Over the course of the past year, RBA Governor, Glenn Stevens has bemoaned the low level of entrepreneurial risk-taking across Australia's corporate sector and implored businesses to invest for future growth prospects. ‘Animal spirits’ remain dormant in Australia and across most of the developed world thanks to persistent revenue headwinds and high discount rates that companies are assigning to expected future cash flows for potential new projects. The propensity for CEOs to lift dividend payouts rather than commit to new capital investment reflects a desire to cater to investors' insatiable appetite for income.
At first glance, the persistence of a high cost of capital is difficult to reconcile with the risk free rate or yields on sovereign bonds being at record lows. But in a wide-ranging speech delivered on 21 April 2015 (‘The World Economy and Australia’) in New York, Glenn Stevens acknowledged that lower returns on safe assets have not pulled down the cost of capital because there has been an offsetting rise in the equity risk premium (the return required to compensate investors for taking on the higher risk of the equity market). The Governor argued that the stability of earnings yields in the face of declining long term interest rates implies that the risk premium has lifted, reflecting more risk being assigned to future earnings and/or lower expected growth in future earnings (see Chart 1). He also highlighted anecdotal evidence of stickiness in hurdle rates used by corporate Australia when assessing projects.
Chart 1: Earnings and sovereign bond yields
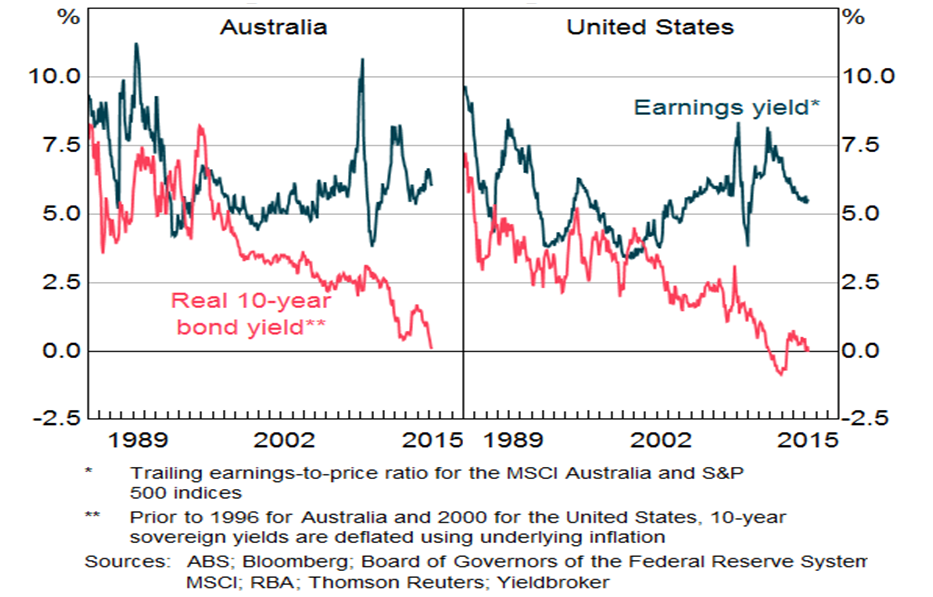
Investors have gravitated towards safe assets as they perceive a high level of risk in the world, despite the fact they are receiving record low interest rates. As Mr Stevens noted:
“Compensation in financial instruments for various risks is very skinny indeed. Investors in the long-term debt of most sovereigns in the major countries are receiving very little – if any – compensation for inflation and only minimal compensation for term.”
The risk premium and cost of capital
While lower rates have encouraged investment in ‘defensive’ sectors like banks and property trusts, stock multiples in cyclical sectors such as media and consumer discretionary are not receiving the assist from a lower risk free rate that might otherwise be expected due to caution about lower earnings and growth prospects.
There is a common misconception that record low interest rates should be associated with a re-rating of stocks. The risk free rate (the government bond rate) is directly observable on a daily basis, so our familiarity with low long term interest rates informs our mental framing of the cost of capital. But the equity risk premium is not directly observable, and so we are likely to neglect it as a source of variation in the cost of capital.
In fact, from the perspective of monetary policy, it is a key channel in which a central bank can influence the psychology of risk-taking, and hence the RBA Governor’s speech. If a central bank is seeking to revive ‘animal spirits’ in the corporate sector, it must do so by reducing the expected equity risk premium, as well as lifting expectations of revenue growth.
The defensive sectors in the Australian market are trading at a premium (based on dividend multiples) to their 10-year median estimates, while cyclical sectors are trading at or below their historical medians (see Chart 2). The higher equity risk premium has played an important role in driving a wedge in the multiples between defensive and cyclical stocks.
Chart 2: Defensive versus cyclical sectors and long term earnings multiples
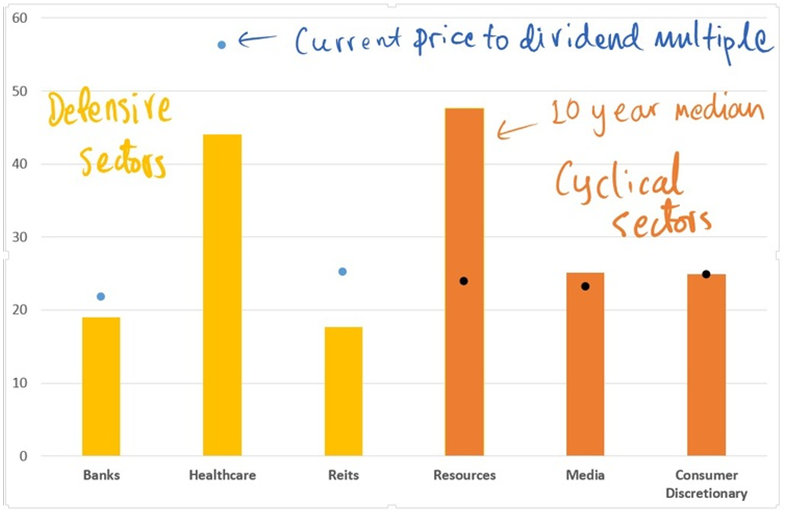
High defensive stock valuations may persist
It might be tempting to think that either defensive stocks or high-yielding stocks with strong and sustainable sources of competitive advantage are exhibiting bubble-like valuations. But shifts in the risk premium and cost of capital matter for portfolio construction. This analysis suggests they have contributed to the relative rise in valuations for defensive (lower beta) stocks. Those high valuations may persist while the corporate sector's animal spirits remain dormant. The unwinding of the defensive trade will eventually happen abruptly, but that remains way off as long as output remains below potential, there is deficient aggregate demand, unemployment is well above the natural rate, and inflation remains subdued.
Sam Ferraro is founder and principal of the independent financial consulting firm, Evidente. This article is for general educational purposes and investors should seek professional advice about their personal circumstances.