Policymakers in both developed and emerging markets are attempting to reopen their economies as they manage the virus , with varying degrees of success. Despite the short-term uncertainty, there are plenty of attractive opportunities for investors in emerging markets.
1. Inflation is transitory amid central bank discipline
Inflation in emerging markets is often misunderstood. About 85% of the MSCI Emerging Markets Index is made up of six countries: Brazil, Russia, India, China, Korea and Taiwan. Add South Africa and Mexico and almost the entire index is concentrated in a relatively small number of countries.
Supply chain dislocation and numerous bottlenecks due to COVID-19 have caused a big pop in inflation both in emerging and developed markets. We anticipate this will be transitory as disruptions diminish and headline inflation begins to reduce, allowing lower monetary policy rates to be sustained.
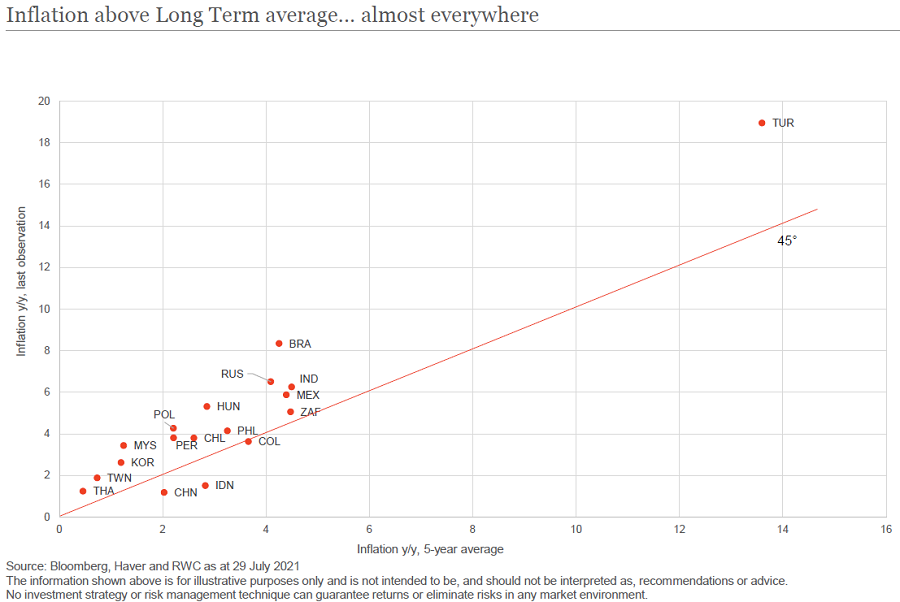
Most importantly, it’s been vital for emerging market countries to maintain the hard-fought credibility of their central banks. So far, the signs are good. As an example, at present there’s a night-and-day difference in the improved quality of central bank management in Brazil compared with what we saw in 1991.
2. Emerging markets are maturing
The pandemic has shown that the emerging market complex is looking more mature, with Brazil and Russia hiking interest rates to maintain credibility. This is a stark shift from 2020, where central banks across the world were forced to cut rates in order to protect economies following the onset of the virus. While developed markets remain mired in emergency level policy settings, it is pleasing to see the emerging world pivot to a more proactive stance.
In fiscal stimulus terms, there haven’t been substantial moves outside of those countries with large international reserves or the ability to borrow capital on the international market. The emerging markets approach has been cautious and supportive. For example, China has been very restrained relative to what it did in 2008, while still providing ample stimulus to return its economy to a strong growth footing. Ironically, because emerging market countries couldn’t borrow as much as the West, there’s a lot less pressure placed upon their currencies and debt levels than in developed countries.
Overall, it looks like the emerging market complex will get through this period of unprecedented monetary and fiscal policy response while actually strengthening the credibility that has been built up over the last 20 years.
3. Emerging markets currencies and commodities are attractive
Emerging markets currency (EMFX) is reaching levels we haven’t seen since 2002. From 2001 to 2008, there was a very substantial rally in EMFX. One of the great convergence trades was when China, India, Brazil, Korea and Taiwan emerged on the global scene. Their GDP developed well, resulting in a dramatic rerating of emerging markets.
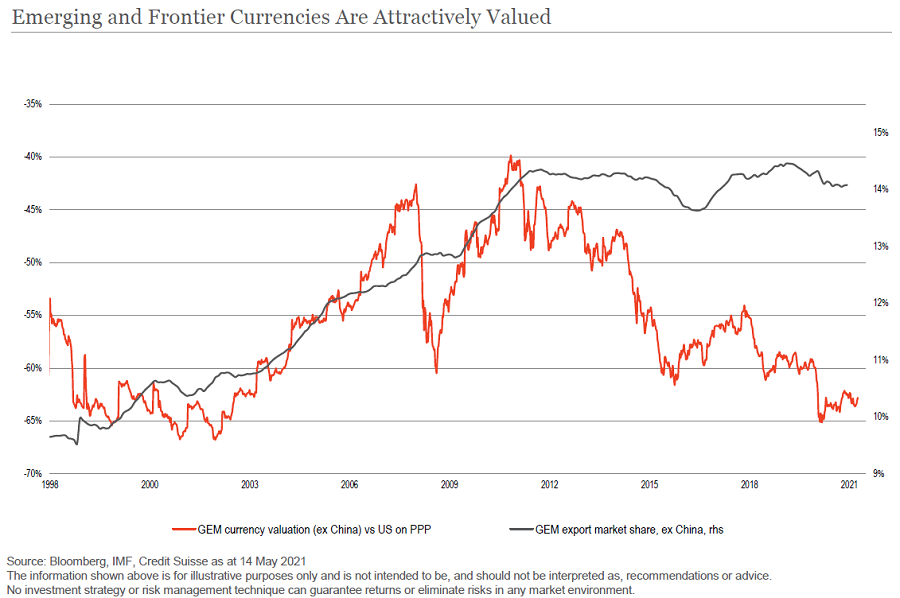
Since the bounce after the GFC, these countries have performed poorly relative to the S&P500. But that is set to change as emerging market countries benefit from surging demand for commodities on the back of significant global stimulus, infrastructure spending and recovery.
We’re more bullish on commodities than most, but the street is catching up with our numbers. The outlook is positive for lithium (due to short-term demand and a lack of supply), copper (it is integral to decarbonisation and electric vehicles) and aluminium (thanks to supply base issues and the need to ‘greenify’ production). We’re less bullish on steel and we’re very bearish on iron ore relative to the consensus due to significant supply capacity in Australia and Brazil.
Commodities remain important for the emerging market complex in supporting economic growth. Therefore, we believe emerging markets countries will provide strong outperformance over the next couple of years, if not the next decade, versus the developed markets. As a result, EMFX now looks very attractively valued.
4. Chinese regulatory risk is manageable
The recent China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) meeting with executives of major investment banks attempted to ease market fears about Beijing’s crackdown on the private education industry.
The regulator made clear that China will continue to welcome foreign capital and that there is no intention of any economic decoupling. The authorities will allow time for policy adjustments and public consultation. Unsurprisingly, the CSRC also outlined a positive economic growth outlook for the country.
We believe this gives reassurance that the tutoring industry decision was a unique case. If China can convince the market that the regulatory changes are not an attack on profitable companies, confidence should slowly return.
The last 30 years of investing in China has shown that you don’t want to be fighting against the authorities. The key point about managing Chinese regulatory risk is that if you align yourself with the authorities, there are very substantial returns to be made.
Which emerging markets sectors could outperform?
The pace of COVID-19 vaccine rollout is accelerating in larger emerging market countries, which is helping their cyclical recoveries. This trend is expected to continue throughout the second half of the year and may allow emerging markets to reopen their economies faster than expected, resulting in significant GDP growth throughout 2021.
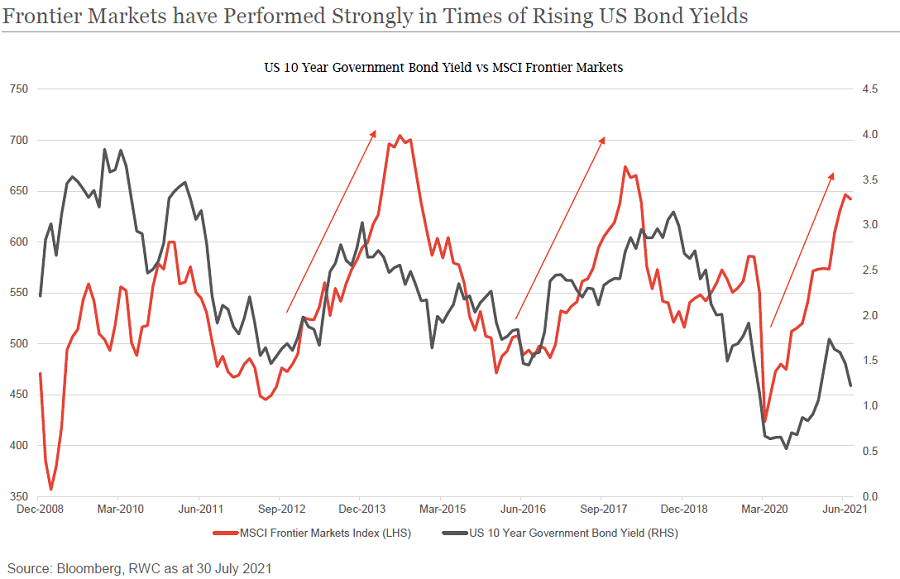
As an asset class, MSCI emerging and frontier market equities are expected to be up 7-12% in the next 6-9 months (source: RWC Partners and Bloomberg as at 30 July 2021). This will see the so-called ‘Fragile Four’ – Brazil, India, Turkey, and South Africa – outperform, while long-term upward pressure on the price of oil will also see Russia and Saudi Arabia benefit. China will continue to be weighed down by geopolitical forces and the lack of flows into emerging markets.
Thematically, we expect everything climate change-related to do well, including copper, lithium, solar energy, alternative energy, and electric vehicles. The EMFX carry trade remains intact which should support the financial services and housing sectors, especially in high yielding countries. In emerging markets, the COVID-19 recovery will be fuelled by travel, modern retail, and consumer discretionary spending.
James Johnstone, Co-Head of Emerging & Frontier Markets at RWC Partners, a Channel Capital partner. Access to the RWC Global Emerging Markets Fund is available to Australian investors via Channel Capital, a sponsor of Firstlinks. This article is genral information and does not consider the circumstances of any investor.
For more articles and papers from Channel Capital and partners, click here.
The webinar “RWC Partners: Adapting to the future – long term trends in emerging and frontier markets” can be viewed here.