Complexity is one of the challenges of our information society, and we typically respond by making simplifying assumptions. This helps us manage the complexity but increases the risk of focusing on the wrong things. Worse, our prejudices easily lead us to simple answers which are consistent with our views but are often biased and misleading.
The complexity of longevity
Increasing longevity is one of the most challenging and complex issues we face – as a community and as individuals. It’s easy to fall into the trap of making sweeping statements. Prejudice, often fuelled by personal fear of our own mortality or that of our parents, can lead to big errors of judgment.
Why, for example, is there a disproportionate number of professional ice hockey players in Canada born in the first months of the calendar year? Readers of Malcolm Gladwell’s Outliers know that the selection of young players for higher-level ice hockey coaching starts in year seven or eight. Children born early in a calendar year are more mature than their age peers born late in the same year. So they tend to be chosen for further coaching. Same ‘age’ but different capabilities.
We become increasingly individual and different as we mature. Our community largely avoids using age as a basis for judgment until around age 60 when quite suddenly ‘age’ again becomes an issue. It’s used as a decision point if we want to ‘retire’ or access our super or get a free transport pass. In its report ‘Access All Ages – Older Workers and Commonwealth Laws’ (March 2013) the Australian Law Reform Commission identified a plethora of areas in which age has become more obviously a basis for discrimination than it might have been at the time the original legislation appeared.
‘The end of the Age of Entitlement’ has now entered our vocabulary as a justification for a series of age-based changes to government support (along with many other changes).
Has the notion of a numerical age outlived its usefulness? We are already evolving more sophisticated ways of evaluating ourselves. Could we be heading for a new ‘Age of Enlightenment’ where we create more contemporary models to help us know and manage ourselves better with increasing longevity? If so, this should lead to more effective allocation of expensive resources. Benefits would accrue to both individuals and governments.
Personal capital or value
At My Longevity, we developed a simple model which a person can use to help with their ‘retirement’ decisions. It shows how our personal value (capital) can be seen as a simple combination of our capability and experience. These accrue and eventually decline at different rates over our working life. The model invites people to consider the impact of retiring on their personal value. Each of us is different so the individual model varies accordingly. It can help shift the retirement focus to one of personal value rather than just financial value, and introduces the notion of a personal time frame to underpin decisions. It also fosters the important notion of mastery over personal circumstances which in turn supports the quest for independence.
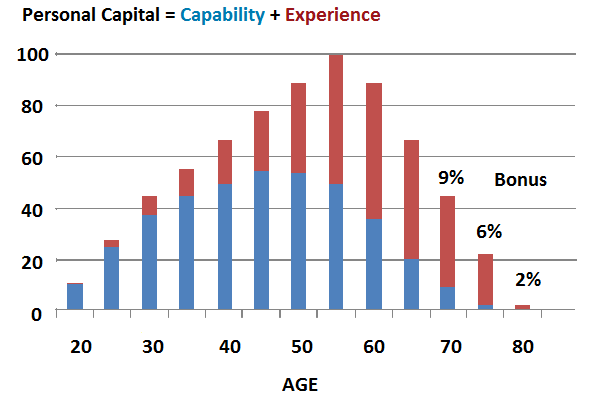
Source: My Longevity Pty Ltd
This illustration shows how personal capital can accrue over time with a potential bonus from deferral of retirement. Personal circumstances can vary a lot from this model. Although our capability might decline in later years, it can be compensated for by our experience.
There are many other ways of showing people the diversity of options that can open up with greater longevity awareness.
Older people are increasingly seeking information and services which help them manage their lives better. Many of them want to continue to contribute to society and do so.
When governments discriminate in delivering services using outdated metrics like age, they risk giving the message that they are behind the times and out of touch with reality. They attract criticism and waste opportunities to encourage informed independence.
Success in managing longevity requires an effective partnership between individuals and governments. Maximising personal capability requires an environment that is supportive and nurturing.
As Malcolm Gladwell suggests: “It’s true in sports and it’s true in the rest of our lives as well. We need to wake up to the fact that as a society we haven’t been doing our part.”
David Williams began longevity research in 1986 and was a Director with RetireInvest and CEO of Bridges. He chaired the Standards Australia Committee on Personal Financial Planning. David founded My Longevity Pty Limited in 2008.