S&P Dow Jones Indices recently released its updated Index Versus Active (SPIVA) Australian Scorecard covering fund manager versus index performance to June 2018.
The results of the analysis have again found that, with the exception of small-cap equities, the average Australian actively-managed fund underperformed comparable market indexes over the 1-year and longer periods. That is, more than 50% of active funds underperformed the index.
Unfortunately, the S&P SPIVA analysis is not comparable to, and is therefore irrelevant for, institutional superannuation funds, and may be for some individual investors.
Three key problems with the analysis
If we take Australian equities as an example (general or large-cap style), there are three problems:
1. Managers
The SPIVA analysis is based on over 300 actively-managed funds defined by Morningstar as large-cap. It is not disclosed how many managers actually manage these 300 funds.
From an institutional perspective, there are probably less than one-third that number of large-cap managers and strategies that would even be considered as potential investments, due to the tight compliance and eligibility rules they use.
2. Equal versus asset weightings
S&P Dow Jones Indices does publish some asset-weighted results (that is, weighting the results by funds under management, not giving equal weights to tiny and large fund managers) in the SPIVA. However, the tables of results which are the sources of the outperformance comparisons over 1, 3, 5, 10 and 15 years showing that x% of funds underperform the benchmark are based on equal-weighted returns. A manager with a small portfolio is given the same weight as one with many billions.
Notably, in the tables in the SPIVA Report which give both equal and asset-weighted return levels, the asset-weighted active funds outperform the equal-weighted funds by 30-50 basis points per annum. This suggests that either:
- larger investors are able to select better-performing actively-managed funds, and/or
- larger actively-managed funds have lower fee levels.
In either case, the asset-weighted funds would have had better performance relative to the index over time if these figures had been used for the outperformance comparisons.
3. Retail fees
The SPIVA analysis is based on fund performance provided by Morningstar, which are after-fee returns. Given the large number of funds (over 300), many have 'retail' fee levels. Moreover, even those ‘wholesale’ funds included would have fee levels significantly greater than those paid by institutional superannuation funds investing through mandates, and some options accessible by retail.
The charts in the SPIVA analysis which show cumulative (growth of a dollar) performance versus the benchmark show clear outperformance by the asset-weighted funds over the equal-weighted across essentially all periods, and for all asset classes (with the notable exception of small-cap funds). This indicates that larger investors select better performing investments.
Adjusting the results
If the SPIVA analysis was adjusted to reflect an institutional manager selection process and institutional fee levels, it would be likely that the average super fund investor would be found to consistently outperform the benchmark.
Actual results delivered by Australian super funds support this conclusion, with the SuperRatings SR50 Australian Shares Index of after-fee (i.e. actual) returns to super fund members outperforming the S&P/ASX 200 index (before fees) in every period (1, 3, 5, 10 and 15 years).
S&P Dow Jones Indices claim that they are ‘the de facto scorekeeper of the ongoing active versus passive debate’. It should be born in mind that the SPIVA Scorecard is only relevant to retail investors, and even there, should be qualified by the above analysis.
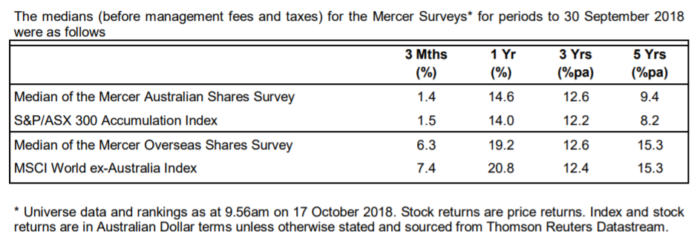
[Editor's note: The SPIVA data is often quoted to demonstrate active manager underperformance, but it is not the only company which monitors managers. The latest Mercer Investment Survey results were recently released for September 2018, as shown below. Perhaps supporting John Peterson's analysis, Mercer shows the median Australian shares manager outperformed the S&P/ASX300 by 1.2% (9.4% versus 8.2%, before fees) over five years. Even after fees, this result is likely to show outperformance].
John Peterson is the Founder of Peterson Research Institute Pty Ltd and has 40 years of experience in the financial services and investment industry. The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author. This article is provided for general information only and does not constitute financial or any other advice.