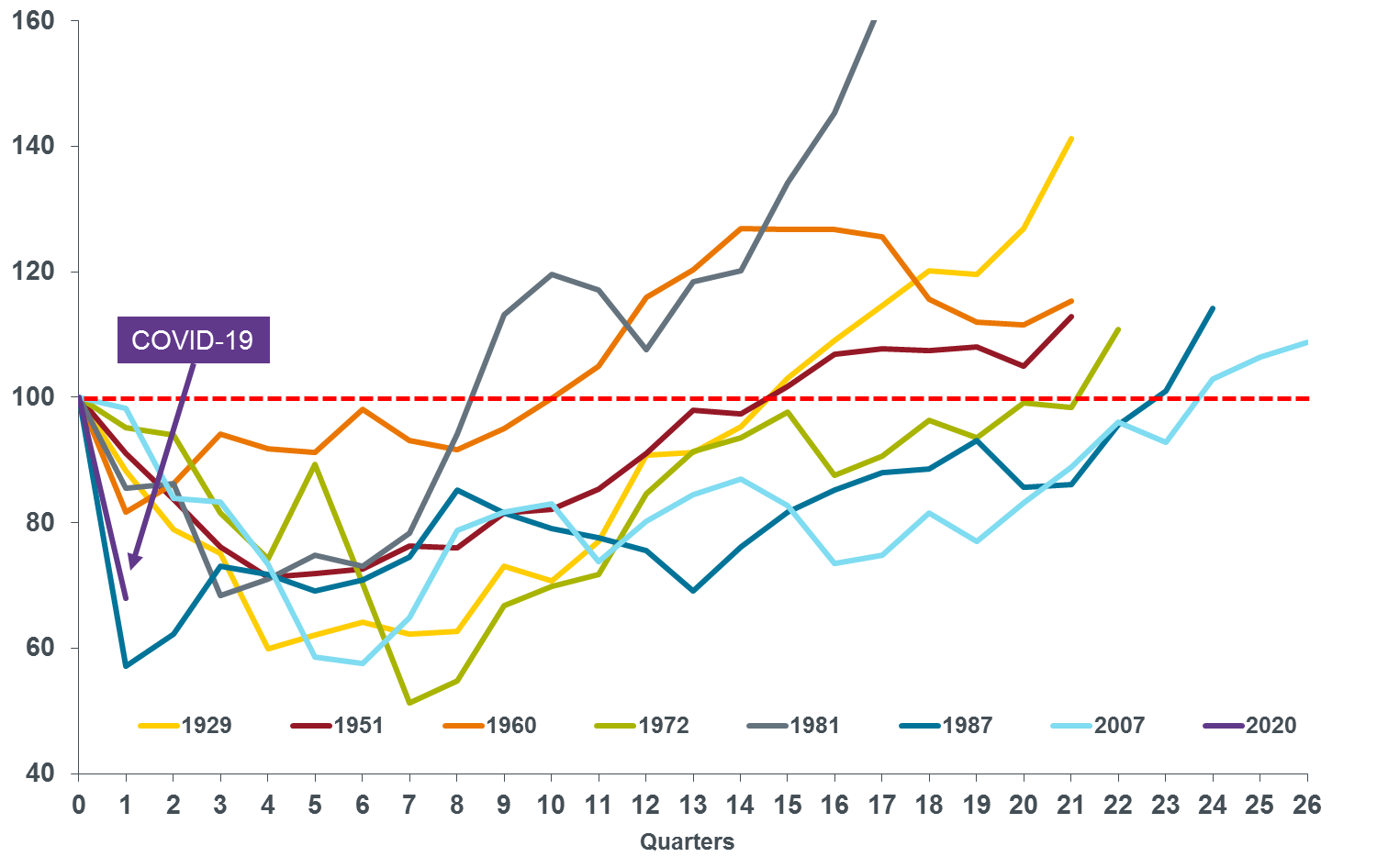
Source: Janus Henderson, does not include the subsequent rise in the All Ords of about 15% to end March 2020.
Frank Uhlenbruch is an Investment Strategist in the Janus Henderson Australian Fixed Interest Team. This article is general information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.